Experiment 7 Synthesis of Aspirin
advertisement
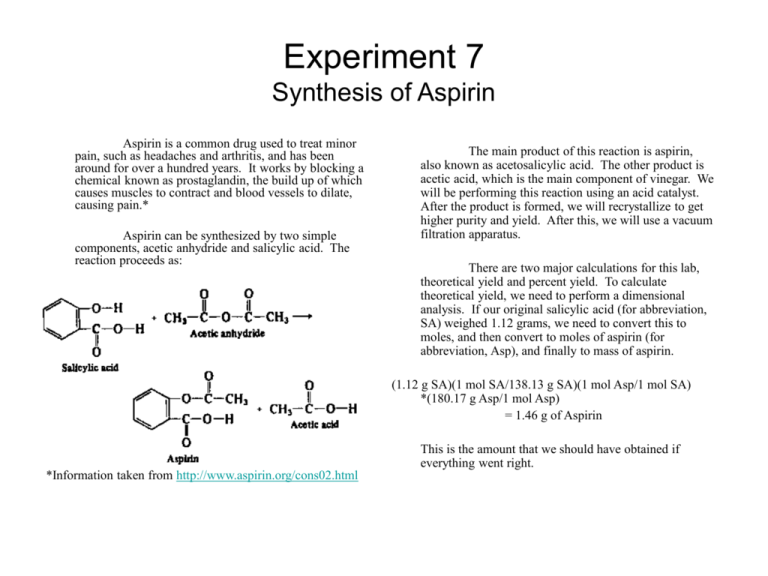
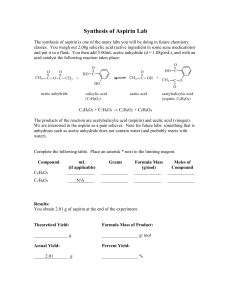
Experiment 7 Synthesis of Aspirin Aspirin is a common drug used to treat minor pain, such as headaches and arthritis, and has been around for over a hundred years. It works by blocking a chemical known as prostaglandin, the build up of which causes muscles to contract and blood vessels to dilate, causing pain.* Aspirin can be synthesized by two simple components, acetic anhydride and salicylic acid. The reaction proceeds as: The main product of this reaction is aspirin, also known as acetosalicylic acid. The other product is acetic acid, which is the main component of vinegar. We will be performing this reaction using an acid catalyst. After the product is formed, we will recrystallize to get higher purity and yield. After this, we will use a vacuum filtration apparatus. There are two major calculations for this lab, theoretical yield and percent yield. To calculate theoretical yield, we need to perform a dimensional analysis. If our original salicylic acid (for abbreviation, SA) weighed 1.12 grams, we need to convert this to moles, and then convert to moles of aspirin (for abbreviation, Asp), and finally to mass of aspirin. (1.12 g SA)(1 mol SA/138.13 g SA)(1 mol Asp/1 mol SA) *(180.17 g Asp/1 mol Asp) = 1.46 g of Aspirin This is the amount that we should have obtained if everything went right. *Information taken from http://www.aspirin.org/cons02.html Now, if we only obtained 0.97 grams of aspirin, how do we calculate percent yield? Percent yield is similar to percent error, except we do not subtract by our actual value. So, our percent yield would be: (actual / theoretical)*100% = (0.97/1.46)*100% = 66% This means that we obtained two thirds of what we should have. To determine purity of our sample, we will be determining the melting point. The actual melting point of aspirin is between 132 oC and 135 oC. We will also be performing the acid test. We will dissolve some of our sample in a water/ethanol mixture, and add a few drops of dilute ferric chloride solution. It should react with the aspirin and turn it violet.