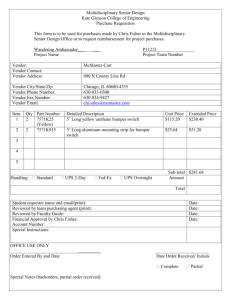
File - Restaurant management system
advertisement

CHAPTER 1: PROJECT CHARTER 1. PROJECT BACKGROUND A Vendor Management System helps in monitoring of vendor’s information, their products and services. Vendor Management System helps in competitive advantage as well as cost savings. It is aimed at increasing the efficiencies in effectively managing the process right from Vendor Identification, Recruitment, Monitoring the Performance/Quality in each region. The ultimate objective is to consider the use of right resource at the right place, at the right time. A vendor management system (VMS) is an Internet-enabled, often Web-based application that acts as a mechanism for business to manage and procure staffing services – temporary, and, in some cases, permanent placement services – as well as outside contract or contingent labor. Typical features of a Vendor Management System (VMS) application include order distribution, consolidated billing and significant enhancements in reporting capability that outperforms manual systems and processes. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 1 The proponents introduce Vendor Management System (VMS) that will improve the process of Restaurant Management System (RMS) via Franchising and Catering. Franchising is a method of doing business wherein a franchisor licenses trademarks and tried and proven methods of doing business to a franchisee in exchange for a recurring payment, and usually a percentage piece of gross sales or gross profits as well as the annual fees. Various tangibles and intangibles such as national or international advertising, training, and other support services are commonly made available by the entity licensing the ‘chain store’ or franchise outlet (commonly shortened to the one word: franchise), and may indeed be required by the franchisor, which generally requires audited books, and may subject the franchisee or the outlet to periodic and surprise spot checks. Failures of such tests typically involve non-renewal or cancellation of franchise rights. A continuing relationship in which the franchisor provides a licensed privilege to the franchisee to do business and offers assistance in organizing, training, merchandising, marketing, and managing in return for a consideration. Franchising is a form of business by which the owner (franchisor) of a product, service, or method obtains distribution through affiliated dealers (franchisees). The product, method, or service being marketed is usually identified by the franchisor’s brand name, and the holder Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 2 of the privilege (franchisee) is often given exclusive access to a defined geographical area. While catering is the activity of providing food and beverage for events. Caterers, which are either independent vendors or individuals within a particular department of a facility (such as a hotel, restaurant, institution, venue, etc.). Catering is provided at a full range of events, including business meetings, conferences, exhibitions, special events, weddings, and other social occasions. In addition to responsibilities for food and beverage, many caterers also handle event decor, A/V and other aspects of the program. In this online system, The Restaurant can avail to make transactions regarding the borrowing of products to the other branches that would be monitored by in the Main office. Every transaction done by one branch to another branch regarding borrowing of products will be recorded to the Vendor Management System. This is also capable to receive incoming and outgoing messages as well as the documentation of “new product launching” that will be sent of main office via email, including its ingredients, process of cooking, etc. As an expanding business in Restaurant, this would be a great help in monitoring their franchise using the online system and promoting their restaurant through Internet because it is widely used nowadays. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 3 1.1 PROBLEM/OPPORTUNITY DESCRIPTION Vendor management is a discipline that enables organization to control costs, drive service excellence and mitigate risks to gain increased value from their vendors throughout the deal life cycle. It is also the discipline of managing, administering, and guiding product and service vendors in an organized way. The term vendor originally represented property vendors. However, today it means supplier of goods or service. A vendor or a supplier is a supply chain management term that means anyone who provides goods or services to a company. In this project, the proponents propose a sub-system that can helps the proposed company to response upon the said problems such as: Poor Communication Poor communication and feedback, Lack of Interaction to keep the information between the company and the vendors. Security Vendor management System main problem is unsecured data because VMS is a web base application it can cause leakage of franchisees application records, reports and other confidential files like franchising Tern and Condition Agreement of franchisee. It can be altered by the unauthorized personnel. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 4 Database Cabinet Files are commonly used as storage of those records and files in Franchisor main office. It is necessary to have a permanent database for these confidential records which directly connected to the process to ease the searching and data retrieval for updating and reports generation. Franchise Monitoring Difficulty in Monitoring- Franchise monitoring the borrowing of supplies through phone conversations only. Availability of Products in every branch- They are not aware if the product that are borrowing is available. Promoting new products Rolling out new products to every franchise is via documents only. Franchising Advertisement Their franchising is not well promoted. Interested entrepreneurs have to inquire to any branch and ask on how the application goes. Reports Inaccurate Information- Wrong input of details because of Typographical errors. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 5 1.2 BENEFITS Vendor Management System Helps the Franchisor, Franchisees and even the Clients to have a standardize procedure of Franchising and Catering with Food and Services. This propose system is not only for identifying the problems of the propose company, it also includes the better transaction that the propose system can do and know the improvement of their ways of processes. For the Franchisor Access to a maximum number of vendors Ability to monitor vendors during the term of the contract. Easy way of investing- It provides better service without wasting too much time for preparing the contracts. Improve asset management- When income is increasing, asset is increasing too. To create a system that allows them to cancel or edit request to help them avoid errors in every transaction. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 6 For the Franchisees Vendor performance metrics- It helps the Franchisees to practice their skills and enhance the knowledge for handling a business. Reduced financial statement- it helps the Franchisees to reduce financial statement that may provide by the investors. For the Guest To provide fully equipped accommodation that will enable guests to prepare their own meals. Time and Cost saved- A good catering service provides takes care of the entire planning, execution and management giving you ample time to invest on the other aspects of your event. Taking benefit of the pristine catering packages will let you save on overall costs and make your event a big success. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 7 For the Project Team This Vendor Management System (VMS) is a project study developing by the proponents. If this Vendor Management System (VMS) accomplish, fulfilled and developed, it would be considered as another milestone and success. In other words, it might be exploited and utilized to any Vendor Departments from different enterprise. For the Future Proponents There are future proponents out there and even in this institution that can use this research as their reference to their own project study. If this project study becomes successful, likewise to their project study, because it showed up strives and endeavors that the proponents experienced just to build and developed successfully. Interested Entrepreneurs Through this project they are able to acquire knowledge about application on Max’s Franchising with the use of Internet. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 8 1.3 GOALS The proponents aimed to develop a Vendor Management System to create possible solutions for the problem that the restaurant currently experiencing and to achieve the benefits lead by this system. The system will cover the works easier for the Franchisor and also for the Franchisee. Poor Communication Internal Communication One successful tool is having a regular meeting for the easiness of transmitting new information, new strategy, or any important things happen between the management and the vendors. It serves as the start of building good relationship between the management and the vendor. The vendor management office should establish communication with the groups that discuss the contract activities and to gather information about the ongoing contract requirements and issues. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 9 Security Before someone could access the Vendor Management System, the designated personnel will be required to enter their username and password. There are a maximum of five (5) persons that can create an account and to serve as the Administrator to use or access the system. Here, the proponents limit the number of persons that can create an account to secure the data and information of the restaurant inside the system. They are the only persons allowed to view, edit and update all the information seen in the system. Each of them can only have three (3) attempts in logging into system. This also covers the security of data and information of the previous transaction done by: The Branch, their previous transaction will be saved in the database of the system in their restaurant. The Administrator, the previous successful transactions by every branch they are monitoring will be also saved in the database of the online system. These designated personnel authorized by the system are the only persons who can access the viewing of the data and information inside the system. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 10 Database Efficient Database that can handle large number of transaction that the Administrator or even the user can easily update and a maintainable database records for any type of vendor histories. Franchise monitoring When there is a new franchise that is approved by the Board of Directors, and all things are settled before them and the restaurant will be operating, they have to register in the Vendor management system so they can be part of the monitoring branch. Here, the proponents made the monitoring of every branch easier for the Main office. The branch that would make a borrow request transaction will just have to fill up the transaction form in the online system in their restaurant and send it to the Administrator. And the Administrator is responsible to contact other branch or supplier to confirm the availability of the product that is borrowing by the other branch. They can also be easily identify the availability of borrowing product in a specific branch because the Vendor Management System enables to send email to every branch for confirmation of the availability of the products. And every system is capable of receiving email/ message coming the Administrator and also Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 11 sending back email going to Administrator. And every successful transaction between branches will be saved in the database of the system. This kind of monitoring will be more efficient and accurate. Promoting New Products Promotion of new Products is a responsibility of the Administrator. Since the administrator is monitoring every branch, The Administrator is also responsible to promote the new product of Restaurant in each of them. The Administrator is capable of putting all information’s in the Vendor Management System about the product to be launched as well as its ingredients and process of cooking/making. The Administrator is capable of sending this information’s through internet that can be received by every branch. This process is easier than the process they are doing before. Franchising Advertisement The Proponents proposed a Vendor Management System that would help the Restaurant in advertising their franchising to the market with use of Internet connection. The Administrator can put information’s about franchising of the restaurant and it will be seen by the internet users, so that interested entrepreneurs can easily be informed about Restaurant franchising. They can also avail a downloadable form than can be fill up and just send via email. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 12 Reports This Vendor Management System can able to generate and print reports. This also answers the problem of the manual process doing by The Restaurant nowadays. The typographical errors is the main problem of every reports of their previous transactions, but with the use of Online Vendor Management System, the transaction are not risky from error because we will be implementing a Vendor Management System with the transaction form that allows user to edit or cancel request. Also with the use ofcategory list, that the Branch managers can choose the forms without doing any typing and making errors from it. The reports will be accurate and easier to monitor. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 13 1.4 STAKEHOLDERS/CLIENTS Vendor Management Department (Franchisor) This stakeholder affected by the system development because this department will be the most beneficiary and the main user of the system and this department, – who manage and have investment on the restaurant. Also produce financial budget. Restaurant Manager The Restaurant manager is also assigned to manage the Vendor Management system (VMS). Only the Manager can accomplished the entire task per division or areas of the restaurant. Group Team This stakeholders is the proponents, which will be the project handler and will developed the system. The proponents is carefully analyze all the possible details and problems where the solution will include on the developed system. User The user of this projected system will be the employee or only the authorized person in Vendor Management Department to handle all the records and confidential files of the Franchisee. This will helpful to the user because it will make the work systematic and easy. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 14 2. PROJECT SCOPE 2.1 OBJECTIVES The main objective of the proponents is to make systematic process of this Online Vendor Management System. This must comprise all the activities done and cover up the problem experience on most of the Vendor’s especially to the franchisee. Figure 2.1.1 the figure shows the process or part of Restaurant Management System- Vendor Management System (VMS) Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 15 Figure 2.1.3 the figure shows the Catering Information only for The Costumer or part of Restaurant Management System- Vendor Management System (VMS) Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 16 2.2 DELIVERABLES Objectives 1: Franchise Term and Condition Agreements. Project Deliverables Work Products/ Description The Location/Territory franchise agreement will designate the territory in which you will operate and outline any exclusivity rights you may have. This Operations section details how franchisees are expected to run their units. Training and Ongoing Support Franchisors offer training and training programs for franchisees and their staff. Training may take place at corporate offices or out in the field. All ongoing administrative and technical support will also be outlined in the agreement. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 17 The document will detail the length Duration of the duration of the franchise agreement. There will generally be an upfront initial franchise fee that grants the franchisee the right to use the Franchise fee/investment franchisor's trademark and operating system. Those costs will be clearly outlined. In this section the franchisee will find the details of the franchisor's royalty structure. Most franchisors Royalties/ongoing fees require franchisees to pay An ongoing royalty, usually a percentage of total sales, which is often paid on a monthly basis. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 18 Objectives 2: Types of Franchising Agreement Project Deliverables Work Products / Description In a single-unit franchise system, one person buys a store from the main company and operates it according to Single Unit Franchisee the company's rules. Operating one (Direct Unit) store at a time is a good choice for new business owners. Some successful operators of one store eventually buy more stores. Area Developer Area developer franchises allow a business owner to own all franchises within one location. The location can Multi-Franchisee include a city or neighborhood. The franchisee often has to open a certain number of businesses within a specific time period or follow other stipulations set by the parent company or franchisor. Area development contracts typically require development in an area Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 19 within five years. Master Franchisee The master franchise is a popular way to spread American businesses to international territories. This method allows one entity to find many franchisees in an overseas area. The master franchisor is responsible for training and providing support to the new franchisees within the large area, which can include an entire country. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 20 Objective 3: Franchise Monitoring Project Deliverables Work Product / Description This Section Describe the Borrowing of Products and Supplies of the branch that would make a Borrowing of Products and borrow request transaction will just Supplies have to fill up the transaction form in the online system in their restaurant and send it to the Administrator. And the Administrator is responsible to contact other branch or supplier to confirm the availability of the product that is borrowing by the other branch. This Available Products and Supplies Section Describe the availability of borrowing product in a specific branch the Vendor Management System enables to send email to every branch for confirmation of the availability of the products. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 21 Objectives 3: Franchise Advertisement Project Deliverables Work Products / Description The Proponents proposed a Vendor Management System that would help the Restaurant in advertising their franchising to the New Product Promotion market with use of Internet connection. The Administrator can put information’s about franchising of the restaurant and it will be seen by the internet users, so that interested entrepreneurs can easily be informed about Restaurant franchising. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 22 Objectives 4: Catering Project Deliverables Work Products / Description Social Event’s Social events catering offer a Birthday, Catering Debut, Baptismal etc…., VMS will Display the information packages for the costumer’s. Wedding Wedding Event’s Rehearsal events catering Dinner, offer Bachelor a and Bachelorette party, Bridal Shower and Catering Wedding Reception. the information VMS will Display packages for the costumer’s. Corporate Event’s Catering offer a Corporate Event’s company activities such as Teambuilding/ Training, Company all Catering day Meetings, Seminars and etc… VMS will Display the information packages for the costumer’s Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 23 2.3 OUT OF SCOPE Billing Billing is related in vendor management system, it is the records of all the finances having between the company and the vendor’s but the system cannot manage it as a part of propose system. Procurement/Inventory This part is considered to be closely related to the Vendor Management System (VMS) for the Supplies / materials needed to be borrowed of the branch, it is only a part in the propose system but it cannot generate records needed for inventory. Staffing for managing the branch or franchised restaurant is also included in VMS. Generally, it is more suits to Human Resource Management. Reservation of Catering Reservation of catering is cannot performed by the propose system only the catering category Information needed by the costumer can the Vendor management can do.The Restaurant Reservation and Table Management System will handle the Reservation for Catering. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 24 3. PROJECT PLAN 3.1 Approach and Methodology The proponent will use the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) for the techniques in doing the proposed system. A system request describes problems or desired changes to an information system. The company request for some development to their current system. The proponent found out that the current system struggle a lot of problems in their inventory system. System planning This is the first stage in creating the system. First, the proponent identify the problem’s that occurs during the propose system to the Restaurant. After identifying the problem, the proponent started to think of the possible features that the proponents may develop to the propose vendor management system. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 25 System Analyst On this stage, the proponent started analyzing the process of the propose system to create a good flow of system. The proponent analyzes the information gathered during the planning phase and started to study the flow of the propose system. After analyzing their current system and the problem that the researchers encountered using it, the proponent decided to should use a database that could handle all of the information they need to save. System Design System design is the next step that the proponents done. On this part, the proponents will design an interface of the proposed VMS. This system design will determine and discuss different system specifications and requirements needed to make VMS possible. Design must be well planned, in order to meet the clients’ need and user-friendly GUI. The design of the transitions and process must also be consider. The contents of Vendor management system must be consisting of the entire franchising activities and processes. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 26 System Implementation System implementation will be done after the development of the software. This will test the affectivity of the software product if this will work and meet the requirements and needs of the client. When there are problems occurred on the system implementation that is the time that the system must furnish the errors and bugs to make the system work flawlessly. System Operation The system operation, support and maintenance are aiming to incessantly satisfy the needs of the client by maintaining the operation and the support of the system inside the business transaction. In order to support and operate the VMS the franchising activities, the project team must maintain the system for the future errors or sudden supplementary changes of features and content. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 27 3.2 PROJECT TIMELINE ID Task Name 1 The proponents do a research regarding Date July 2, Vendor 2014 to Start Finish Duration 1:00 pm 5:00 pm 5 Hours 1:00 Pm 5:00 pm 5 Hours Management System 2 The proponent talked what are the process Management of System Vendor (VMS). July 4, 2014 Based on their research. (Brain storming) 3 Each of the proponent should make a 10 each question for the July 56, 2014 Bench Marking in Makati on July - - - - - - 9, 2014 (1:00 pm). 4 The proponents go to Makati for Bench Marking, and to get the specific idea / to know more about Vendor July 7, 2014 Management System. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 28 Chapter 1: Project Charter (TASKING) ID 6 7 8 9 1 0 1 1 Task Name 1. Project Background 1.1 Problem/Opportunity 1.2 Benefits 1.3 Goals 1.4 Stakeholders and clients Encoding of Project Background 2. Project Scope 2.1 Objectives 2.2 Deliverables 2.3 Out of Scope Encoding of Project Scope 3. Project Plan 3.1 Approach and Methodology 3.2 Project Timeline 3.3 Success Criteria 3.4 Issues and Policy Implication 3.5 Risk Management Plan 3.6 Service Transaction 3.7 Option Analysis Encoding of Project Plan Date Start Finis h Duratio n 11:0 0 pm 4:00 am 5:00 Hours July 8, 201 4 2:00 pm 3:30 pm 1 Hour July 8, 201 4 1:00 pm 5:30 pm 5½ Hours July 910, 201 4 10:0 0 pm 12:00 pm 2 Hours July 910, 201 4 1:00 pm 5:00 pm 5 Hours July 10, 201 4 1:30 pm 3:30 pm 2 Hours July 7, 201 4 Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 29 1 2 1 0 1 1 4. Technical Features 5. Project Organization Staffing 6. Project Budget Appendix A - Additional and July 1415, 201 4 Encoding of all content in CHAPTER 1 July 15, 201 4 11:0 0 pm 1:00 pm 2 Hours 1:00 pm 5:00 pm 5 Hours Submission of Chapter 1. Project Charter in online RMS team website. July 17, 201 4 - - - Chapter 2: Review of Related Studies and System (TASKING) ID 12 TASK NAME Date Start Finish Duration - - - - - - 2.1 Foreign Studies 2.1.1 Arizona AIM System July 2.1.2 Waterfall FMS 2.1.3 Burger King 2.1.4 erecruit VMS 21, 22, 23, 2014 2.1.5 Beeline vms 13 2.2 Local Studies 2.2.1 Max’s 2.2.2McDonald's 2.2.3Mang Inasal July 25, 26, 27, Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 30 2.2.4Shakey’s 2014 2.2.5 Adobo Connection 14 2.3 Synthesis and Relevant to the studies (Matrix – comparative analysis) 15 16 Encoding of Chapter 2: Review of Related Studies and System July 2829, 2014 July 30, 2014 11:00 pm 1:00 pm 3:00 am 4 Hours - - - - Submission of Chapter 2. Review of Related Studies and System in online RMS team July 31, 2014 - website. Chapter 3: EIS Project Management and Development (TASKING) ID 17 TASK NAME Date Start Finish Duration Risk Mitigation, Monitoring and Management Plan 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Scope and Intent of RMMM actives 1.2 Risk Management Org. Role 18 2.0 Functional Data Description 2.1 Risk Table 2.1.1 Description Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 31 of Risks M 2.1.2 Probability and Impact for Risks M 19 3.0 Risk Mitigation, Monitoring and Management 3.1 Risk Mitigation for Risk M 3.1.1 Product Size 3.1.2 Business Impact 3.1.3 Costumer (USERS) Risks 3.1.4 Process Risks 3.1.5 Technology Risks 3.1.6 Development Risks 3.1.7 Employee Risk 20 3.2 Risk Mitigation for Risk M 3.2.1 Product Size 3.2.2 Business Impact 3.2.3 Costumer (USERS) Risks 3.2.4 Process Risks 3.2.5 Technology Risks 3.2.6 Development Risks 3.2.7 Employee Risk 21 3.3 Risk Mitigation for Risk M 3.3.1 Product Size 3.3.2 Business Impact 3.3.3 Costumer (USERS) Risks Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 32 3.3.4 Process Risks 3.3.5 Technology Risks 3.1.6 Development Risks 3.1.7 Employee Risk 22 4.0 Special Condition 23 Encoding of Risk Mitigation, Monitoring and Management Plan Software Configuration and Management Plan I D Task Name Dat e Star Finis t h Duratio n 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Scope and Intent of SCM Activities 1.2 SCM Org. Role 2.0 SCM Tasks 2.1 Identification 2.1.1 Description 2.1.2 Work Product and Documentation 2.2 Configuration Control 2.2.1 Description 2.2.2 Increasing version number 2.2.3 Work Product and Documentation 2.3 Configuration Status Accounting (CSA) 2.4.1 Description 2.4.2 Work Product and Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 33 Documentation 3.0 Software Quality Assurance overview Scope and Intent of SQA Activities 3.1 Generic Review Guidelines 3.2 Formal Technical Review 3.3 SQA Audits 3.4 Problem reporting and Corrective Action/ Follow-Up 3.4.1 Reporting Mechanism 3.4.2 Responsibilities 3.4.3 Data Collection and Evaluation Encoding of Software Configuration /management Plan Software Quality assurance Plan ID Task Name Date Start Finish Duration 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Scope and Intent of SQA activities 1.2 SQA Org. Role 2.0 SQA Tasks 2.1 Task Overview 2.2 Standard, practices and conventions (SPC) 2.3 SQA Resources 3.0 Review and Audits 3.1 Generic Review Guidelines 3.2 Formal Technical Reviews 3.3 SQA Audits 4.0 Problem Reporting and Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 34 Corrective Action/Follow-Up 4.1 Reporting Mechanism 4.2 Responsibilities 4.3 Data collection and Valuation 4.4 Statistical SQA 5.0 Software Process Improvement Activities 5.1 Goal and Object of SPI 5.2 SPI Tasks and Responsibilities 6.0 Software Configuration management and Overview 7.0 SQA Tools, Techniques, Methods Encoding of Software Quality Assurance Plan SYSTEM SPECIFICATION I D Task Name Dat e Star t Finis h Duratio n 1.0 Introduction .1.1 Goals and Objectives 1.2 System statement of Scope 1.2.1 Version1 Gen.Reg 1.2.2 Version2 Gen.Reg 1.2.3 Extended Enhancement Requests 1.3 System Context 1.4 Major Constraints 2.0 Functional Data Description 2.1 System Architecture 2.1.1 Architecture Model Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 35 2.1.2 Current Subsystem Overview 2.2 Data Description 2.2.1 Major Data Objects 2.2.2 Relationships 2.3 Human Interface Description 3.0 Subsystem Description 3.1 Subsystem Flow Diagram 3.1.1 Create checklist 3.1.2 Print Checklist 3.1.3 Generate Letter 4.0 Enhanced interface Prototyping Requirements Encoding of System Specification SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION I D Task Name Dat e Star t Finis h Duratio n 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Goals and Objectives 1.2 System Statement of Scope 1.3 System Context 1.4 Major Constraints 2.0 Usage Scenario 2.1 User Profile 2.2 Use-Cases Read Only