The structure of alkanes

Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
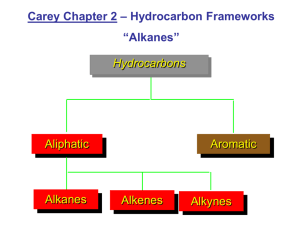
Hydrocarbons
(contain only carbon and hydrogen) a) Saturated: (Contain only single bonds)
Alkanes (C n
H
2N + 2
)
Cycloalkanes (C n
H
2N
) b) Unsaturated: contain
Alkenes : double bonds (,,,C n
H
2N
)
Alkynes : triple bonds ((C n
H
2N - 2
)
Aromatic : benzene like compounds
Sources of alkanes
Petroleum and natural gas are the two most important natural sources of alkanes.
Where do we use alkanes in everyday life?
Propane in grills/stoves, butane in lighters, gasoline in autos, and oil in auto engines
The structure of alkanes
Alkyl groups
Groups attached to the main chain are called substituents . Saturated substituents that contain only carbon and hydrogen are called alkyl groups . An alkyl group is named by taking the name of the alkane with the same number of carbon atoms and changing the ane ending to yl
Alkane Alkyl group
CH
4
Methane
CH
3
-
Methyl
CH
3
CH
3
Ethane
CH
3
CH
2
Ethyl
H
3
C CH
Propane
3
H
3
C propyl
C
H
2
H
3
C CH isopropyl
3
CH
3
H
3
C butane
CH
3
H
3
C CH isobutane
3
H
3
C butyl
CH
3
CH
2
H
3
C CH
2 isobutyl
H
3
C sec-butyl
CH
3
H
3
C
CH
3
CH
3 tert-butyl
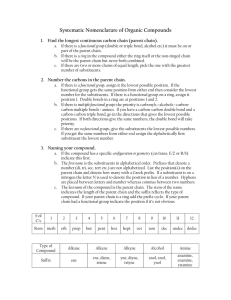
Nomenclature of substituted alkanes
1) Choose the largest continuous chain
2) Start numbering (lowest possible numbering)
3) List substituents alphabitically.
4) Use di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta, octa, nona, deca for identical groups
5) If two or more different types of substituents are present, they are listed alphabetically, except that prefixes such as di - and tri - are not considered when alphabetizing.
Examples
5
4
Cl
3
Br
2
1
3-bromo-2-cholropentane
7
6
5
CH
3
4
3
2
1
H
3
C
2,4-dimethylheptane
7
6
H
3
C
5
H
C
CH
3
4
3
2
H
3
C
1
4-isopropyl-2-methylheptane
If there are two equally long continuous chains, choose the one with most branches
1
H
3
CH
3
3
2
4
C
5 6
7
H
3
C
CH
3
2
3
4 5 6
1
7
3-Ethyl-2-methylheptane not 3-isopropylheptane
Physical properties of alkanes
1) Water insoluble
2) low boiling point, which increases upon increasing the number of carbons in the alkane
3) branched alkanes have lower boiling points than the corresponding long chain alkanes
• Conformations of Alkanes :
• Conformers :
Stereoisomers that are interconvertible by bond rotation
• Cycloalkanes:
• Conformations of Cyclohexane flip axial equatorial
Chair conformation
H
H
3
C flip
CH
3
5% 95% methylcyclohexane
Boat conformation
H flip
0% 100% tert-butylcyclohexane
Reactions of Alkanes :
1. Oxidation and Combustion; Alkanes as Fuels
Combustion of hydrocarbons is an oxidation in which C-H bonds are replaced by C-O bonds
Exothermic reactions produce heat.
2. Halogenation of Alkanes
• Draw the monochloro and dichloro products expected from chlorination of propane
H
3
C CH
2
Cl
Cl
Cl
H
3
C
Cl
CH
3
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl