AP Psych: The Core Elements
advertisement

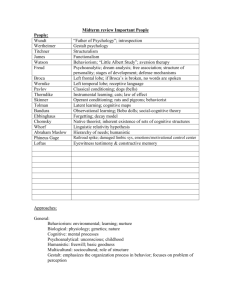
AP Psychology Review The following resources are available Review documents for each unit Practice exam FRQ Practice questions and rubrics Documents: Critical terms Confusing Pairs Famous Research Studies Content Percentages on Test 2-4% history and approaches 8-10% research methods 8-10% biological bases of behavior 6-8% sensation and perception 2-4% states of consciousness 7-9% learning 8-10% cognition 6-8% motivation and emotion 7-9% developmental psychology 5-7% personality 5-7% testing and individual differences 8-10% Social psychology Research Correlation vs. Exp. IV vs. DV Control vs. Exp. Group Random Ass. / Random Sample Confounding Var. Controls Op. Def. of Variables Correlation Coefficient Central Tendency Measures of variability Z score Bell Curve Valid, Reliable Replication Statistical Significance APA guidelines Neurobiology Neurotransmission Sensory / Motor neurons Nervous System Endocrine System Parts of Brain Brain hemispheres Brain imaging Plasticity Aphasia Split-Brain Developmental Psych Teratogens Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Attachment (imprinting) Critical Period Habituation Heritability Maturation Menarche / menopause Longitudinal v. cross-sectional Fluid v. Crystallized Parenting styles Theorists Piaget Kohlberg Gilligan Erikson Harlow Ainsworth Sensation Bottom Up / top Down Absolute Threshold JND / Weber’s Law Trichromatic v. Opponent Process Feature Detection Eye / Ear Audition / Olfaction Place v. Frequency theory Vestibular Sense Kinesthesis Perception Gestalt Binocular Cues Monocular Cues Perceptual Set Selective Attention Size / Color Constancy States of Consciousness / Personality Sleep stages Sleep Disorders Activation Synthesis v. Information Processing Lucid Dreaming Hypnosis Post-Hypnotic Suggestion Dissociation Drugs: Withdraw, tolerance, Depressants, stimulants, hallucinagens Personality Psychoanalysis / Freud Psychodynamic • Projective Tests Humanistic Trait Social-Cognitive • Albert Bandura • Aaron Beck Learning / Memory Pavlov= Classical Watson= Aversive Skinner= Operant Skinner Box Thorndike: Law of Effect Encoding, Storage, Retrieval Three Stage Processing Theory Iconic v. Ehoic Short-term = working memory LTP Theory Explicit v. Implicit Amnesia (types) Interference (types) Thinking / Language Concept / Prototype Representative Heuristic Availability Heuristic Insight Trial and Error Algorithm Obstacles to Problem solving Phonemes v. Morphemes Syntax v. Semantics Chomsky = nature Critical period / LAD Skinner = nurture Testing / Intelligence IQ = MA / CA x 100 Standardized Testing Reliability / Validity Achievement v. Aptitude Savant Syndrome Flynn Effect Bell Curve Factor Analysis Theorists Spearman- G Factor / Factor analysis Gardner: Mult. Intelligences Goleman- EQ Sternberg: Triarchic theory (analytical, creative, practical) Motivation / Emotion Drive-Reduction Homeostasis Push / pull factors Arousal Incentive Maslow’s Hierarchy Hunger Lateral v. Ventromedial Hypothalamus Set Point / BMR Sexual Motivation Achievement Motivation Conflicting motivations Emotions Facial expressions = universal Catharsis Feel good-do good James Lange theory Cannon-Bard Theory Schacter’s TwoFactor theory Stress Type A personality Type B personality Type A + negative anger = heart disease General Adaptation Syndrome Holmes and Rahe: Social Readjustment Rating Scale (numerical value on sterss) Abnormal Psychology DSM IV Psychiatrist v. Psychologist 2 weeks Neuroticism Psychotic Delusions / Hallucinations Disorders Anxiety Mood Disorders Somatoform Dissociative Schizophrenia Personality Disorders Therapy Psychotherapy Hans-Seyle General Adaptation Syndrome Social Readjustment Rating Scale A type, B type Types of Therapy Psychoanalysis Humanistic Behavioral Cognitive Biomedical Eclectic approach! Social Psych Cognitive Dissonance Foot in door / Door in Face Attribution Theory Fundamental Attribution Theory Just-World Belief Frustration-Aggression theory By-stander effect Social facilitation Social loafing Deindivuation Group Polarization Group Think Milgram Experiment Robber’s Cave Asch Experiment Stanford Prison Experiment Theorists Developmental Psych Piaget: Cognitive • Sensorimotor, Preoperational, Concrete Operational, Formal Operational Kohlberg: Moral • Preconventional, Conventional, Postconventional Erikson: Social (8 stages) Harlow: Touch and attachment Ainsworth: Secure, insecure attachment Theorists Formation of Personality Freud: Psychosexual Stages / Unconscious Adler, Jung: Psychodynamic Humanistic perspective • Carl Rogers: UPR, • Maslow: Self-actualization Trait Perspective (personality in the genes..) Personality Inventories Social Cognitive • Bandura: Reciprocal Determinism, self-efficacy • Julian Rotter: Locus of control • George Kelley: Personal constructs Theorists Intelligence Spearman Factor Analysis / G Factor Gardner: Multiple Intelligences (8) Howard Gardner: EQ (Emotional intelligence) Sternberg: Triarchic theory (analytical, creative, practical) Theorists Therapy Psychoanalysis (Unconcious) Humanistic Rogers: UPR, Active listening, non-directive Maslow: self-actualization, self-concept Gestalt: whole body Behavioral Systematic Desensitization Invivo Aversive Conditioning Cognitive Julian Rotter: locus of control / Seligman: LH Beck: Cognitive Triad / Bandura: Self-efficacy Depression Serotonin Seligman’s learned helplessness Beck’s cognitive triad Explanatory Style