Users Read/Write/Modify own Users Read/Writer/Modify all Users 3.0 Data Model and Description 3.1 Data Description 3.1.1 Data Objects and Dictionary 3.1.2 Relationship Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 36 4.0 Functional Model and Description 4.1 Subsystem Flow and Description 4.1.1 Create Checklist 4.1.2 Print Checklist 4.1.3 Generate Letter 4.2 Human Interface 5.0 Restriction, Limitations and Constraints 6.0 Validation Criteria SOFTWARE DESIGN SPECIFICATION I D Task Name Dat e Star t Finis h Duratio n 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Goals and Objectives 1.2 System Statement of Scope 1.2.1 Gen.Req 1.3 System Context 1.4 Major Constraints 2.0 Data Design 2.1 Database Description 3.0 Architecture & Components – Level Design 3.1 Program Structure 3.1.1 Overall 3.1.2 Create Evaluation 3.1.3 During Evaluation 3.1.4 Post- Evaluation 3.1.5 Approval 4.0 User Interface Design 4.1 Description of the User Interface 4.1.1 Screen Images 4.1.2 Objects and Action Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 37 4.2 Interface Design Rule 4.3 Components Available 4.3.1 Components available 4.3.2 Active controls 5.0 Restriction, Limitation and Constraints 6.0 Testing Issues 6.1 Classes of test 6.2 Performance Bounds 6.3 Identification of critical Components Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 38 3.3 SUCCESS CRITERIA The proponent aimed to develop a Vendor Management System (VMS) that the Restaurant can achieve the following success: Poor Communication Internal Communication One successful tool is having a regular meeting for the easiness of transmitting new information, new strategy, or any important things happen between the management and the vendors. It serves as the start of building good relationship between the management and the vendor. The vendor management office should establish communication with the groups that discuss the contract activities and to gather information about the ongoing contract requirements and issues. Security Before someone could access the Vendor Management System, the designated personnel will be required to enter their username and password. There are a maximum of five (5) persons that can create an account and to serve as the Administrator to use or access the system. Here, the proponents limit the number of persons that can create an account to secure the data and Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 39 information of the restaurant inside the system. They are the only persons allowed to view, edit and update all the information seen in the system. Each of them can only have three (3) attempts in logging into system. This also covers the security of data and information of the previous transaction done by: The Branch, their previous transaction will be saved in the database of the system in their restaurant. The Administrator, the previous successful transactions by every branch they are monitoring will be also saved in the database of the online system. These designated personnel authorized by the system are the only persons who can access the viewing of the data and information inside the system. Database Efficient Database that can handle large number of transaction that the Administrator or even the user can easily update and a maintainable database records for any type of vendor histories. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 40 Franchise monitoring When there is a new franchise that is approved by the Board of Directors, and all things are settled before them and the restaurant will be operating, they have to register in the Vendor management system so they can be part of the monitoring branch. Here, the proponents made the monitoring of every branch easier for the Main office. The branch that would make a borrow request transaction will just have to fill up the transaction form in the online system in their restaurant and send it to the Administrator. And the Administrator is responsible to contact other branch or supplier to confirm the availability of the product that is borrowing by the other branch. They can also be easily identify the availability of borrowing product in a specific branch because the Vendor Management System enables to send email to every branch for confirmation of the availability of the products. And every system is capable of receiving email/ message coming the Administrator and also sending back email going to Administrator. And every successful transaction between branches will be saved in the database of the system. This kind of monitoring will be more efficient and accurate. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 41 Promoting New Products Promotion of new Products is a responsibility of the Administrator. Since the administrator is monitoring every branch, The Administrator is also responsible to promote the new product of Restaurant in each of them. The Administrator is capable of putting all information’s in the Vendor Management System about the product to be launched as well as its ingredients and process of cooking/making. The Administrator is capable of sending this information’s through internet that can be received by every branch. This process is easier than the process they are doing before. Franchising Advertisement The Proponents proposed a Vendor Management System that would help the Restaurant in advertising their franchising to the market with use of Internet connection. The Administrator can put information’s about franchising of the restaurant and it will be seen by the internet users, so that interested entrepreneurs can easily be informed about Restaurant franchising. They can also avail a downloadable form than can be fill up and just send via email. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 42 Personalize Reports This Vendor Management System can able to generate and print reports. This also answers the problem of the manual process doing by The Restaurant nowadays. The typographical errors is the main problem of every reports of their previous transactions, but with the use of Online Vendor Management System, the transaction are not risky from error because we will be implementing a Vendor Management System with the transaction form that allows user to edit, cancel request and the user has the option what to display. Also with the use ofcategory list, that the Branch managers can choose the forms without doing any typing and making errors from it. The reports will be accurate and easier to monitor. Personalized Screen according to role (Portal based) This Restaurant Management system – Vendor Management System can be able to Personalized the screen that according to the role of the user. Analytics or Graphical Report presentation for percentage, quantity or statistical Report. This Vendor management System can able to visualize the percentage of the availability of materials and product and what are the material and product who are in critical stocks. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 43 3.4 ISSUES AND POLICY IMPLICATION Good thing for the proponents, because any business firms and restaurants that the proponents interviewed, they never hesitate to give the information and problems related to Franchise. They are very cooperative and approachable in providing factual information regarding franchising activities and processes, to begin the system development. