Cells and Cell Organelles ppt
advertisement

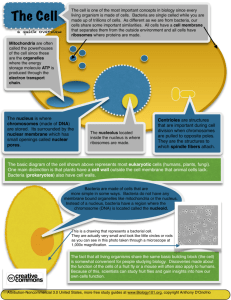
Cells What cell can be up to 3 ft. long In your body? Cell - is the basic unit of all structure and function of living organisms. Organelle – “little organ”, cell parts Write down the sequence of Developmental Steps from Conception to Birth of a Human! Union of Sperm + _______ makes Zygote (_______ _____) which forms into B____________ (hollow ball with many Stem Cells) This mass of cells is beginning of an Embryo S_______ Cells in embryo differentiate into specialized cells 6. That form T________ then O________ Organ systems Organism called a Fetus 7. Fetus is Born Infant (baby) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. True or False 1. Stem Cells can become any kind of eukaryotic cell. Stem Cells •Stem cells found in all multi-cellular organisms, they divide and differentiate into diverse specialized cell types and can self renew to produce more stem cells. •Humans stem cells: 2 types (1) embryonic stem cells – in embryos, fetus and post-birth children (responsible for becoming all the different cell lines for the development of a baby) (2) adult stem cells which are found in many various tissues. (Adult stem cells are found in the body after birth. Until recently, it was believed that adult stem cells could only become blood cells, bone cells and connective tissue) * Recent scientific studies have shown: that adult stem cells can transform into all For example: adult stem cells can become brain cells, kidney cells, heart cells, muscle cells, etc., etc. types of cells in the body. EuKaryote Cells, Multicellular Organism, Specialized Cells • Write in your own words how this baby represents all 3 terms – eukaryote cells, multicellular organism, and specialized cells What are the 2 basic cell types? 1. P_____________ 2. E_____________ Which is believed to have appeared on earth first? Cells and their Organelles Organelles – little organs, cell parts Cell – smallest unit of life Eukaryote Cells – Cells with a true nucleus, and membrane bound organelles. Prokaryote Cells – Cells with No nucleus Membrane bound Organelles – cell parts which are surrounded with a membrane. Name 2 structures both cells have in common? Prokaryotic Cells Cell with NO _____________, and NO Membrane-bound ____________. Prefix Check Matching: EuPro“cell” -Karyote -elle ______ little room ______ little ______ true ______ before ______ nucleus Eubacteria “true” bacteria What does the plasma membrane always surround in any cell? ____________ Bacteria Cell (Prokaryote) Largest known rod-shaped bacterium. (0.6 mm). Lives in the intestine of Sugeonfish. Epulopiscium fisheisoni Borrelia burgdorferi Spiral-shaped bacteria which causes Lyme Disease Cocci (sphere) shaped bacteria Bacteria Cell Structures • Cell Wall – (unlike plant cell wall), protection. • Loop of DNA – not surrounded or in a nucleus, instructions for making protein. • Plasmid – small circular piece of DNA, use in recombinant DNA. • Capsule – (not all bacteria have these), usually found in disease causing bacteria, added protection. • Flagella - movement All cells have 3 basic parts 1. Plasma Membrane 2. Cytoplasm (watery part of cell) 3. Genetic material (DNA & RNA) Cell Membrane How many Layers do You see? Hint: Red Plasma or Cell Membrane Besides having 2 phospholipid layers, WHAT are the round purple, orange, green structures? Eukaryotic Cells Let’s add to our definition of Eukaryote Cell A cell with a true nucleus AND contains M_____________ B_________________ O_________________ Prokaryote cells – have NO nucleus and NO Membrane Bound Organelles Membrane Bound Organelles Mitochondria Golgi Bodies Animal Cell X X X X Shape of Cell Determines __________ of the Cell. Animal Cell Organelles “little organs” • Nucleus - contains DNA, and controls all cell activity. • Ribosome – makes protein. • Mitochondria – “ powerhouse” of the cell, makes ATP, where cellular respiration occurs. • Nuclear membrane – around the nucleus, controls what enters and exits the nucleus. • Plasma (cell) Membrane – around the cell, controls what enters and exits the cell. • Nucleolus – makes ribosomes. • SER (smooth endoplasmic reticulum) – make more membrane, lipids. • RER (rough endoplasmic reticulum) – transports protein throughout cell. • Golgi Bodies – sorts, packages, and sends out protein. • Lysosome – contains protein digesting enzymes. • Centrioles (only in animal cells) – aid cell division. • Cytoplasm – watery part of the cell, location of organelles. Soldiers of the Blood! Plant Cell (Eukaryote) Plant Cells • Notice the shape. • Name the purple structure made up of cellulose. • Notice each green structure and name them. Additional Organelles in Plant Cells • Chloroplast – location of photosynthesis. Contains green pigment called chlorophyll. • Vacuole – holds water. • Cell Wall – protection, provides shape, and support to cell. Plant or Animal Cells? Identify 3 cell parts / What caused the blue color? Other Eukaryotic Cells Fungi Cell • Image taking with an SEM • Unicellular • Color enhanced (blue) are scars from budding. Example: Yeast cell Protist Cell - Paramecium Protist Cell (Paramecium) Organelles Cilia - hair like appendages that help the paramecium move food into the oral groove Contractile Vacuole - contracts and forces extra water out of the cell Food Vacuole - storage pocket for food Euglena (Protista) • What does this unicellular organism use its green chloroplast for? • What is the flagella used for? Amoeba (Eukarytic Cell) • Can you identify 3 noticeable “false feet”. • Do amoeba have a particular shape? Explain. Paramecium Dividing (Protista) • How many paramecium do you see? Can you identify the macronucleus and micronucleus in both? Amoeba Dividing (asexual) Can you identify the cells Psuedopods? Nucleus? Get a computer and log into http://learn.genetics.utah.edu Go to Cell Biology, then Amazing cells Receptor Proteins Marker Proteins