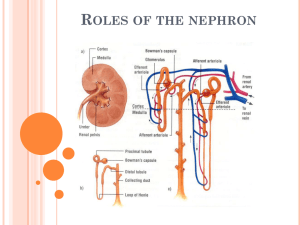
Renal
advertisement

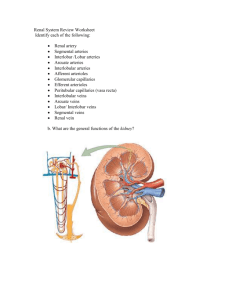
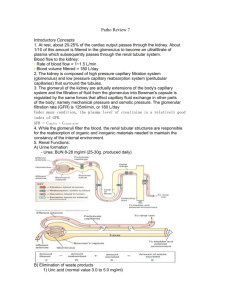
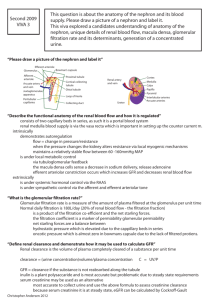
S 10 Secretion Reabsorption Filtration Drink plenty of water the day of lab; Avoid coffee, caffeine, salty foods 60 min 1 Hr before Lab Empty bladder; note time Drink Test Beverage 30 min 800 ml tap water 800 ml tap water + 7 g NaCl 80 ml tap water + 7 g NaCl 30 min 30 min At 30 min interval, collect urine measure V and [NaCl] Beginning of Lab: Collect Urine, measure V and [NaCl] 30 min 30 min S 11 Renal Physiology • Structures of the kidney • Four fundamental renal mechanisms – – – – Filtration Reabsorption Secretion Metabolism • Functions of the kidneys – Homeostasis • Fluid balance (blood pressure) • Electrolyte balance (blood pressure, membrane excitability) • Acid-base balance (in concert with lungs) Table 14.02 Lab: Extra 800 ml intake! Sidebar: some desert animals never drink and must obtain all their water in the diet. Table 14.04 Lab: Extra 7 g intake! Kidneys are source of 3 hormones: Renin, EPO, and Vit D. Kidneys are targets of 3 hormones: ADH, Aldosterone, ANH S 15 Nephron = tubule Tubular fluid vs urine Topics discussed: cortex, medulla, kidney stones, micturition (detrussor, internal and external urethra sphincters and innervation), incidence of bladder infections by gender, urethral sphincters Renal artery = One way in. Two ways out of kidney (renal vein or ureter) S 16 S 19 Juxtamedullary and Cortical Nephrons Fig. 14.02a Renal corpuscle Peritubular Capillaraies and branch thereof called vasa recta S 20 The nephron S 21 Fig. 14.03a Fig. 14.05 Glomerular Filtration Rate is 180 L/day Three stimuli for secretion of renin from JGC Ultrafiltrate of plasma enters Bowman’sFigure space 14.03 Composition same as plasma except no formed elements and no proteins and no substances bound to proteins Starling Fig. 14.08 Forces variable What substances can cause this constriction? Ways to alter GFR Fig. 14.09 What happens during hemorrhage? Fig. 14.02a Membrane proteins are segregated into apical (luminal) and basolateral membranes. Figure 14.10 reabsorption secretion Amino acid metabolism glucose Special terms • Filtration: movement of fluid from blood into the lumen of the nephron • Reabsorption: the movement of specific compounds from the lumen back into the blood (peritubular capillaries) • Secretion: the transport of specific compounds from blood into the lumen • Excretion: elimination from the body in urine Reabsorption and secretion in proximal tubule is NOT under hormonal control. Primary active transport of Na+ establishes a gradient for reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, etc. Reabsorption and secretion in DCT & CCD is under hormonal control. Hormones that act here: ANH, ADH, Aldosterone. Here, reabsorption of Na+ is linked to the secretion of K+. Effect of ADH: insertion of more aquaporins in the membranes Effect: Increase H2O reabsorption Normally, all14.31 filtered Figure bicarbonate is “reabsorbed” Filtration is controlled by aa and ea diameters! Consider a substance that in filtered only, no reabsorption, no secretion. Excretion of this substance = GFR Clearance of this substance = GFR • Clearance = volume of plasma from which a substance is completely removed (cleared) by the kidneys per unit time. • Clearance of Inulin is 120 ml/min • Cinulin or Ccreatinine = Glomerular Filtration Rate • If C x is greater than GFR ( which is Cinulin) then that substance undergoes NET TUBULAR SECRETION • If C x is less than GFR ( which is Cinulin) then that substance undergoes NET TUBULAR REABSORPTION Calculating clearance Clearance of s = Urine concentration of s X Urine Volume Plasma concentration of s “24 hour urine catch” + blood sample Special cases: Clearance of • Inulin and creatinine (filtered only; use to measure Glomerular Filtration Rate.) • Para Amino Hippurate (filtered and completely secreted, use to measure Renal Plasma Flow) Renal Handling of Substances Filtration + complete Secretion Ex: Para AminoHippurate (PAH) Measure Renal Plasma Flow Filtration + partial reabsorption Filtration + 100 Reabsorption Ex: Sodium Ex: Water Ex: Glucose Ex: Amino Acids A little more on Clearance: Clearance of glucose = 0 ml/min which means…. Clearance of X = 120 ml/min which means…. Clearance of antibiotic XXX = 500 ml/min which means… Who Cares? S 17 pp X P? S 18 Fluid-filled cysts Polycystic Kidney Disease Symptoms? Genetics? Prognosis & Treament? Fig. 14.04