Nomenclature of Organic compounds
advertisement

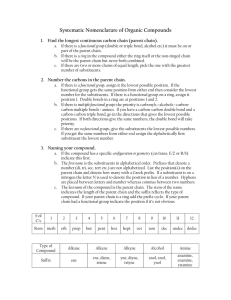
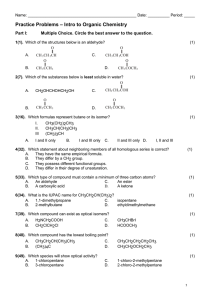
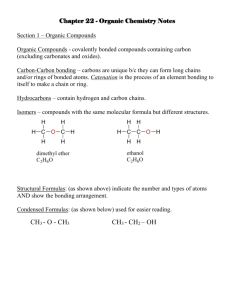
O Organic chemistry i h i Nomenclature of Organic compounds Bridge course Nomenclature of organic compounds Th are two There t systems t off naming i 1 Trivial system 1. 2. IUPAC system y Trivial system: When a few organic g compounds p were known,, they were named on the basis of their history or source. source Eg: HCOOH –Formic acid (red ants) CH3COOH‐Aceticacid COOH A ti id (acetum‐vinegar) ( t i ) IUPAC system: (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) By using this system one can name any B i thi t complex organic compound easily. The name assigned to an organic compound on the basis of latest IUPAC p rules is known as systematic name. W iti IUPAC name off a compound Writing d y The IUPAC name of the compound p built from 4 parts y Prefix y word root y primary suffix y secondary suffix Prefix y It denotes the substituent group if present in the organic compound p g p Substituent group prefix ‐F Fluoro l ‐Cl Cl chloro ‐Br Bromo substituent prefix ‐I Iodo ‐NO2 Nitro NO2 Nitro ‐CH3 Methyl ‐C2H5 Ethyl ‐C3H7 Propyl 3 7 py Word root y It indicates the number of carbon atoms in the longest possible chain. N off carbon No. b atoms 1 2 3 word d root meth‐ eth‐ prop‐ No.of carbon atoms Word root 4 but‐ 5 6 7 8 9 10 pent‐ hex‐ hept‐ p 0ct‐ non‐ dec‐ Primary Suffix yIt denote the nature of carbon to carbon bond compounds. yane: b d bond yene: bond yyne: bond in the organic S Secondary d suffix ffi It represents the functional group if present in an organic molecule and is attached h d to the h primary i suffix ffi while hil writing the IUPAC name. Class of functional secondaryy compounds group suffix Alcohol ‐OH ‐ol Aldehydes ‐CHO ‐al Ketones >C=O ‐one Carboxylic acids COOH oic acid Carboxylic acids ‐COOH ‐oic acid Amines ‐NH2 ‐amine E t COOR t Esters ‐COOR ‐0ate Writing W ii IUPAC name off an aliphatic compound IUPAC= prefix (es)+word root + primary IUPAC fi ( ) d t i suffix +secondary suffix Eg: g H3C 3 Word root root-:: prop CH 2 CH3 H2 C 1 OH Prefix -: methyl Pi Primary suffix-: ffi -ane Secondary suffix-: -ol IUPAC name- 2-Methyl-1-propanol (terminal ‘e’ of the p-suffix is dropped if the sec-suffix begins with ith a,e,i,o,u) i ) IUPAC rules for naming organic compounds 1.Longest chain rule: Select the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as “parent” chain 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 5 6 CH3-CH-CH2-CH2-CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-CH2-CH3 | | CH2-CH CH3 CH2-CH CH3 2 1 2-Ethylpentane 2 Ethylpentane 33-Methyl Methyl hexane (wrong) (correct) 2.Lowest number rule The carbon chain selected is numbered from the end nearest to the side chain or substituent so as to give the lowest number to the carbon carrying the side chain. 