Chapter 26
advertisement

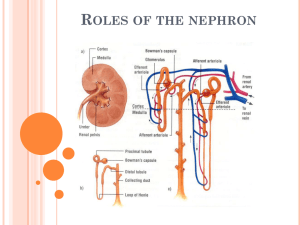
Chapter 26 The Urinary System I. Overview of the Urinary System (Independent review of material - text pages 952-955, figs 26.1-26.5) II. The Nephron A. Basic Nephron Anatomy • The renal corpuscle • The renal tubule B. Nephron functions include: • • • • Production of filtrate Reabsorption of organic nutrients Reabsorption of water and ions Secretion of waste products into tubular fluid C. Nephron Classification • Cortical nephrons • Juxtamedullary nephrons D. Blood flow to/around nephron E. Glomerulus/Bowman's Capsule anatomy F. Functional anatomy of the nephron • • • Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) • Reabsorbs needed nutrients, water and ions from filtrate Loop of Henle • Concentration of urine via reabsorption of water Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) • • Actively secretes ions, toxins, drugs into tubular fluid Reabsorbs sodium ions and water from tubular fluid III. Basic Principles of Renal Physiology A. Urine production maintains homeostasis • • Regulating blood volume and composition Excreting waste products • • Urea Creatinine B. Basic processes of urine formation • Filtration • Reabsorption • Secretion IV. Renal Physiology - Glomerular Filtration A. Filtration pressures - Glomerular filtration pressure (GFP) • • • In response to glomerular hydrostatic pressure (GHP) • Capsular hydrostatic pressure (CsHP) opposes GHP • Blood colloid osmotic pressure (BCOP) opposes GHP Net hydrostatic pressure (NHP) = GHP – CsHP Net hydrostatic pressure (NCOP) = BCOP – CsCOP Filtration (GFP) = NHP – NCOP B. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) • Amount of filtrate produced in the kidneys each minute Factors controlling the GFR V. Renal Physiology – Reabsorption and Secretion A. Reabsorption and secretion at the PCT • • • Glomerular filtration produces fluid similar to plasma without proteins The PCT reabsorbs 60-70% of the filtrate produced • • • Reabsorption of most organic nutrients Active and passive reabsorption of sodium and other ions Reabsorption of water Secretion also occurs in the PCT B. The loop of Henle and countercurrent multiplication C. Reabsorption and secretion at the DCT • • DCT performs final adjustment of urine • Active secretion or reabsorption Reabsorption • • • Tubular cells actively reabsorb Na+ and Cl- and water - controlled by hormones Usually in exchange for potassium or hydrogen ions (secreted) Urea is reabsorbed in collecting ducts D. Control of urine volume and osmotic concentration • Urine volume and osmotic concentration are regulated by controlling water reabsorption