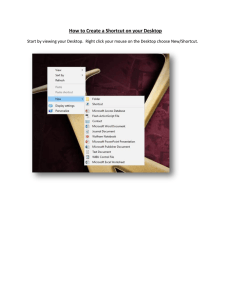
File
advertisement

Is a part of the Microsoft Windows graphical user interface which allows users to view and manipulate basic system settings and controls, such as adding hardware, adding and removing software, controlling user accounts, and changing accessibility options. Full of specialized tools that are used to change the way Windows looks and behaves. Some of these tools help to adjust settings that make your computer more fun to use. › use Mouse to replace standard mouse pointers with animated icons that move on your screen, › use Sounds and Audio Devices to replace standard system sounds with sounds you choose. › Other tools help you set up Windows so that your computer is easier to use. For example, if you are left-handed, you can use Mouse to switch the mouse buttons so that the button on the right performs the primary functions of selecting and dragging. Click Start Panel Click Settings Choose Control There are a few commonly used items/functions in Control Panel : › Add or Remove Hardware › Add or Remove Programs › Display › System Refer to notes given Provides information about programs and processes running on your computer. Use to monitor key indicators of your computer's performance. See the status of the programs that are running and end programs that have stopped responding. Assess the activity of running processes using as many as fifteen parameters, and see graphs and data on CPU and memory usage. If connected to a network, you can view network status and see how your network is functioning. If more than one user are connected to your computer, you can see who is connected, what they are working on, and you can send them a message. Use Ctrl+Alt+Del to access the Task Manager anytime. To start Task Manager, do any of the following: 1. Press CTRL+ALT+DELETE, and then click Task Manager. 2. Press CTRL+SHIFT+ESC. 3. Right-click an empty area of the taskbar, and then click Task Manager. Click the Performance tab in Task Manager to view a dynamic overview of the performance of your computer, including the following measures: › Graphs for CPU and memory usage. › The total number of handles, threads, and processes that are running. › The total number of kilobytes (KBs) used for physical, kernel, and commit memory. Windows Housekeeping Chores Move within the Windows Desktop and select items › Shortcut Key: Tab, Arrow, Enter. Open the Run dialog box › Shortcut Key: Windows-R › It will open the windows Run dialog. Start Windows Explorer › Shortcut Key: Windows-E › It will start Windows Explorer Find a File (from the Windows desktop) › Shortcut Key: Windows-F or F3. › It will open Windows Find file dialog box. Open the System Properties dialog box › Shortcut Key: Windows-Break. › It will open the System Properties Rename the selected object: › Shortcut Key: F2. › It will rename the selected object. › E.g. Select My Computer icon, press F2 and you’ll be able to change the name of My Computer to another name.