幻灯片 1
advertisement

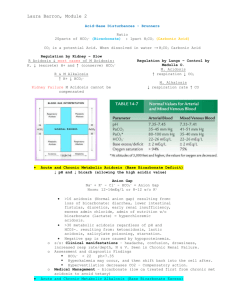
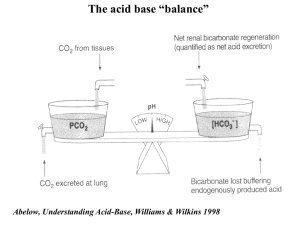
Acid-base balance and disturbance Normal acid-base balance Parameters of acid-base balance Simple acid-base disturbance Mixed acid-base disturbance Normal acid-base balance Concepts of acid and base Sources of acids and bases Regulation of acid-base balance Concepts of acid and base H2CO3=H++HCO3HHb=H++ Hb- H2PO4-=H++HPO42HPr=H++Pr- Acid base H+donor H+ receptor Sources of acids and bases mainly produced during the catabolism of intracellular nutrients, with a small part of them from food. Volatile acid Acid carbonic acid Nonvolatile acid or fixed acid sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, lactic acid, acetoacetic acid, βhydroxybutyric acid Regulation of acid-base balance Buffer systems Respiratory regulation of acid-base balance Renal regulation of acid-base balance Buffer systems Buffer system in the blood Buffer effect of cells Buffer system in the blood H2CO3=H++HCO3H2PO4-=H++HPO42HPr=H++PrHHb=H++HbHHbO2=H++HbO2- Buffer acid Weak acid buffer base conjugate base Converting strong acid or base into weak acid or base Buffer effect of cells Ion exchange between intracellular and extracellular fluids H+ HCO3- k+ Cl- Intracellular buffer systems H2PO4-/HPO42HPr/Pr- Respiratory regulation of acid-base Central chemoreceptor Peripheral chemoreceptor H+ H+, PaCO2, PaO2 Respiratory center ventilation Renal regulation of acid-base balance Excretion of H+ and reabsorption of HCO3in proximal convoluted tubule Excretion of H+ and reabsorption of HCO3in distal tubule Excretion of NH4+ and NH3 Parameters of acid-base balance pH 7.35-7.45 H2CO3=H++HCO3[H+]=pKa.[H2CO3]/[HCO3-] [H2CO3]=0.03PaCO2=1.2 PaCO2 PaCO2 is the partial pressure of CO2 dissolved in artery plasma, the normal range is 3346mmHg with a average value of 40mmHg. PaCO2 reflects the situation of alveolar ventilation. PaCO2↑ respiratory acidosis or metabolic alkalosis after compensation PaCO2↓ respiratory alkalosis or metabolic acidosis after compensation Standard bicarbonate (SB) and actual bicarbonate (AB) SB is the bicarbonate under “standard condition” which refers to a temperature of 38℃, PaCO2 of 40mmHg and 100% oxygen saturation of hemoglobin. Normal range: 22-27mmol/L Average value:24mmol/L SB↑ metabolic alkalosis or chronic respiratory acidosis SB↓ metabolic acidosis or chronic respiratory alkalosis AB AB is the bicarbonate measured under “actual condition” which refers to the actual status of the patient. A comparison between SB and AB can provide some information for the differentiation of respiratory acid-base disturbance from metabolic acid-base disturbance. Buffer base (BB) BB is the sum of all all alkaline buffer substances in the blood, which is also measured under standard condition. Normal range: 45-52mmol/L Average value: 48mmol/L Base excess (B E) BE describes the amount if a fixed acid or base that must be added to a blood sample to achieve a pH of 7.4 under standard condition. If an acid must be added, the BE value is positive. If an base must be added, the BE value is negative. The normal value is -3-+3mmol/L Anion gap (AG) AG is the difference between unmeasured anion (UA) and unmeasured cation (UC). AG=UA-UC=Na+-(Cl-+HCO3-)=140-10424=12mmol/L AG↑ metabolic acidosis Simple acid-base disturbance Metabolic acidosis respiratory acidosis Metabolic alkalosis Respiratory alkalosis Metabolic acidosis Metabolic acidosis is defined as a decrease of pH induced by primary decrease in plasma bicarbonate concentration. etiology Excessive production of fixed acid lactic acidosis (glycolysis) keto-acidosis (lipolysis) Disorders in the excretion of acidic metabolites renal failure, renal tubular acidosis I Excessive loss of HCO3loss of intestinal juice, bile, and pancreatic juice renal tubular acidosis II Excessive intake of exogenous acids NH4Cl, aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) hyperkalemia Classification Normal AG metabolic acidosis loss of HCO3- from intestinal of renal route excessive intake of chloride- containing medicine High AG metabolic acidosis lactic acidosis, keto-acidosis renal failure, salicylic poisoning compensation Compensation by the buffer system Compensation by the lung ventilation↑→PaCO2↓ △PaCO2=1.2△HCO3-±2 Compensation by the kidney Changes of acid-base parameters pH ↓, SB ↓, AB ↓, BE ↓PaCO2 ↓ AB<SB Alterations of metabolism