Chapter 6 Photosynthesis
advertisement

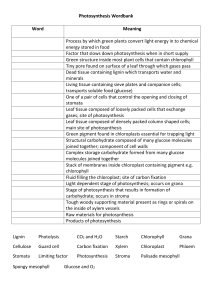
Chapter 6 Photosynthesis autotroph An organism that can make its own food Includes plants, algae, some protists, and some bacteria photosynthesis The process of converting sunlight to chemical energy Equation for photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water yields glucose + oxygen heterotroph An organism that obtains its nutrition by eating other organisms ATP Energy is released from ATP when a phosphate group is broken off. An energy storing molecule; stores chemical energy produced from photosynthesis chloroplast A structure found in plants; where photosynthesis occurs thylakoid Membrane of grana where first stage of photosynthesis takes place; light energy is absorbed grana Structures in the chloroplast that are the site of photosynthesis; (a stack of thylakoids) chlorophyll A green pigment that absorbs certain wavelengths of light pigment Compounds that absorb light carotenoid Compounds that are accessory pigments (they help chlorophyll) Absorb wavelengths of light that chlorophyll can’t Produce yellow, orange and brown colors stomata Holes in plant leaves that take in CO2 and give off O2 and water Solution stroma in the space around the grana (pl.) Granum (s.) photosystem Cluster of pigment molecules in thylakoid membrane