Chapter 7 Photosynthesis_student version
advertisement

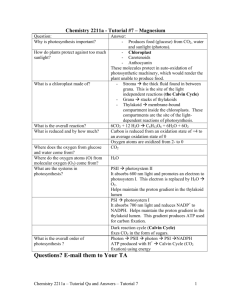
CHAPTER 7 PHOTOSYNTHESIS: USING LIGHT TO MAKE FOOD General Biology CM Lamberty BIOLOGY AND SOCIETY Green Energy Wood…fossil fuels….biomass/biofuels Renewable, less S, wildlife habitats, reduce erosion, disversification 4% of all E in US THE BASICS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS Process by which plants, algae and certain bacteria transform light E into chemical E Uses CO2 and H2O as starting materials Chemical E then stored in bonds of sugar Plants = autotrophs CHLOROPLASTS: SITES OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS Chloroplasts: Found Chlorophyll Stomata: Stroma: Thylakoids: Grana: THE OVERALL EQUATION FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 CO2 and H2O were waste products of cell. resp A PHOTOSYNTHESIS ROAD MAP 2 stages of photosynthesis Light Reactions Calvin Cycle THE LIGHT REACTIONS: SOLAR…CHEMICAL THE NATURE OF SUNLIGHT Radiation Electromagnetic energy Waves Wavelength EM spectrum Light hits object and is either absorbed or reflect CHLOROPLAST PIGMENTS Chlorophyll a Chlorophyll b Carotenoids HOW PHOTOSYSTEMS HARVEST LIGHT E Photon: Shorter wavelength Pigment MQ absorb photon Thylakoid membrane HOW LIGHT RXNS GENERATE ATP & NADPH 2 types of photosystems cooperate Water-splitting photosystem Transfer between systems NADPH-producing photosystem HOW LIGHT RXNS GENERATE ATP & NADPH Light reactions taking place in thylakoid membrane 2 photosystems and electron transport chain ATP production is similar to cellular respiration Difference: THE CALVIN CYCLE: MAKING SUGAR FROM CO2 Sugar factory within stroma of chloroplast Cycle: starting material regenerated each turn SOLAR DRIVEN EVOLUTION Hot, dry climates plants continue photosynthesis while conserving water C4 CAM