and function Cardiovascular system Central nervous system Cardiovascular system Cardiac arrhythmia hyperkalemia Negative inotropic action H+ can competitively inhibit the combination of Ca2+ with troponin and influence the influx of Ca2+ from extracellular space and the release of Ca2+ into cytoplasm from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Decreased response of vascular system to CA Central nervous system Weakness, fatigue, lethargy, disorder of consciousness, coma Activities of Glutamate decarboxylase ↑ Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) ↑ Activities of oxygenase in mitochondria ↓ ATP ↓ Principles of prevention and treatmen Correction of underlying disorders Administration of NaHCO3 Attention should be paid to prevent hypokalemia and convulsion induced by decreased free Ca2+ Respiratory acidosis Respiratory acidosis is defined as a decrease of pH induced by primary increase in plasma H2CO3 concentration. Etiology Suppression of respiratory center Cerebrovascular accident Trauma or infection of brain Excessive sedatives, narcotics, alcohol Acute radiculitis Acute poliomyelitis Disease of respiratory muscles Organophosphorus pesticide poisoning Severe hypokalemia Disease of chest wall Pneumothorax, hydrops of thoracic cavity, chest deformity Drowning Aspiration of foreign bodies Obstruction of airways Laryngeal edema Laryngospasm Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Extensive inflammation Pulmonary disease Consolidation fibrosis Excessive inspiration of CO2 compensation H+-K+ exchange Acute respiratory acidosis Buffer effect of red blood cells Cl- -HCO3- exchange △[HCO3-]=0.1△PaCO2±1.5 Chronic respiratory acidosis Kidney excretion of H+ and NH4+↑,reabsorption of HCO3-↑ △[HCO3-]=0.4△PaCO2±3 Changes of acid-base parameters pH ↓, PaCO2↑ SB ↑, AB ↑, BE ↑ AB>SB Alterations of metabolism and function Central nervous system Cardiovascular system Nervous system CO2 narcosis headache, fatigue, mental derangement, tremor, lethargy, coma Pulmonary encephalopathy and hypoxia hypercapnia Cardiovascular system Dilation of brain blood vessels , intracranial hypertension, brain edema Cardiac arrhythmia and decreased cardiac contractility Principles of prevention and treatmen Keep the airway unobstructed and to improve ventilation Tracheotomy, intratrachea intubation, mechanical ventilation Metabolic alkalosis Metabolic alkalosis is defined as a increase of pH induced by primary increase in plasma bicarbonate concentration. Etiology Excessive loss of fixed acid loss from the stomach vomiting, gastric suction loss from the kidney diuretics, hyperaldosteroism Excessive intake of alkaline substances NaHCO3, stored blood (citrate) Hypokalemia paradoxical acidic urine Classification Saline-responsive alkalosis vomiting, gastric suction, diuretics Saline-resistant alkalosis hyperaldosteroism , severe hypokalemia Compensation Compensation by the buffer system Compensation by the lung ventilation↓→PaCO2↑ △PaCO2=0.7△HCO3-±5 Compensation by the kidney Changes of acid-base parameters pH ↑, SB ↑, AB ↑, BE ↑ AB>SB PaCO2↑ Alterations of metabolism and function Central nervous system restless, mental derangement, delirium, disorder of consciousness, GABA↓ Oxygen dissociation curve of hemoglobin shifts to left Free calcium ↓ convulsion, tendon hyperreflexia hypokalemia Principles of prevention and treatmen Saline-responsive alkalosis NaCl, KCl, CaCl2 Saline-resistant alkalosis antisterone, potassium, carbonic anhydrase (CA) Respiratory alkalosis Respiratory alkalosis is defined as a increase of pH induced by primary decrease in plasma H2CO3 concentration. Etiology Psychogenic factors nervousness, anxiety, hysteria Hypoxemia Some pulmonary disease ARDS Brain diseases encephalitis, meningitis Misuse of mechanical ventilation Compensation H+-K+ exchange Acute respiratory Buffer effect of red blood cells alkalosis Cl- -HCO3- exchange △[HCO3-]=0.2△PaCO2±2.5 + and Kidney excretion of H Chronic respiratory NH4+↓,reabsorption of HCO3-↓ alkalosis △[HCO3-]=0.5△PaCO2±2.5 Changes of acid-base parameters pH ↑, PaCO2 ↓ ,SB ↓, AB ↓, BE ↓, AB<SB Alterations of metabolism and function Disturbance in CNS vertigo, disorder of consciousness, coma Increased neuromuscular excitability, tetany, convulsion Principles of prevention and treatmen Treatment of primary disease Prevention mechanical hyperventilation Inspiration of oxygen-containing 5% CO2