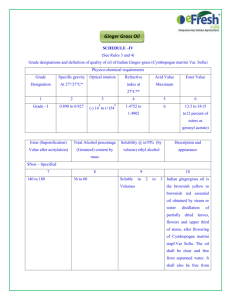
Lesson 5 - Making Esters
advertisement

+ + After completing this topic you should be able to : • State esters are formed by the condensation reaction between an alkanoic acid and an alcohol. • State the ester link is formed by the reaction of a hydroxyl group with a carboxyl group. • Name an ester given the names of the parent alkanol and alkanoic acid or from shortened and full structural formulae. • Can draw shortened and full structural formulae for esters given the names of the parent alkanol and alkanoic acid or the names of esters. • Describe an experiment where an ester is produced. • Give examples of the uses of esters. When a CARBOXYLIC (ALKANOIC) ACID molecule reacts with an ALCOHOL (ALKANOL) molecule a molecule called an ESTER forms. The hydroxyl group of the alcohol reacts with the carboxyl group of the acid. + hydroxyl group + carboxyl group ester link water molecule (carboxylate group) During the reaction the H atom of the hydroxyl group and the OH of the carboxyl group break off and join to form a water molecule. The alcohol and acid molecules join to form an ester link (carboxylate group). A reaction where a molecule of water is eliminated as two molecules join, is called a CONDENSATION REACTION. Making an ester is a CONDENSATION REACTION. The name of an ester comes from the alcohol and carboxylic acid from which it is made. The alcohol molecule gives the ester its first name. The alcohol name changes to ALKYL. The carboxylic acid molecule gives the ester its second name. The acid name changes to ALKANOATE. propanol + ethanoic acid methanol ethanol propanol methyl ethyl propyl butanol butyl methanoic acid ethanoic acid propanoic acid methanoate ethanoate propanoate butanoic acid butanoate propyl ethanoate + water Making an ester is a condensation reaction. The reaction is called ESTERIFICATION as the reaction produces an ester. alcohol + carboxylic acid propanol + ethanoic acid ester propyl ethanoate + H C C C O H H H H CH3CH2CH2OH + + water ester link (carboxylate group) H O + water + water molecule eliminated H H H + C H O C H HOOCCH3 H H H H H C C C H H H O O H C C H + O H H CH3CH2CH2OOCCH3 + H2O H ethanol + H H H C C O H H H O + H H CH3CH2OH ethyl methanoate methanoic acid + C H water O O H + H CH3CH2OOCH + H2O H C C H O HOOCH + O C H H A CONDENSATION REACTION is a reaction where molecules join with the elimination of a small molecule (often water). Making an ester by reacting an alcohol with a carboxylic acid is a condensation reaction. Making an ester is also called ESTERIFICATION. H Esters can be recognised by the two oxygen atoms from the CARBOXYLATE GROUP (COO or OOC) in the middle of the formula. The formula / structure of an ester can be written with the alcohol part followed by the acid part or vice-versa. H H H C C H H O O H H H C C C C H H H H OR H H H H O C C C C H H H O H H C C H H H alcohol part acid part acid part alcohol part 2 carbons 4 carbons 4 carbons 2 carbons butanoate butanoate ethyl ethyl ethyl butanoate The following examples shows how to name an ester from its shortened structural formula or molecular formula. SHORTENED STRUCTURAL FORMULA MOLECULAR FORMULA CH3CH2OOCCH2CH2CH3 C2H5OOCC3H7 ethyl ethyl butanoate butanoate OR CH3CH2 CH2 COOCH2CH3 butanoate ethyl C3H7 COOC2H5 butanoate ethyl To prepare an ester an alcohol (ethanol) has to be reacted with a carboxylic acid (propanoic acid). The rate of the reaction is slow at room temperature and the yield of ester is low. The rate of the reaction can be increased by heating the reaction mixture and by using concentrated sulphuric acid as a catalyst. The presence of the concentrated sulphuric acid increases the yield of ester. paper towel soaked in cold water hot water alcohol (ethanol) and carboxylic acid (propanoic acid) + a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid The mixture is heated for a short time (10 mins). After heating pour the contents of the test tube into a solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate. This reacts with any unused acid. ester floats as an oily layer on top of the solution sodium hydrogencarbonate solution The ester can be carefully smelled. Esters have a pleasant fruity smell. Esters are found in fragrances giving flowers, fruit, perfumes their characteristic smell. Esters are also used in flavourings. Many esters have pleasant smells and flavours. They are found in nature in common fruit flavours. They are found in coffee, tea, wine and beer. Ester Parent Alcohol Parent Carboxylic Acid Flavouring / Fragrance propyl pentanoate propan-1-ol pentanoic acid pineapple ethyl butanoate ethanol butanoic acid apple octyl butanoate octan-1-ol ethanoic acid orange pentyl ethanoate pentan-1-ol ethanoic acid banana Esters are good solvents for varnishes, paints and adhesives. For example, butyl ethanoate and ethyl ethanoate. These esters have a low boiling point and evaporate easily i.e. they are volatile liquids. Esters are found in medicines. They are used in local anaesthetics. For example, benzocaine, cocaine, novocaine. Aspirin, a common pain killer, is the ester called ethyl salicylate.