Layered Liquids information and question sheet
advertisement
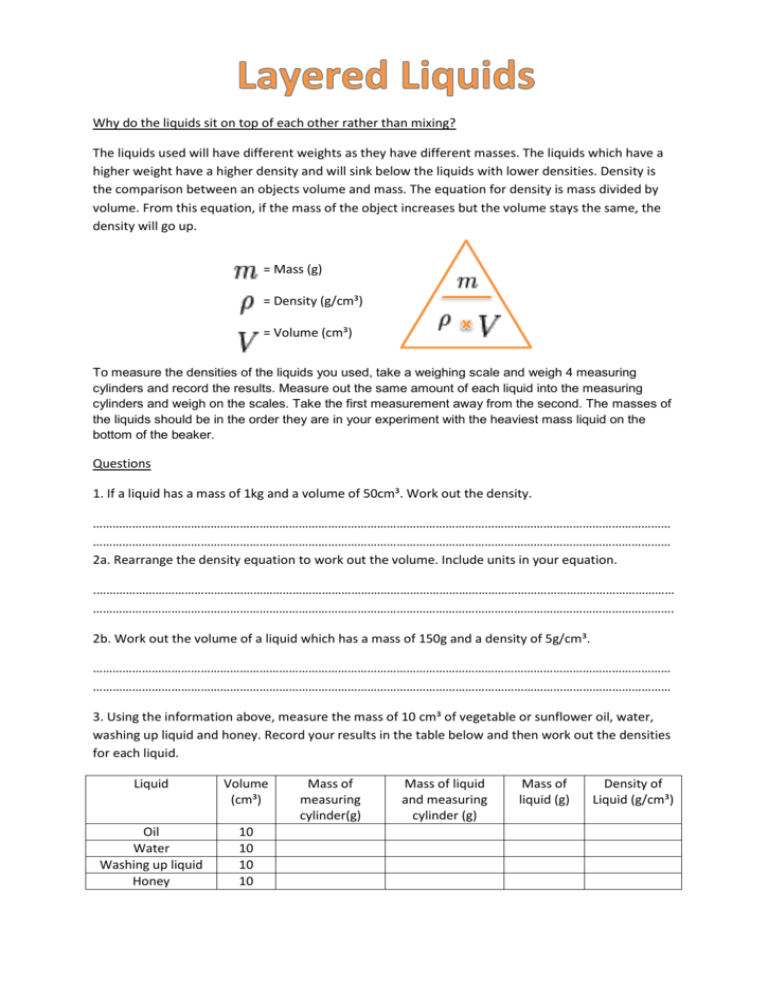
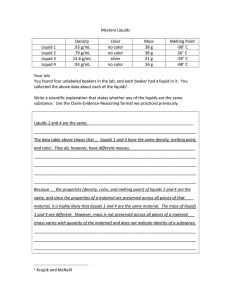
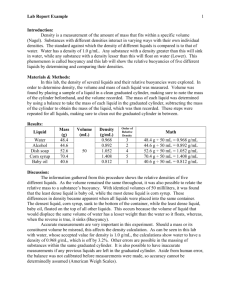
Why do the liquids sit on top of each other rather than mixing? The liquids used will have different weights as they have different masses. The liquids which have a higher weight have a higher density and will sink below the liquids with lower densities. Density is the comparison between an objects volume and mass. The equation for density is mass divided by volume. From this equation, if the mass of the object increases but the volume stays the same, the density will go up. = Mass (g) = Density (g/cm³) = Volume (cm³) To measure the densities of the liquids you used, take a weighing scale and weigh 4 measuring cylinders and record the results. Measure out the same amount of each liquid into the measuring cylinders and weigh on the scales. Take the first measurement away from the second. The masses of the liquids should be in the order they are in your experiment with the heaviest mass liquid on the bottom of the beaker. Questions 1. If a liquid has a mass of 1kg and a volume of 50cm³. Work out the density. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2a. Rearrange the density equation to work out the volume. Include units in your equation. .…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 2b. Work out the volume of a liquid which has a mass of 150g and a density of 5g/cm³. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3. Using the information above, measure the mass of 10 cm³ of vegetable or sunflower oil, water, washing up liquid and honey. Record your results in the table below and then work out the densities for each liquid. Liquid Volume (cm³) Oil Water Washing up liquid Honey 10 10 10 10 Mass of measuring cylinder(g) Mass of liquid and measuring cylinder (g) Mass of liquid (g) Density of Liquid (g/cm³)