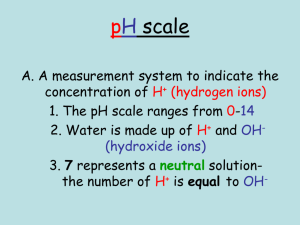
Reaction of an acid with a base (neutralization) always produces... HCl +
advertisement
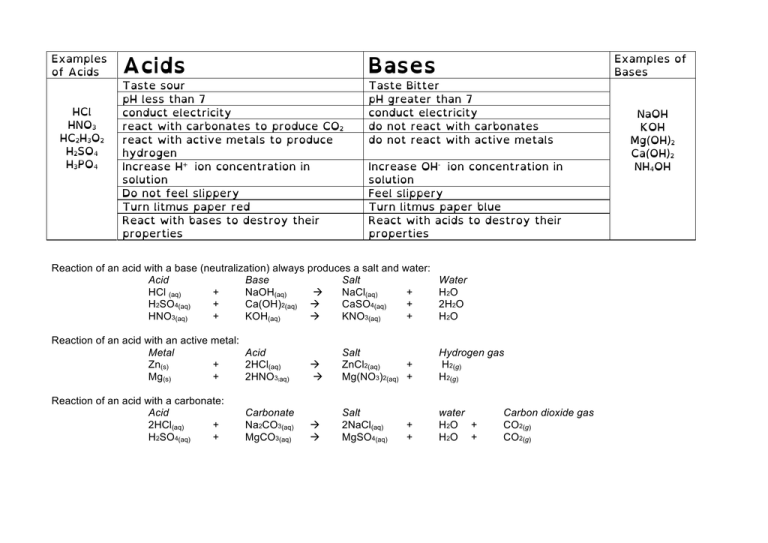
Examples of Acids HCl HNO3 HC2H3O2 H2SO4 H3PO4 Examples of Bases Acids Bases Taste sour pH less than 7 conduct electricity react with carbonates to produce CO2 react with active metals to produce hydrogen Increase H+ ion concentration in solution Do not feel slippery Turn litmus paper red React with bases to destroy their properties Taste Bitter pH greater than 7 conduct electricity do not react with carbonates do not react with active metals Increase OH- ion concentration in solution Feel slippery Turn litmus paper blue React with acids to destroy their properties Reaction of an acid with a base (neutralization) always produces a salt and water: Acid Base Salt HCl (aq) + NaOH(aq) à NaCl(aq) + H2SO4(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) à CaSO4(aq) + HNO3(aq) + KOH(aq) à KNO3(aq) + Water H 2O 2H2O H 2O Reaction of an acid with an active metal: Metal Acid Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) Mg(s) + 2HNO3 aq) à à Salt ZnCl2(aq) + Mg(NO3)2(aq) + Hydrogen gas H2(g) H2(g) Reaction of an acid with a carbonate: Acid 2HCl(aq) + H2SO4(aq) + à à Salt 2NaCl(aq) MgSO4(aq) water H 2O + H 2O + ( Carbonate Na2CO3(aq) MgCO3(aq) + + Carbon dioxide gas CO2(g) CO2(g) NaOH KOH Mg(OH)2 Ca(OH)2 NH4OH Acids and Bases are Everywhere! Most liquids have characteristics that are either acidic or basic. Svante Arrhenius came up with a definition for acids and bases in 1887. When something is dissolved in water that releases excess hydrogen ions, he saw that it had all the characteristics of an acid. When something dissolved in water that released excess hydroxide (OH-) ions, he saw that it had all the characteristics of a base. Pure water (distilled water) will naturally have a very small amount of it’s molecules split up into H+ ions and 2H2O --> H3O+ + OH- OH- ions. So when something dissolves into water that adds hydrogen ions, it will become acidic. HCl --> H+ + Cl- And when something dissolves into water that adds hydroxide ions, it will become basic (alkaline). NaOH --> Na+ + OH- The pH scale measures the amount of H+ ions in a solution. The pH scale is an inverse scale. This means that the higher the number, the less acidic it is. The pH scale is also logarithmic. This means that a change from a pH of 7 to a pH of 6 is 10 times more acidic. A change from a pH of 7 to 5 is 100 times more acidic.