(T/F) Acute health effects. 4.
advertisement

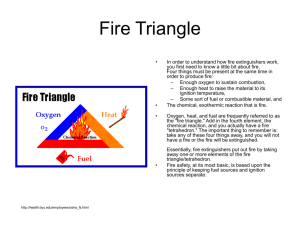
Safety @ WFU • http://www.wfu.edu/chem/courses/organic/ • Explore this site • Turn in Safety “Quiz” by Monday. Must make an 80%. Must Do Rules • #1 Wear Safety Glasses when in lab (all the time). An absolute. – 1 Warning then asked to leave lab • #2 Wear Gloves when in lab • #3 Clean spills with paper towels. Rinse acids/base spills with baking soda. • #4 Dispose of chemicals in back hood. • #5 No chemicals down drain unless told it’s OK. Must Do’s • • • • • • #5 No open toed shoes #6 No shorts #7 Keep long hair pulled back #8 No loose sleeves #9 No drinks or food in lab #10 Know where all safety equipment is located!!! Layout of Lab waste exit Enter Leave Book Bags outside lab Things that have happen • Cut by glass. Multitude of ways to cut yourself. • Lubricate thermometers before inserting. Do not force!!!! • Chemicals into eyes. Rinse with lots of water. • Fire!!!! Organic solvents have low flash points and hot plates WILL ignite them into a thermonuclear fire ball!!! • Allergic reactions, i.e. Asthma, hives, etc.. MSDS • physical data (melting point, boiling point, flash point, etc.), • Toxicity • health effects • first aid • Reactivity • storage, disposal, protective equipment, and spill-handling procedures. NFPA Diamond Fire Triangle • • • • http://health.byu.edu/employees/osha_fs.html In order to understand how fire extinguishers work, you first need to know a little bit about fire. Four things must be present at the same time in order to produce fire: – Enough oxygen to sustain combustion, – Enough heat to raise the material to its ignition temperature, – Some sort of fuel or combustible material, and The chemical, exothermic reaction that is fire. Oxygen, heat, and fuel are frequently referred to as the "fire triangle." Add in the fourth element, the chemical reaction, and you actually have a fire "tetrahedron." The important thing to remember is: take any of these four things away, and you will not have a fire or the fire will be extinguished. Essentially, fire extinguishers put out fire by taking away one or more elements of the fire triangle/tetrahedron. Fire safety, at its most basic, is based upon the principle of keeping fuel sources and ignition sources separate. 29 CFR 1910.106 • Flammable or Combustible? • To understand OSHA requirements for the safe storage of flammable and combustible liquids, we must begin by defining the two. A flammable liquid is any liquid having a flashpoint below 100° F (37.8° C) (except any mixture having components with flashpoints of 100° F (37.8° C) or higher, the total of which make up 99 percent or more of the mixture)(1910.106(a)(19)). Flammable liquids are categorized into three groups, as follows: • Class IA : Liquids having flashpoints below 73° F (22.8° C) and having boiling points below 100°F (37.8°C) (1910.106(a)(19)(i)). Examples: Acetaldehyde, ethyl ether and cyclohexane. Class IB: Liquids having flashpoints below 73° F (22.8° C) and having boiling points at or above 100° F (37.8°C) (1910.106(a)(19)(ii)). Examples: Acetone, benzene and toluene. Class IC: Liquids having flashpoints at or above 73° F (22.8° C) and below 100° F (37.8°C) (1910.106(a)(19)(iii)). Examples: Hydrazine, styrene and turpentine. A combustible liquid is any liquid having a flashpoint at or above 100° F (37.8° C) (1910.106(a)(18)). Combustible liquids are divided into two classes: Class II: Liquids having flashpoints at or above 100° F (37.8° C) and below 140° F (60° C), except any mixture having components with flashpoints of 200°F (93.3°C) or higher, the volume of which make up 99 percent or more of the total volume of the mixture (1910.106(a)(18)(i)). Examples: Acetic acid, naphtha and stoddard solvent. Class III: Liquids having flashpoints at or above 140°F (60°C) (1910.106(a)(18)(ii)). Class III liquids are subdivided into two subclasses: Class IIIA: Liquids having flashpoints at or above 140°F (60°C) and below 200°F, except any mixture having components with flashpoints of 200°F (93.3°C) or higher, the total volume of which make up 99 percent or more of the total volume of the mixture (1910.106(a)(18)(ii)(a)). Examples: Cyclohexanol, formic acid and nitrobenzene. Class IIIB: Liquids having flashpoints at or above 200°F (93.3°C) (1910.106(a)(18)(ii)(b)). Examples: Formalin and picric acid. Per 1910.106(a)(18)(ii)(b) "Class IIIB liquids" shall include those with flashpoints at or above 200°F (93.3°C). This section does not cover Class IIIB liquids. Where the term "Class III liquids" is used in the section, it shall mean only Class IIIA liquids. (Class IIIB is used in this document for reference purposes only.) *Note: When a combustible liquid is heated for use to within 30°F (16.7°C) of its flashpoint, it shall be handled in accordance with the requirements for the next lower class of liquids (1910.106(a)(18)(iii)). The flashpoint and boiling point determine the class of a liquid. However, these should not be the only criteria used to determine the hazards of a liquid. Many other factors should also be considered for the proper use and storage of hazardous liquids. These factors include: ignitions temperature, explosive limits (LEL or UEL), vapor pressure, specific gravity and vapor density. • • • • • • • • • • • Combustible materials have a flash point above 100° F (37.8° C)