Chapter 5: Classical Greece
advertisement

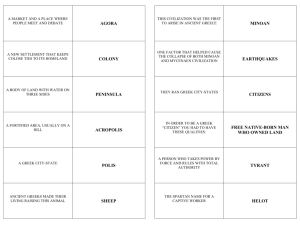
CHAPTER 5: CLASSICAL GREECE * GREEK STATION STAMPS • Use your worksheet from the Greek Stations to complete the following assignment on your own paper. • Imagine the post office has announced a contest to create a commemorative Greek stamp. • Choose 4 Greek accomplishments from your worksheet & design a commemorative stamp for each accomplishment. Each stamp should be labeled and in color. • Under each stamp, briefly explain the accomplishment is. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. Describe the creation and development of Greek government. 2. Compare the development of Athens and Sparta. SECTION ONE: CULTURES OF THE MOUNTAINS AND THE SEA I. Geography Shapes Greek Life • Very mountainous • 2,000 islands that are located in the Aegean and Ionian Seas • Physical geography shaped Greek traditions and customs A. The Sea • Greeks’ lives revolved around the sea • Aegean Sea, Ionian Sea, Black Sea all important transportation routes- linked most parts of Greece and other societies • Poor in natural resources, lacked wood, metals, and farmland B. The Land • ¾ of Greece is covered by mountains= difficult to unite Greece under a single gov’t • Most formed small independent communities • Travel was very difficult - 60 miles could take up to 7 days • Only 20% of land usable for farming • Poor farmland= Greece never able to support a large population C. The Climate • 48 degrees F in the winter, 80 degrees in the summer • These moderate temps supported an outdoor life for the ppl II. Mycenaean Civilization Develops • Settled the Greek mainland around 2000 BC • name from their city Mycenae • City located on a steep rocky ridge surrounded by a 20 foot thick wall • Warrior kings ruled surrounding villages and farms (1600-1100 BC) MYCENAE A. Culture and Trade • Sometime around 1500 BC Mycenaean’s came into contact w/ the Minoans through trade • Saw importance of seaborne trade • Adapted much of Minoan culture to their own including writing system • Influenced religion, art, politics, and literature B. The Trojan War • A 10 year war b/w the Mycenaean’s and Troy (located on Anatolia) • Believed to have started w/ the kidnapping of Helen, wife of a Greek king • Trojans lose b/c of Greek trick- Trojan horse • Thought at first to be a story, evidence gathered shows that Trojan War may have been based on real ppl and events MYCENAE AND TROY * III. Greek Culture Declines • Mycenaean’s collapsed after the Trojan War • 1200’s a new group moved in called the Dorians • far less advanced- economy collapsed, trade halted • so interesting b/c it looks like Greeks forgot how to write, no written records for the next 400 years A. Epics of Homer • With no written record, ppl learned their history through spoken word • Greatest storyteller was a blind man named Homer • Greatest epics were The Iliad and The Odyssey • The Iliad was about the Trojan War B. Greeks Create Myths • Greeks dev. a rich set of myths - traditional stories about their gods • Explained the mysteries of nature and the power of human passion • Contribute human qualities- love, hate, and jealousy to gods • Greek gods argue/compete w/ each other constantly- much like humans. But the gods live forever Zeus, ruler of gods, lives on Mt. Olympus, with his wife Hera and their daughter, Athena- the goddess of wisdom Section 2: Greece’s Warring City States I. Rule and Order in Greek City States • 750 BC polis was fundamental political unit in ancient Greece • Each polis made up of 50- 500 sq miles • less than 10,000 residents • Each polis is a city-state A. Greek Political Structures • Greek City-states had various forms of gov’t, 3 main types: 1. Monarchy- ruled by king 2. Aristocracy- ruled by groups of wealthy nobles (landowners) 3. Oligarchy- ruled by a few powerful people (merchants and artisans) B. Tyrants Seize Power • rulers & common ppl often clashed • nobles sought to gain power by appealing to the lower classes for support- called tyrants • Unlike today, tyrants in ancient Greece generally not harsh- most started building programs to help the common ppl II. Athens Builds a Limited Democracy • Some city-states moved toward a democracy- rule by the ppl, to avoid power struggle between rich & poor A. Building Democracy • First step 621 BC- made by Draco, developed a legal code based on equality of all citizens under the law • Draco’s code dealt harshly w/ criminals and introduced debt slavery- work as slaves to