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 44 3.5 RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN Probability Impact Risk Factor Risk Management Action (H,M,L) (H,M,L) Financial risk refers to the budget or allocations in order to support the product Financial Risk H H or software development. It supports the procurement, development and requirements of the system. This risk refers to the cooperation and willingness of M Customer Risk M the client software in helping development with the project team to create a well-developed, assurance and quality effective software. If the client fails in giving the factual information needed for the business, the Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 45 project might not be the one that helps the business. This risk refers to the failure of the client to support and provide all necessary M H Development equipment for the development and the execution of the software which can cause the project Risk to fail. On this scenario, project team must think another options or ways to continue the development of the product. This risk describes the caliber, potential and the willingness of the proponents Employee Risk M M to create operational and functional product like VMS. Coordination, interdependence and initiative are necessary for Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 46 formulation of ideas, planning and development of the product. it is excellence, about the quality and effectiveness of the product or software developed. To achieve this the project team M H Process Risk will set a guidelines that might be used during the software development process. This will help the project team to meet the standard requirements of the client. It M Product Size M refers misjudgment to between the the client and project team. The project team must know the scope of the development to software avoid spending too much money or Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 47 budget of the project. This risks involves of using technology that is soon to be stale. As the result of M H this risks the software developed will be functional for the short period of time. Since the technology change of nowadays is rapidly the proponents and the client should keep eye for the current technology. Technical Risk Technical risk might be result by accidents happen to the computer like accidental plugging of the power supply, un expected computer shutting down or even the accidental brown out might be happen. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 48 3.6 SERVICE TRANSITION In impact mitigation, there will be a great impact that will affect end users. The proponents will be the maintenance of the proposed system in the restaurant; the machines will be operated by the Management or the Individual who in charge to do franchise monitoring in the vendor management system of the restaurant. If there will be changes the proponents can communicate with the staffs to apply possible changes in the proposed system, tools references or checklist will be distributed in the least possible time. In transitional support, the proponents will be contact if there will be errors which regards to the vendor management system; this is needed in order to have a full service. 3.7 OPTION ANALYSIS Records of Monitoring and Activities Reports- produces reports on monitoring activities and their outcomes. Create Records Audits- provide records of audits that may use as a compliance investigation that may help for comparing the volume of sale at the end of the month. Track for vendor pricing- captures information about their current pricing. This pricing information is used to compare to the other vendor. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 49 4. TECHNICAL FEATURES In this section, it provides the broad description about the technical features being used in the proposed project. System Requirements Hardware Requirements At least single core processor 512mb RAM or Higher 8 GB Memory DVD Writer Mouse, keyboard, Speaker, AVR HP Printer Flash Drive Software Requirements Works in any version of Windows 7 Windows 7 is the commonly used Microsoft Operating System and will be the minimum request of the Vendor management System application. Java Programming Language (Net Beans version 7.3) This platform using 4thgeneration java language and will be used as a front-end for the system development. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 50 MS SQL Database MS SQL application is will be using as the backend of the System Development which is the Vendor Management System MS SQL will the storage of all the data and information inputs in the system. Internet connection Internet connection will be the primary needs of the Vendor Management System, because this propose software is online. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 51 5. Project Organizations and Staffing The vendor Management System is a project, an idea formed due to the needs of the restaurant. The project will be possible by the enlisted organization and staff below. ROLE RESPONSIBILITIES Manage, review, and prioritize project work plans. Provide status report. Manage project team. Recommend changes, escalate issues, and mitigate risk. Project Manager Managing project progress and performance. Final approval of the design specification. Provides status reports to project sponsor and project adviser. System Analyst Participate in project activities, including planning, implementation of deliverables, and quality control. Work with the Project Manager for the requirement development and the system priorities. Set up and maintenance of security right and Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 52 access permission. Participate in project activities, including planning and quality control. Provide worthy intelligent ideas in developing Business Analyst documentation. The who responsible for the gathering and understanding the business needs of the member within specific project. Collaborate with the system developer to establish the technical vision of the analyzed problem and needs of the business. Document Specialist Participate in project activities. Creating the documentation. Studying the conduct interview information. The one who ensure that all documents are free form typographical error. Lead Programmer Participate in project activities, programmed the system, maintaining the system. Working with the project Manager. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 53 Project Advisor Participate in project activities. Act as the project primary consultant. Reminding the project team about the do’s and don’ts that may be include and eliminate for the goods of the system progression. