Renal System Review Worksheet Identify each of the following
advertisement

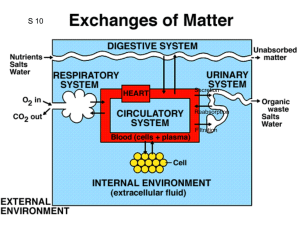
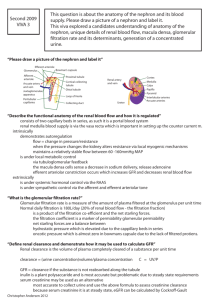
Renal System Review Worksheet Identify each of the following: Renal artery Segmental arteries Interlobar /Lobar arteries Arcuate arteries Interlobular arteries Afferent arterioles Glomerular capillaries Efferent arterioles Peritubular capillaries (vasa recta) Interlobular veins Arcuate veins Lobar/ Interlobar veins Segmental veins Renal vein b. What are the general functions of the kidney? Describe the kidney’s role relative to the following: i. water-soluble substance blood levels ii. blood volume – iii. pH iv. hormones v. enzymes Where is blood “filtered? How/where is the filtrate altered? Describe filtration direction tubular reabsorption tubular secretion What is the function of juxtamedullary nephrons? Identify the three processes responsible for urine formation. Hydrostatic fluid pressure physically forces fluid across the filtration membrane. Identify the actual filtering membrane within the glomerulus. What “elements” remain in the bloodstream? Define the glomerular filtration rate. Describe each of the three pressures that determine filtrate movement a. Glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP) – b. Capsular hydrostatic pressure (CHP) – c. Blood colloidal osmotic pressure (BCOP) Define the Net Filtration Pressure (NFP). What are the two main ways glomerular filtration rate can be adjusted? What is renal autoregulation? Compare sympathetic stimulation with autoregulation of glomerular filtration while at rest. What is the affect of angiotensin II? With a sudden increase in blood pressure, the heart atria secrete ANP. What is its affect on glomerular filtration? Where does renal absorption and secretion occur? What part of the tubule achieves most of the reabsorption? Describe paracellular reabsorption. Describe transcellular reabsorption. What kind of transport mechanisms are used for reabsorption? Describe the role of primary active transport with regard to sodium ions Na+. What nutrients are transported in this fashion? Describe the role of transporter proteins with regard to nutrient movement What determines the direction of water movement? How is the sodium gradient maintained? Describe reabsorption along the descending limb of the loop of Henle. Describe reabsorption along the ascending limb of the loop of Henle. Describe reabsorption along the distal convoluted tubule. Describe H+ and NH4+ ion secretion into the urine. What solutes are secreted at the collecting duct Water homeostasis is crucial to life. Define blood osmolarity. Describe the ADH affect on collecting ducts. What stimulates renin secretion from the juxtaglomerular cells in kidney nephrons? Renin promotes formation of angiotensin II. What affect does angiotensin II have? Summarize aldosterone’s affect on reabsorption of ions What affect does ANP have