Nomenclatura dei Composti Organici: Alcani, Alcheni e Gruppi Funzionali
advertisement

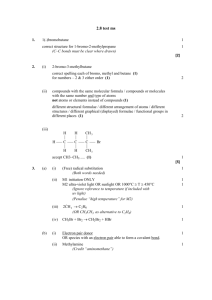
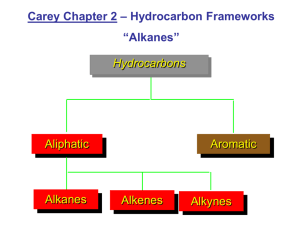
Naming Organic Compounds Alkanes H H CH3 H C C C H H H H 2-methylpropane Rules 1. Pick longest Carbon chain 2. Number from end so the SUM of substituent groups is smallest 3. Substituents should be arranged alphabetically Example 1 H H H C C H H H H H 3 C H 4 C H 5 H 2 C 1 C C H H 6 C H H 7 C H H CH3 H H Longest chain 7 long, chose to “go round the corner” on the chain as that was the simplest method for substituents. 2 substituents smallest numbering method results in 2 – methyl 3 – ethyl Full name is: 3-ethyl-2-methylheptane Questions H H H H C C C H H H H C H C H C H H H H C H H H C C C C H H CH3 H H H H C C H C H H H C CH3 H H H H H H C H H C C C C H H C H H C H H H H H H C C C C H CH3 H H H3C C H3C C H3C C H3C H3C H3C H H H CH3 H H H H H C H H H H H C C C C C H H H H C C H H H H H H H C H H H H H H C C H CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 H H H H H C H H C C C C H H H H C H H H H H H H C H H H C C C H C H H H H C H H H H H H H C C C C H H H H H CH3 CH3 H C C H H C H H H C H C H H H C C C H H H H C H H H H H C H H H C H C H H H H C C H H C C C C C H H H H H H C H H H H H C H H C CH3 CH3 H Alkenes Alkenes have another level of isomerism as the double bond cannot rotate, therefore if both carbons are attached to two different then they are said to exhibit E/Z isomerism (commonly referred to as cis-trans isomerism) H3C H3C CH CH CH3 CH CH CH3 E-but-2-ene Z-but-2-ene In cis – trans terms The cis-isomer is the Z isomer (Z comes from Zusammen, for together) The trans-isomer is the E isomer (E comes from entgegen, opposite The terms have to be applied carefully as the attached groups are given priorities dependant on their atomic number if the highest priority groups are on the same side then they are known as Zisomers and if they are opposite then they are E-isomers H3C 1 Cl C 2 1 H3C C C 2 H 1 2 CH3 Z-2-chlorobut-2-ene H 2 CH3 C Cl1 E-2-chlorobut-2-ene Alkene substituents H H H C H C H H C 1-butenyl C H H H H H C C 2-butenyl C C H H H H H C C H H C H H C H 3-butenyl Questions H H H C H H H C C C H H H C C H C H H H H C H H C C H C H H H C H H H H H H C H3C H H C C C C H H C H H C C H H C C H C CH3 H H H H H H C H C H H H C C C H C C H C C H H H H H H C H H C H H3C H H H C H C C H H C C H C H H H H H C H H H H C C C H H C H C C C H H H H H H H H C H H C H H H H H C H C H C C H H C H H H C H H C C C Do E/Z isomers exist here? H H H C C H H H H CH3 H C H H H Functional groups Organic chemistry also investigates other substituents on these carbon chains. There are many different possible substituents. We will be looking at some of the most important functional groups. To name organic compounds and explain which functional group follow a similar course to the method used for alkanes and alkenes. Deduce the functional group Find the longest chain Number from the end so that the SUM of the substituents are smallest Arrange substituents alphabetically. Type of compound Alkane Formula Prefix Suffix -ane C C Alkene -ene C C C Cyclic* -cyclo(size of ring)ane/ene C C F Cl Br I OH O Halogenoalkane Alcohol Aldehyde* FluoroChloroBromoIodoHydroxy- -ol* -al C H O Ketone* Oxy(used very rarely) C -one O Carboxylic acid* -oic acid C OH O Ester* Alkyl (i.e. methyl, ethyl, propyl etc) C O -oate C If multiple functional groups exist the name must explain where and how. The suffixes are preceded by di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa… for 2, 3, 4, 5, 6… identical functional groups Cl Br Br Br Br Cl H H H H C C C C C C C C C Cl Cl Cl H Cl H H F H H 1,2,3,4-tetrabromo-1,1,2,3,5,5-hexachloro-8-fluorononane Functional groups marked with * do not get numbered according to the SUM of the substituents rather from the end of the chain with the functional group on. The chain must also end in the functional group even if it is not the longest. Questions Cl H H H C C C H H H Cl H H C C H H H O Cl H C H Cl H C C C H Cl H H Cl H H O OH H C H H C C C H H C C C H H H F Cl H C C C H Cl F H Cl H H C H H OH C C H H F O C H H H H O H C C H C H H Cl C H C H H C H Cl H C H OH Cl H H C C C O C H Cl H O H H C H C H H H F C F C C Br Cl H H H F C H I C C H H I C F C Cl I Br C I Br