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 54 CHAPTER 2: REVIEW OF RELATED STUDIES AND SYSTEM 2.1 FOREIGN STUDIES 2.1.1 Arizona AIM System - 2010 The Vendor Management functional area supports the management of the retail vendor aspect of the Pita Pit Restaurant. It tracks the vendor authorization process; captures information about authorized vendors; monitors vendor education; records prices for approved foods; records vendor peer groups; helps identify potentially abusive vendor practices for which additional monitoring or investigation may be needed; supports record audits; maintains a comprehensive vendor profile, including information about compliance activities and sanctions (including suspensions and terminations); supports coordination of sanctions with the Food Stamp Program; and supports routine communication between Pita pit restaurant staff and vendors. Track Vendor Authorization Process Capture Owner Information Capture Vendor Prices Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 55 2.2.2 Waterfall Franchise Management System (FMS) 2014 – India The Waterfall Franchise Management System (FMS) with Catering Food and Services is created and developed primarily by Ruby on India, WATERFALL SOFTWARE’s franchise software offers a comprehensive, turn-key franchise technology solution. It enables the creation and distribution of franchise with catering food and services websites and intranets as well as full dashboard-based business intelligence analytics. Waterfall Franchise Management System (FMS) With Catering Food and Services is the computer software that is intended for improvement of its software quality via franchising and catering automation of the basic routine objective and daily activities. The Waterfall Franchise Management System delivers increased franchise leads and franchise sales at least two ways: First, Waterfall provides the franchise management tools that help franchisees be more productive and successful. Happy and successful franchisees refer more franchise prospects and validate more positively. One in four franchise referral leads become new franchisees. This statistic was front and center for the development team at Waterfall as they developed the franchise management Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 56 system features that combined to deliver better relations between franchisor and franchisee as well as deliver added value to the franchise business as a whole. Second, Waterfall delivers a unique and innovative way to increase online franchise leads without any additional cost to the franchisor. The Waterfall ‘virtual location lead generator’ provides strategic deployment of geo-targeted virtual franchise locations to help drive franchise expansion. This strategy allows franchisors to develop virtual real estate on the web that delivers local and targeted search engine results for your franchise in areas you want to develop. Waterfall franchise software delivers this service to you at zero additional cost; we consider ourselves partners in the success of your franchise. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 57 Components of Waterfall Franchising Consolidated management organization’s consumerfacing assets. The Waterfall Content Management System (CMS) empowers organizations to manage the content and SEO marketing of the organization’s online assets, including the Corporate website, location and or affiliate websites, mobile websites, and customized social media websites. Rapid deployment of brand consistent affiliate, partner or franchisee websites. The Waterfall software platform delivers the ability to customize and deploy sub-sites for all partners, affiliates, locations, and franchisees organization. Using Waterfall, organization is able to scale and grow with confidence: brand equity and message consistency is maintained. Social Media Integration Integration of all associated social media pages into the Waterfall system allows for the organization’s administrator to monitor postings and push content to one or all sites with the push of a button. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 58 Customer Relationship Management The built-in CRM allows for easy lead and customer management. The Waterfall CRM also allows headquarter admins to see all leads that enter the system. This level of transparency enables corporate leaders to deliver greater support to their associates and partners and help close more business. In addition, Waterfall software easily integrates with third-party CRM platforms that your organization might currently be using. User management and internal communication The Waterfall system allows for greater knowledge of the user activity in the system. Complete with user logs, the ability to assign roles and permissions, and robust user forums, the administrators of the organization will better understand their users operational activities and enjoy enhanced communication throughout the organization. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 59 Document Management Manage documents of all kinds with the filing cabinet. Assign files to specific users or to everyone. Provide approved content for the web assets, marketing material, instructional documents, and other information to your users. Private filing cabinets are provided for each user to store documents, for example. Executed contracts, performance profiles, and compliance reports. E-Commerce All websites support E-commerce functionality with robust product, promotion, and shopping cart management. Easily opt in or out of this feature with a push of a button. This feature is ready to integrate with the payment gateways and credit card companies of your choice. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 60 2.1.3 Burger King Alex Macedo - 2010 Every day, Burger King Restaurant is having a more than 11 million guests visit around the world. And they do so because the burger king restaurants are known for serving high-quality, greattasting, and affordable food. Founded in 1954, Burger King is the second largest fast food hamburger chain in the world. The original home of the whopper, our commitment to premium ingredients, signature recipes, and family-friendly dining experiences is what has defined our brand for more than 50 successful years. The Burger King is offering a world class system to support the franchising TRAINING programs to design and create a Bold, Empowered, Accountable and Fun culture, for their client to perform at the highest levels, and your business can grow and be profitable. The OPERATIONS EXCELLENCE mission is to ensure that a guest's experience is equally outstanding whether in Miami, Madrid or Manila. Burger King Restaurant Support Center operations team and our field team will work directly with you and your teams to provide you with the tools you’ll need to operate at the highest level and maintain the reputation of the brand. MARKETING AND ADVERTISING team turns innovative ideas into winning programs that resonate with our guests and expand our brand on a global level. Whether it's in your franchise-owned restaurant or halfway Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 61 around the world, burger king ensure that our guests know exactly what to expect when they see our logo. No matter where the client goes, no matter what language you speak, the BURGER KING brand represents quality you can trust.Director of Franchise Performance (DFP) The DFP consults the clients on all aspects of restaurant operations and provides ongoing support as the business grows. In addition, the DFP acts as the primary above restaurant level Burger King Corporation contact, offering insight and coaching to help the client to achieve success. The DPF plays a key role in helping and to implement Burger King Corporation’s world-class operating systems throughout your organization. