Lesson 2 - Aldehydes and Ketones

After completing this lesson you should be able to :
• Many flavour and aroma molecules are aldehydes.
• Straight-chain and branched-chain aldehydes and ketones, with no more than eight carbon atoms in their longest chain: can be named from structural formulae. structural formulae can be drawn from names molecular formulae can be written from names
• Structural formulae and names of isomers of straight and branch chain aldehydes and ketones.
• Aldehydes, but not ketones, can be oxidised to carboxylic acids. Fehling’s solution, Tollens’ reagent and acidified dichromate solution can be used to differentiate between an aldehyde and a ketone. Positive test results:
Fehling’s — blue solution to a brick red precipitate
Tollens’ — formation of a silver mirror acidified dichromate test
— colour change from orange to green
• In terms of intermolecular forces, explain the influence of functional groups, including hydroxyl, carbonyl and carboxyl, on solubility, boiling points and volatility
• When applied to carbon compounds, oxidation results in an increase in the oxygen to hydrogen ratio and reduction results in a decrease in the oxygen to hydrogen ratio.
Aldehydes and Ketones
Learning intention
Learn about the characteristic functional groups and chemical reactions of aldehydes and ketones. Study how aldehydes and ketones are named and drawn.
Aldehydes and Ketones
H
H
CH
3
H
+ -
C = O
C = O
CH
3
CH
2
C = O
CH
3
Methan al , a 40% solution in water is formalin, and is used to make polymers
Ethan al , Its trimer (CH
3
CHO)
3 is used as a sleep inducing drug. It also causes a hangover
Butan one , is a solvent used to make VHS tapes.
Butan-2-one C
4
H
8
O
COPY
CH
3
CH
3
C = O Propan one , nail varnish remover and is used in the making of perspex
COPY
Aldehydes and Ketones
Distinguishing tests (Using mild oxidising agents.)
Aldehydes are oxidised to carboxylic acids
Ketones do not react with mild oxidising agents
1. Fehlings solution contains Cu 2+ ions (blue) which form Cu + ions
(orange-red) in the presence of aldehydes.
2. Tollens’ reagent contains Ag + ions, which form Ag in the presence of aldehydes (silver mirror test)
3. Acidified Potassium dichromate orange Cr
2
O
7
2(aq) to green Cr 3 (aq)
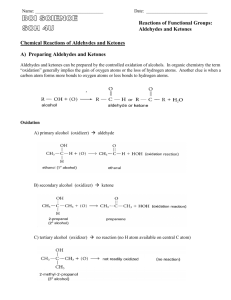
Oxidation
INTRODUCTION
Both aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl group.
COPY
C O
In aldehydes a hydrogen atom is bonded to the carbonyl group but in ketones the carbonyl group is always flanked by carbon atoms:
O O
C aldehyde
H C C ketone
C
This structural difference accounts for the fact that aldehydes can undergo mild oxidation to form carboxylic acids but ketones resist oxidation. Oxidising agents can therefore be used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
The aim of this experiment is to use the mild oxidising agents, acidified potassium dichromate solution, Benedict's solution and Tollens' reagent, to distinguish between two given carbonyl compounds one of which is an aldehyde and the other a ketone.
Oxidation
Collect a workcard
Procedure
1. Before collecting the carbonyl compounds X and Y set up a water bath and heat the water until it boils. Turn off the Bunsen.
2. Add sulphuric acid to each of two test tubes to a depth of about 2 cm. Then add
potassium dichromate solution to both to give a total depth of about 3 cm in each.
3. To one of these test tubes add about 5 drops of compound X and to the other add about 5 drops of compound Y.
4.Place both test tubes in the water bath and observe and record any changes.
5.Add Benedict's solution to each of two test tubes to a depth of about 3 cm.
6. Repeat steps 3 and 4.
7. Add Tollens' reagent to each of two very clean test tubes to a depth of about 3 cm.
8. Repeat steps 3 and 4 and immediately after, wash the contents of the test tubes down the drain with large amounts of water.
Oxygen to Hydrogen Ratio
COPY
These are different definitions from those met previously and only apply in carbon chemistry.
oxidation eg C
2
H
5
OH → CH
3
CHO
O:H 1:6 1:4
Oxidation of ethanol to ethanal has increased the
O:H ratio. Ethanal can also be reduced back to ethanol and this would be a decrease of the ratio.
Try examples in your notes
Higher Chemistry
Unit 2 Nature’s Chemistry
Aldehydes & Ketones
Multiple Choice Questions
This is designed to be used by teachers to help students develop skills in answering multiple choice questions.
Douglas Racey, Waid Academy, Anstruther, Fife, Scotland
Higher Chemistry Unit 2 - Aldehydes and Ketones….
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following is an isomer of hexanal?
A. 2-methyl butanal
B. 3-methylpentan-2-one
C. 2,2-dimethylbutan-1-ol
D. 3-ethylpentanal
Answer
B.
Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Aldehydes and Ketones ….
Multiple Choice Questions
2.
Which of the following cannot be classed as oxidation?
A. CH
3
CH
2
OH
CH
3
CHO
B. CH
3
CH(OH)CH
3
CH
3
COCH3
C. CH
3
COCH
3
D. CH
3
CH
2
OH + O
2
CH
3
CH(OH)CH
3
CO
2
+ H
2
O
Answer
C.
Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Aldehydes and Ketones ….
Multiple Choice Questions
3.
Which alkanol will produce a ketone on oxidation using acidified potassium dichromate?
A. 2-methyl butan-2-ol
B. pentan-1-ol
C. 3-methyl hexan-2-ol
D. 2-methyl propan-2-ol
Answer
C.
Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Aldehydes and Ketones ….
Multiple Choice Questions
4.
The alcohol shown below will
A. oxidise to form an aldehyde
B. oxidise to form a ketone
C. oxidise to form an aldehyde and a ketone
D. not oxidise
Answer
D.
Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Aldehydes and Ketones ….
Multiple Choice Questions
5.
Oxidation of 4-methylpentan-2-ol to the corresponding ketone results in the alcohol
A. losing 2g per mole
B. gaining 2g per mole
C. gaining 16g per mole
D. not changing in mass
Answer
A.
Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Aldehydes and Ketones ….
Multiple Choice Questions
6.
When propanal is heated with Fehling’s solution there is
A. a colour change from green to orange
B. a colour change from blue to red/orange
C. a negative test with Tollen’s reagent
D. no colour change
Answer
B.
Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Aldehydes and Ketones ….
Multiple Choice Questions
7. When butanone is heated with Fehling’s solution there is
A. a colour change from orange to green
B. a colour change from blue to red/orange
C. a silver mirror formed
D. no colour change
Answer
D.
Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Aldehydes and Ketones ….
Multiple Choice Questions
8
. When the vapour of liquid X is passed over hot copper(II)oxide, a reaction occurs and the vapour produced gives an orange precipitate with Fehling’s solution. X could be
A. propan-1-ol
B. propan-2-ol
C. propanal
D. propanone
Answer
A.
Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Aldehydes and Ketones ….
Multiple Choice Questions
9.
Butan-1-ol is converted to butanal by warming it with potassium dichromate acidified with sulphuric acid. The purpose of the acidified dichromate is to
A. reduce the alcohol
B. dehydrate the alcohol
C. hydrate the alcohol
D. oxidise the alcohol
Answer
D.
Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Aldehydes and Ketones ….
Multiple Choice Questions
10.Which compound is formed by the oxidation of propan-2-ol
A. CH
3
CH
2
CHO
B. CH
3
COCH
3
C. CH
3
CH
2
COOH
D. CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
OH
Answer
B.