CH 2 - Learning
advertisement

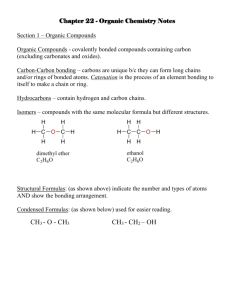
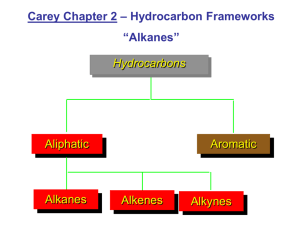
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic chemistry is the study of ................containing compounds derived from living organisms. Oil is formed over millions of years from the break down of dead ................and ...................... 80+ million compounds- natural & synthetic. Crude Oil (petroleum) is a mixture of many thousands of these different compounds and is the main source of many of these chemicals. They are called .................. because they predominantly contain the elements hydrogen and carbon. Distillation of Crude Oil ................... Lower boiling point substances ............... and move up. As the temp drops substances .............. and run off. ..................temp temp Homologous series This is a series of compounds which all contain the same ........................ group, and have similar chemical properties. ALKANES ALKENES ALCOHOLS CH4 CH2 =CH2 CH3OH CH3-CH3 CH2 =CH –CH3 CH3CH2OH Each has a ...........................formula: ......................: CnH2n+2 The members of the series differ by the number of ...... units. CH3-CH3, CH3-CH2-CH3, CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3 Graduation in physical properties: eg: boiling points. CH4 (......), C8H18 (..........), C30H62 (..............) ALKANES SATURATED HYDROCARBONS – contain maximum amount of ……………………………. - only ……………………….. bonds (no ……………………….. bonds) NAMING ALKANES No of C atoms Prefix Formula Alkane 1 Meth CH4 Methane 2 Eth CH3CH3 Ethane 3 Prop CH3CH2CH3 Propane 4 But CH3CH2CH2CH3 Butane 5 Pent CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 Pentane 6 Hex C6H14 Hexane 7 Hept C7H16 Heptane 8 Oct C8H18 octane Functional groups The functional groups are ………………. or ………………….. of atoms which determine the ……………………. of organic molecules. STRUCTURES OF ALKANES METHANE ………. Bond Angle ……………. Can be illustrated as: Shape ……………………… ETHANE. Molecular formula …………... Structural formula:……………………….. OR ………………… ……………. ETHANE. Molecular formula C2H6 Structural formula: CH3 CH3 or H Atoms are able to spin around a single bond there is free rotation. H H C C H H H PROPANE. ....................formula: C3H8 .....................formula: CH3 CH2 CH3 or Both ethane and propane are “……………………” chain molecules BUT!! H H H H C C C H H H H Bonds are ……… 90o molecules are NOT…………….!!! Schematic formula PROPANE. Molecular formula: C3H8 Structural formula: CH3 CH2 CH3 or Both ethane and propane are “straight” chain molecules BUT!! H H H H C C C H H H H Bonds are NOT 90o molecules are NOT STRAIGHT!!! Straight = no branches! Schematic formula Ethane and propane are also colourless and odourless flammable gasses. They have slightly higher boiling points due to their greater molecular weights. ISOMERS C4H10 - can have two different structures Straight chain. CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 Branched chain CH3 CH CH3 CH3 BUTANE METHYL PROPANE branch Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formula are said to be ISOMERS of each other. TASK: illustrate the structures of the three different isomers of C5H12. Use models OR CHEMSKETCH to help you. Names & Structures Examples 2- methylbutane The 2 can be left off as there are ……………………………………………… 2 and 3-methylbutane are the same molecule! 2,2 – dimethyl propane TASK: illustrate the structures of: 2-methylpentane. 2,3 – dimethylbutane. 2,2,3 -trimethylpentane THE RULES FOR NAMING ORGANIC COMPOUNDS 1. Choose the longest unbroken chain of Carbon atoms and assign a name for the carbon chain using the prefixes; meth-1, eth-2 etc. 2. Identify any carbon chain branches (alkyl groups). These are assigned names using the same prefixes as above along with the suffix “-yl” – methyl, ethyl etc. 3. Identify the functional groups present in the molecule. Assign a prefix or suffix according to their homologous series. These will be written in front of the name of the carbon chain. 5. Number the Carbon atoms in the longest chain so that the branches/functional groups have the lowest number possible. Allocate a number for every group/branch no matter how many times it occurs. Where groups are on the same carbon write their names in alphabetical order. 6. Prefixes are used for groups that occur more than once. Di – 2 Tri – 3 Tetra – 4 Penta – 5 etc. 7. Groups are written in alphabetical order. 8. The final name is written as one word with commas between numbers, hyphens separating numbers from words. Give the names of the following alkanes (a) CH3 CH2 CH CH2 CH3 CH3 (b) CH3 CH CH3 CH2 CH CH3 CH3 (c) CH3 C(CH3)2 CH2 CH(CH3) CH2 CH3 (d) CH3CH2CH(CH3)C(CH3)3 Structure of Alkenes The shape around the double bond is …................... The bond angle around the double bond is ................. ……………….. Represented as C bond C C C ……….. Examples of Alkenes ………………, C2H4 H H C H PROPENE OR ……………………. C H CH2 CH CH3 TASK: Use ball & stick models or sketches to construct and name 3 different structures for C4H8 each one with one double bond. Alkynes H-C≡C-H H-C≡C-CH3 H-C≡C-CH2-CH3 CH3-C≡C-CH3 …….yne ……..yne Very reactive Triple bond unstable! Attracts electrophiles. C x x x Cx …………-1-yne Alkynes are very unstable ………….yne and reactive. Acetylene burns with very high temp?