Notes Unit 1-2
advertisement

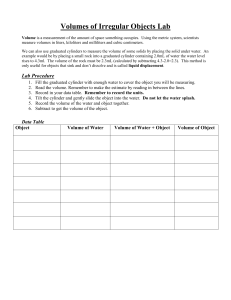
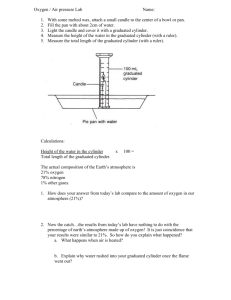
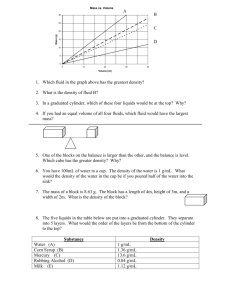
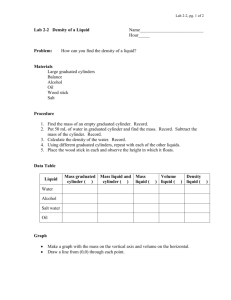
Warm Up 8-21-15 Direction: Copy down the questions and provide answers. 1. What kind of change is mixing soil with water to create mud? Explain why. 2. What kind of change is baking bread? Explain why. 3. Can you fit more atoms of water or iron in this box ? Explain why. Agenda Quiz Lab Safety Notes Unit 1-2 Lab Food dye and volume Homework Extra credit online due before 9PM tonight Safety Quiz • Do not write on the QUIZ • Bubble in your ID # and write your name on the scantron • Bubble in the version # White = version 1 Pink = version 2 • Write in complete sentences for the free response (#13-17) Unit 1-2 Describing Matter • Volume: the amount of space something takes up -solids = the height length width of the object -liquids = use graduated cylinder Meniscus Describing Matter • Mass: The amount of matter contained in that object. Mass can be measured using a balance (for most objects) – Mass is not weight! – Weight is the force produced by gravity acting on a mass. This can be different in different places. Units of Measurement • Quantity: Something that has magnitude, size, or amount • Unit: a quantity adopted as a standard of measurement -For meaningful descriptions, all quantities must be labeled with units. Units of Measurement -Since 1960 scientists world-wide have used the SI system of measurement. -SI = Système international d'unités Quantity Distance or Length Mass Temperature Amount of Substance Unit Abbreviation Meter m gram Kelvin Mole g K mol Conversion Factors • A conversion factor is a ratio that is derived from the equality of two different units and can be used to convert from one unit to the other – Example: 1 kg = 1000 g Conversion Factors Other Frequently Used Units – Length • 2.54 cm = 1 inch – Mass • 0.4536 kg = 1 pound – Volume • 1 cm3 = 1 mL Converting SI Units Example 1 • Express 4 km in meters – Given: 4 km – Find: meters (m) – Plan (conversion factor): 1 km = 1000 m – Solve: 1000 m 4 km x = 4000 m 1 km Example 2 • Express 100 centigram in kilograms – Given: 100 cg – Find: centigrams (cg) – Plan (conversion factor): 100 cg = 1 kg – Solve: 100 cg 1gx = 100 cg 1g Example 3 • Convert 12 kilometers to millimeter Individual Practice • Use the stair-step as a tool to guide you through the Unit 1-2 Conversion Factors Worksheet Volume Lab Part 1: Measure out drops of water into the 10 ml graduated cylinder and record the volume # Drops Volume (ml) drops/ml ml/drop 50 100 150 Part 3: -Measure 3ml of colored water from the tube to the 10ml-graduated cylinder -Drop bleach into your color graduated cylinder until it is cleared & record the # of drops Yellow = Blue = Red = Green = Clean up Procedure • Rinse everything out in the sink • Put the equipment in the front • Clean your lab table Homework • Finish the Lab handout