Change… - Sign In

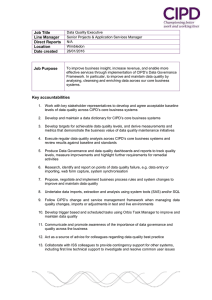
Leadership During
Change
Leadership and Influencing
Practice Module
May 2010
Catherine Lynch
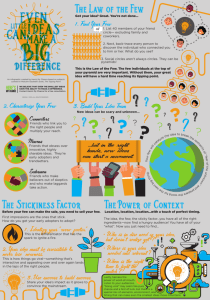
CHANGE
Change is “ … an intended, designed, purposeful attempt to alter the status quo in an organisation, situation or process.”
Lippitt, Watson & Wesley, 1958
Change is “… the process of analysing the past to elicit the present action required for the future.”
Kanter, 1984
“ Change management is not a neat sequential process.” Beckhard & Harris, 1987
Change…
… organisations are undergoing major change approximately once every three years. There are no signs that this pace of change will slow down.
… managers have to be able to introduce and manage change to ensure the organisational objectives of change are met, and they have to ensure that they gain the commitment of their people, both during and after implementation.
CIPD, 2006
Change…
For these reasons, it is important that the way change is managed is carefully considered by organisations.
Whilst each change situation will be unique, there are still a number of common themes that will help ensure that the change process stands the greatest chance of success.
CIPD, 2006
“Change-locally led, patient centred and clinically driven”
Focus of NHS Next Stage Review….
“ help local patients, staff and the public in making the changes they need and want for their local NHS”
(Darzi 2008)
PESTLE - External Influences
Political Economic
Ethical
Social
Legislation
Technological
Responses to change
Coping Cycle (Carnell 1995)
Stage 1: Denial
Stage 2: Defence
Stage 3: Discarding
Stage 4: Adaptation
Stage 5: Internalisation
Individual responses to change
Will depend on:
Personality and background
Broad experience
Attitudes, prejudices & feelings
Perception of the change
Sense of belonging to the organisation
preferences
Individual reactions to change
Missionaries
Believers
Lip-service
Hiders and refugees
Members of the underground
Emigrants
Binney & Williams 1995
Diffusion of Innovation Theory
Innovators: brave, pilot the change
Early Adopters: opinion leaders, try out new ideas
Early Majority: careful, but accepting of change
Late Majority: sceptic about change
Laggards: traditional, hold onto old ways
Rogers 1962
Change adoption distribution
(bell curve) an example
Aggregate of 3 groups of people
Early adopters
(< 10%)
1.
2.
Eventual adopters (the rest)
Never adopters
(< 10%)
Lewin’s Change Theory
Unfreeze
Forces resisting change
Change Refreeze
Forces promoting change
Lewin’s model: Discussion
What do you think are the strengths of
Lewin’s Model?
Are there any weaknesses in this model?
Present State
1a
Diagnose current situation
Future State
1b
Develop a vision for change
5
Assess and reinforce change
4
Implement the change
The Change Agent
2
Gain
Commitment to
The vision
3
Develop an
Action plan
The OD Model For Change
Senior & Fleming 2006
Change Agent Types
External Change Agent
External development consultant / Expert in field
Trouble-shooter/ possess right skills
Objective/ not involved in unit politics
More for technical/strategic stance
Internal Change Agent
Knowledgeable about subject
Formalised role allows clear agenda
Employee / Patient as Change Agent
Change agents
Change Strategists / Generators
Identify need, create vision, decide what is feasible
Change Implementers
Manage day to day change process, gain support and overcome resistance
Change Adopters
Take on change
CHANGE STRATEGIES
Power-Coercive
(Top Down)
Telling
Manipulating (positive)
Rational-Empirical
(Top Down)
Selling
Influencing (knowledge)
Normative-Reeducative (Bottom up)
Persuading
Participating/enabling
Delegating/empowering.
Bennis, Benne & Chin 1969
Planning Change: Leadership
Responsibilities
Possible Options:-
Building Alliances
Using Change Agents
Disseminating information
Education and Support
Supporting Practice.
Suggested Reading
King, N. and Anderson, N. (2002) Managing
Innovation and Change 2nd Ed. London:
Thomson.
Senior, B. and Fleming, J. (2006)
Organisational Change 3rd Ed. Harlow:
Prentice Hall.
Useful website:
http://www.cipd.co.uk/default.cipd