Hammurabi*s Code
advertisement
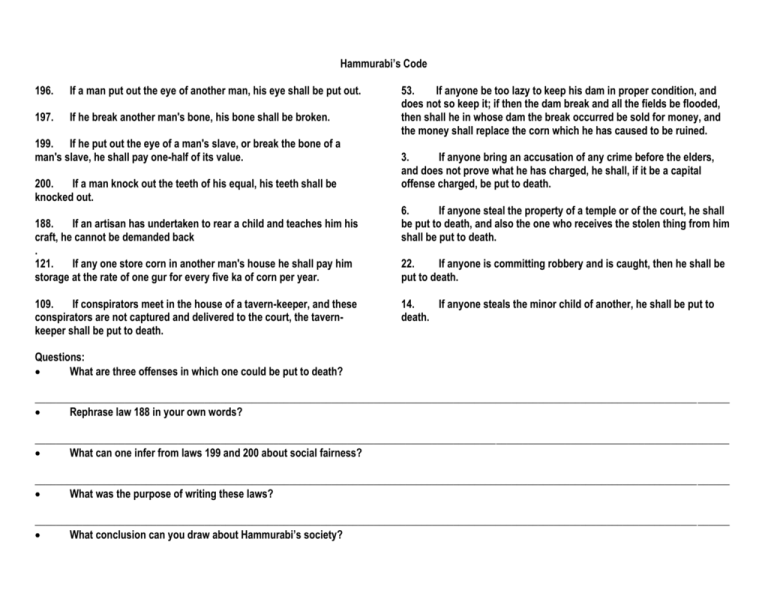
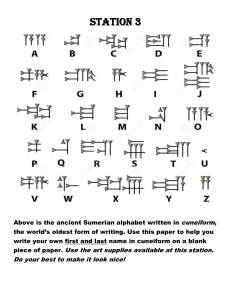
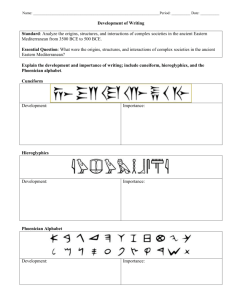
Hammurabi’s Code 196. If a man put out the eye of another man, his eye shall be put out. 197. If he break another man's bone, his bone shall be broken. 199. If he put out the eye of a man's slave, or break the bone of a man's slave, he shall pay one-half of its value. 200. If a man knock out the teeth of his equal, his teeth shall be knocked out. 188. If an artisan has undertaken to rear a child and teaches him his craft, he cannot be demanded back . 121. If any one store corn in another man's house he shall pay him storage at the rate of one gur for every five ka of corn per year. 109. If conspirators meet in the house of a tavern-keeper, and these conspirators are not captured and delivered to the court, the tavernkeeper shall be put to death. 53. If anyone be too lazy to keep his dam in proper condition, and does not so keep it; if then the dam break and all the fields be flooded, then shall he in whose dam the break occurred be sold for money, and the money shall replace the corn which he has caused to be ruined. 3. If anyone bring an accusation of any crime before the elders, and does not prove what he has charged, he shall, if it be a capital offense charged, be put to death. 6. If anyone steal the property of a temple or of the court, he shall be put to death, and also the one who receives the stolen thing from him shall be put to death. 22. If anyone is committing robbery and is caught, then he shall be put to death. 14. If anyone steals the minor child of another, he shall be put to death. Questions: What are three offenses in which one could be put to death? ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Rephrase law 188 in your own words? ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ What can one infer from laws 199 and 200 about social fairness? ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ What was the purpose of writing these laws? ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ What conclusion can you draw about Hammurabi’s society? Writing Some of the first writing was developed in Mesopotamia. Many social scientists credit the Sumerian people for this writing. The writing looked like symbols and was called cuneiform. The Sumerians wrote on clay tablets. Later, the Phoenicians, while still using cuneiform, began to produce their own 22-letter alphabet. This development made it easier for people of the ancient world to learn to read and write. In some ways, their alphabet looked like Egyptian hieroglyphics. The Greeks and Romans adapted the Phoenician writing form to create their own alphabet. Writing was used in commerce. It was especially important communicating the history of people. It was also a powerful way of letting people know the laws. The first written set of laws was called the Code of Hammurabi. (Use the passage to answer questions 1-3) 1. Which form of writing came first? A. Egyptian hieroglyphics B. Greek alphabet C. Sumerian cuneiform D. Phoenician alphabet 2. What is the name of the Sumerian writing system? A. B. C. D. hieroglyphics cuneiform Roman numerals Hammurabi's Code 3. What was a result of the development of an alphabet in ancient times? A. It was easier for people to read and write. B. Trade routes opened up from Rome to the cities of China. C. The Code of Hammurabi Code was declared useless for the average person. D. No one ever used cuneiform again. 4. The Sumerians surrounded their cities with thick walls to protect themselves from enemies. The largest structure in the city was a solid brick platform where the temple to the god of the city stood. What is the name given this platform? A. B. C. D. a ziggurat an oasis an amphitheater a monastery 5. Which feature of geography was the most important in helping the development of early river valley civilizations? A. B. C. D. fertile soils high mountains vast deserts smooth coastlines 6. What civilization developed in the land area between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers? A. Mesopotamia B. Egypt C. India