repay debts BUILDING A DEMOCRACY CONTINUED… • Second Step- 594 BC- Solon came to power, introduced new reforms: • Outlawed debt slavery • Organized Athenian citizens into four social classes according to wealth • Top 3 classes could hold political office • All citizens could participate in the assembly • Any citizen could bring charges against wrongdoers BUILDING A DEMOCRACY CONTINUED… • Third Step- Around 500 BC Cleisthenes introduced new reforms • organized social classes based on geography rather than wealth • Increased power of assembly by allowing anyone to submit laws • Created Council of Five Hundred, proposed laws, managed assembly- members chosen by voting or at random BUILDING A DEMOCRACY CONTINUED… • reforms made Athens a limited democracy, only citizens could participate in gov’t • “citizen”= free, adult, male, property owner, born in Athens • Everyone else excluded from citizenship and had few rights Draco • Equality • Debt slavery Solon • Social classes • Top 3 hold office Cleis. • Geo classes • Council of 500 Limited Democracy B. Athenian Education • Schooling only for sons of wealthy landowners • Began school at the age of seven • Edu aimed at making men good citizens • Studied reading, grammar, poetry, history, math and music • trained in logic and public speaking • Athletics important in edu • Girls learned from females at home III. SPARTA BUILDS A MILITARY STATE • located in southern Greece, nearly cut off from rest of Greece by Gulf of Corinth • Greatly contrasts w/ other city-states, especially Athens. • Instead of a democracy, Sparta develops a military state SPARTA AND ATHENS * * A. Sparta Dominates Messenians • 725 BC- Defeat Messenians ,forced them to farm the land, called them helots, took ½ their crops ea year • Messenians revolt but fail, Spartans, fearful of another revolt, create a new, stronger gov’t B. Spartan Government- Several branches: • Assembly—composed of all Spartan citizens, elected, voted on major issues • Council of Elders—30 older Spartans proposed laws on which the assembly voted • 5 elected officials—carried out laws passed by Assembly, also in charge of edu & court cases • Kings- two kings ruled over the military forces Spartan Government C. Spartan Social Groups • Ruling families, citizens- owned land • Free Non-citizens—worked in commerce and industry • Helots—worked farms or as house servants Spartan Social Classes D. Spartan Daily Life • 600BC- 371BC, Sparta had strongest military in Greece • Individual expression was discouraged, did not value the arts • Spartans valued duty, strength, discipline • At age 7 boys moved into army barracks begin their training. Stayed until age 30. • Trained in all forms of weather, wore a light tunic and no shoes, slept w/o blankets and on hard benches • Girls received some military training, and were granted much freedom to run the household and businesses while the men were on active military duty • Both men and women taught to put Sparta above all else- even above family • Could watch History Channel Video “Spartan boot Camp: Killing Machines” THE PERSIAN WARS (490 BC) IV. The Persian Wars (490 BC) • Greatest threat to Greek city-states- invasion from Persian Empire • Many wars fought b/w Persia & Greek city-states= The Persian Wars A. A new kind of Army emerges • Cheaper iron replaces bronze, making arms and armor cheaper= new, bigger armies made up of all classes of ppl • New army tactic feared by all, Phalanx— formation of soldiers with spears • HC- Sparta Deconstructed B. Battle of Marathon • Persian Wars— b/w Greece/Persian Empire, began in Ionia • Greeks in Ionia conquered by Persians • Greeks revolt, Athens sends ships to help fight off the Persians • Persians win, vow to destroy Athens • Persian army attacks Athens at Marathon • Greeks arranged in phalanx, Persians attack and are defeated • Runner, Phedippides races to Athens to announce Greek victory then dies IONIA * C. Persians attack again • 10 yrs after Marathon, Persians try again to destroy Athens • Persians invade, halted at a mountain pass called Thermopylae- 7,000 Greeks (including 300 Spartans) fight Persians • Greeks betrayed, 300 Spartans volunteer to hold Persians while rest retreat, all 300 killed • Persians finally defeated at Salamis HC: Last stand of the 300 D. Consequences of the Persian Wars • Greek city-states formed an alliance called the Delian League to help protect against future Persian attacks • Athens becomes strongest voice in the Delian League, dominates other city-states