1 2 3 4 4 3 2 1 CH3-CH-CH2-CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-CH3 | | CH3 C CH3 C 2‐Methylbutane ( correct)) 3‐Methylbutane ( (wrong) ) Lowest sum rule: Where there are more than one substituent, numbering of the chain is done in such a way that the sum of the numbers assigned to the substituents is minimum. “The e te term Locant oca t iss used to de denote ote tthe e number u be indicating the substituent attached”. CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 1 2| 3 4| 5 5 4| 3 2| 1 CH3-C-CH2-CH-CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-CH-CH3 | | CH3 CH3 2,2,4‐trimethylpentane 2,2,4 trimethylpentane 2,4,4‐trimethylpentane 2,4,4 trimethylpentane Set of locants= 2+2+4=8 set of locants=2+4+4=10 (correct) (wrong) 3 Arrangement of Prefixes 3. Arrangement of Prefixes If more than one group is attached to the carbon chain, these groups should be arranged alphabetically. When two or more identical substituents are present prefixes like di, tri, tetra, etc. are used. However these prefixes are not considered for alphabetical order. 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 CH3-CH-CH2-CH-CH2-CH3 CH3 CH CH2 CH CH2 CH3 | | 4 5 6 CH3-CH-CH2-CH-CH2-CH3 CH3 CH CH2 CH CH2 CH3 | | CH3 CH2 CH3 CH2 | CH3 | CH3 2-Methyl-4-ethylhexane 4-Ethyl-2-methylhexane (wrong) (right) y If two different groups are located at the equivalent positions, the h numbering b should h ld be b done d in such h a way that alkyl group which comes first in the alphabetical p order g gets the lowest p position. 1 2 3 4 5 6 CH3-CH C C 2-CH-CH-CH C C C 2-CH C 3 | | C2H5 CH3 3-Ethyl-4-methylhexane 4: Lowest Number to the Functional Group p y In case there is a functional group in a molecule, the parent chain is numbered such that the f functional group gets the lowest number, even if ti l t th l t b if the lowest number rule is violeted. CH3 H3C 1 C 2 CH3 CH3 H2 C 3 H C 4 CH3 5 OH 2,2-Dimethylpentan-4-ol 2,2 Dimethylpentan 4 ol wrong H3C 5 C 4 CH3 H2 C 3 H C 2 CH3 1 OH 4,4-Dimethylpentan-2-ol , e y pe o Right 5 Presence of Identical groups If an organic molecule has more than one functional group, prefixes like di, tri, tetra are used before the fi lik di i d b f h suffix indicating the functional group. However, the ‘e’ of the corresponding alkane is retained e of the corresponding alkane is retained. 4 H3C 3 CH OH 2H C 1 CH2 OH OH Butane-1,2,3-triol 2 1 H2C CN H2C CN 4 3 Butane-1,4-dinitrile Nomenclature of unsaturated hydro carbons a ) H 3C 4 H2 C C H2 CH2 H3C 1 1 3 But-1-ene c) b) C C CH3 2 3 4 But-2-yne 5 4 3 2 1 H3C C H C H C H CH2 Penta-1,3-diene IUPAC nomenclature of poly functional compound In case of polyfunctional compounds one of the functional group chosen as the principal group and d the th compound d is i named d on that basis. The order of decreasing priority for functional groups g p Sulphonicacid>carboxylic acid>ester>acid chloride >amide> nitrile> aldehyde> y ketone> alcohol>amine>doublebond>triple bond>ether>other substituents (X>NO2>R) OHC H2 C H2 C H2 C COOH 4 3 2 1 principal functional group substituent group 4-Formylbutanoicacid The IUPAC name of an alicyclic compounds is prefixed with “cyclo”. NO2 1 3 2 2 a)) b) c) 1 Cyclohexane y 3 3-Nitrocyclohexene y 1-Methyl-3-propylcyclohexane Nomenclature of Aromatic compounds NH2 6 5 a) O2N Cl 1 2 4 3 1 b) NO2 CH3 6 2 5 3 4 C2H5 1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene 4-Ethyl-2-methylaniline IUPAC names of organic compounds by bond line notation b b d li i b a But-2-ene 2,3-Dimethylbuta-1,3-diene d c 2,2-Dimethylbutane 3,3-Diethylpentane THANK YOU BRIDGE COURSE‐2012