AP WORLD HISTORY

AP WORLD HISTORY
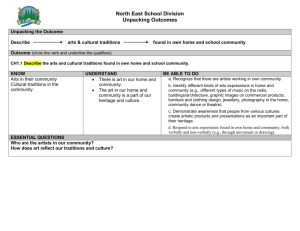
Common Usage Terms
K.M.H.S.
AP World History
Mrs. Farbacher
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
Incorporate the concepts and terms in this presentation throughout the course.
Relate them to each theme and/or topic.
Evaluate/describe:
Political systems= [How do they govern?]
Economic systems= [How do they make a living?]
Cultural systems= [Traditions, Gender roles, etc.?]
Biological systems= [Where do they live? Climate?
Environmental interactions?]
Key Comparisons
All key comparisons/contrasts must be:
Comprised of Venn Diagram
Include small map on the back if applicable
Continuity & Change
TRADITIONAL TENDENCIES WITHIN A SOCIETY
Continuities :
Long-standing traditions within a society
Stay the same over time or are recurring
Example: Confucianism
Changes:
Traditions that are newly adopted
Identifies changes within society
Example: Adoption of Buddhism
TIME MEASURES
B.C.E.
Before Current/Common Era
All measured time before the year 0
C.E.
Current/Common Era
All measured time from year 0 to present
ALL DATES GIVEN ARE RELATIVE AND
COULD BE QUOTED DIFFERENTLY IN
OTHER SOURCES.
CENTURY DESIGNATES
Centuries are quoted thus:
1901 to 2001 = 20 th Century
2001 to 2101 = 21 st Century
Thus the years cited would be designated the later [next] “century”
Ex. 1492 = 15 th Century
Ex. 1776 = 18 th Century
CENTURY DESIGNATES
16 th Century – Spain
17 th Century – Dutch
18 th Century – France
19 th Century – Britain
20 th Century – America
21 st Century - ?????
VERNACULAR
Terms / concepts in the common language of historians .
Using the vernacular implies that you will use the appropriate terms identified throughout the course.
Doing this will get you points on the AP exam.
AND MY EXAMS!
OTHER ABBREVIATIONS
Million
M
Thousand
K
Billion
B
Hundred
C
Circa [Latin term]
c. [means around this time]
Casualty
Statistics:
KIA
Killed in action
MIA
Missing in action
WIA
Wounded in action
Used later in the course
LEGAL TERMS
Dejure`
[Latin term]
Means legal or legally recognized based in law.
Defacto
[Latin term]
Means in practice but not legally recognized or based in law.
LATIN TERMS
Ad hoc
Et al.
et cetera
Habeas corpus
INRI
Mare nostrum
Modus operandi
Pater Familias
Pax
Americana
Romana
Per annum
Per Capita
Per diem
Quid pro quo
Sic.
SPQR
Status quo
Terra incognita
Vae victis
Veni vidi vici
Veto
WORLD RELIGIONS
Polytheism
Belief in a pantheon of gods
[many].
Mesopotamia
Egypt
Greece
Rome
Hinduism
RELIGIONS
Monotheism
Belief in only one god.
Judaism
Christianity
Islam
Buddhist epistemology does not support the existence of one or more gods.
SOCIETAL INFLUENCE
MATRIARCHAL
Early societies
Female deities
Female power base
MATRILINEAL
Inheritance through female
Parallel Descent: [Inheritance]
Boys from father
Girls from mother
PATRIARCHAL s
Agricultural societies
Male power base
Male deities
PATRILINEAL
Inheritance through male
Two Important Terms
[Will be used throughout course]
SYNCRETISM
Degree to which
CULTURAL
IMPERIALISM one society
Degree to which adopts one society traditions of adopts another culture traditions of
Done by choice another culture not coercion
Done by coercion not choice
IS IT ORIGINAL OR A COPY?
INDEPENDENT
INVENTION
Innovation that is new or original
No outside influences involved.
CULTURAL
DIFFUSION
Innovation that is introduced from another group or civilization
Usually through trade or other interaction
.
Enduring Questions
You must be able to evaluate transregional cultural diffusion.
You must be able to identify the role of syncretization and cultural imperialism at work in that diffusion .
ALL EVENTS STUDIED MUST BE
ADDRESSED BY ANSWERING “WHY”.