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 62 2.1.4 erecruit VMS – 2014 erecruit VMS vast experience both in staffing and enterprise software, they have built a distinctly different company that focuses on generating tremendous value for their enterprise staffing clients. erecruit uses modern, standardsbased technologies to provide an integrated front and back office solution, complete with VMS and powerful, real-time analytics that enables today’s best firms to put their clients and candidates at the heart of their businesses. Customers range in size from $20M - $400M and have found that erecruit combines an unparalleled level of configuration, ease-of-use, and reporting with unlimited integration capability, providing them ultimate control over business success. Components of erecruit VMS Support vendor neutral and master vendor business models Support multi-tier MSP programs Track pricing and service levels Publish jobs to vendors and internal recruiters, in tiers or at the same time Communicate between vendor recruiters and vendor managers Streamline vendor submittals and manage duplicates with ease Provide unlimited candidate portals for entering timesheets and expenses Provide unlimited vendor portals for receiving jobs, submitting and tracking candidates Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 63 Provide unlimited client portals for approving timesheets and expenses, receiving consolidated invoices and accessing client-specific reporting, including current job and candidate pipelines, total hours and spend, days-toplacement and diversity 2.1.5 Beeline Vendor Management System – 2011 A Beeline Vendor Management System (VMS) is an internet based software application that enables a business to procure and manage temporary and permanent staff as well as contract and contingent staff. The Vendor Management System usually includes: • Staff ordering processes or job requisition. • Automated billing. • Management reporting. • Business Intelligent (BI) functionality. • Workflow engines. • Service catalogue that includes standardized positions and skills. • Tracking facilities. • Approval processes. The installed Vendor Management System will create a centralized internet based environment that will allow a purchaser to enter their staff resource requirements to numerous staffing vendors. Vendors will be able to reply in real time in a standardized method, proposing their particular staffing solutions. There are a number of advantages to using a VMS: Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 64 • Only approved staff are hired. • The vendors can bid for their staff to be hired so there is competitive bidding. • The purchaser descriptions. • All submitted staff details are available in one place can set up standardized job and many systems can rank the proposals according to the purchasers requirements. • There is a central work flow engine that manages the process end to end. • Questions, interviews and rejections are notated and tracked. • Staff rates are kept low by the competitive environment as opposed to individual negotiations. • The entire process is much quicker and smoother. • No time is spent on reviewing staff that are too expensive. The management of staff on site is also greatly simplified by a Vendor Management System: • The same time cards are used by all staff. • All staff are hired on uniform rates and expenses. • Time can be reported against multiple projects. • All consultants will be on identical time reporting schedules. • There is accurate data about staff utilization removing overlaps and loss of staff. • All timesheets can be seen in one place. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 65 • Overtime can be capped or approved automatically. The vendors benefit from: • Quick approval for their staff. • Invoices are more accurate and presented far quicker and in a uniform manner. • Reporting errors are minimized. • They have far quicker access to staffing requirements. As you can see there are a great deal of advantages to a Vendor Management System and very little disadvantages, which is why so many companies use them. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 66 2.2 LOCAL STUDIES 2.2.1 Max’s Restaurant – 2014 Max's Restaurant franchising objectives is to values close family ties and the Filipino concept of “samahan” (sense of belongingness).Max’s Restaurant treats each and every business partner as a family member. Max's offers a comprehensive totalsolutions package to aid our franchisees in successfully planning, developing, and implementing their very own Max's Restaurant franchise. The scope of max’s vendor management system is the franchise monitoring. Max’s can monitor the borrowing supplies through their web sites; they can easily track the availability of the products that can be borrowed of other max’s branches. The max’s promotion of new products is depend/responsibility of the Administrators is capable of putting all information’s in the Vendor Management System about the product to be launched as well as its ingredients and process of cooking/making. The Administrator is capable of sending this information’s through internet that can be received by every branch. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 67 The Home Page, this would be consists of latest happenings and news about Max’s. The Menu Page will consist of the list of menu of existing products of the Max’s Restaurant Inc. according to its category, as well as its prices. Franchising Page is the page where our interested franchisees could gather information about the franchising processes of Max’s Restaurant such as; qualifications of a franchisee, franchise package fee, steps in franchising, they can also view content where they could get answers of the questions they have in mind about franchising of Max’s. Downloadable Application Form is also available on this page if they are really interested, they can fill it up then send it by an email. New Product is the Page where Administrators can display the launching of Max’s new products which would help them improve the Marketing and Promotional status of their restaurant. Contact Us Page will consist of contact numbers of every branch of Max’s and their emails. About Us Page will consist of Max’s history and all about Max’s that visitors want to know. Aside from it, we will be implementing it in every branch that would be operated by the Branch Managers who will serve as the User of the system. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 68 2.2.2McDonald's Franchise Caroyn Barratt – 2012 The McDonald’s franchising objectives is to give opportunities to people who share the same vision of serving great tasting quality food fast through franchising. More than 80% of McDonald's restaurants all over the world are owned by franchisees. In the Philippines, McDonald's opened its doors to franchising to Filipino entrepreneurs in 1985, and has since expanded its network to over 150 franchised restaurants with more than 65 franchisees (most have been part of the McDonald's Family for around 10 to 15 years!). The McDonald’s restaurant is using franchising advertisement to promote the company assets as an investment, product launching, staff ordering process and job’s offers in the market with the use of internet connection. The Administrator can put information’s about franchising of McDonald’s and it will be seen by the internet users, so that interested entrepreneurs can easily be informed about McDonald’s franchising. They can also avail a downloadable form than can be fill up and just send via email. While the branch monitoring of McDonald’s is using a vendor system to monitor the ability to maintain the difference branches and to maintain the good quality provided by each branches and also to monitor the level of sales of every branch of McDonald’s. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 69 2.2.3 Mang Inasal Restaurant - 2010 The Mang Inasal restaurant is one of the fastest growing fast food chains in the Philippines. The objective of Mang Inasal franchising is to introduce a unique franchising management that can be flexible to the interested costumer, and a wide franchising communication for the different branches located at the different places. The Mang Inasal scope of franchising package’s are franchise monitoring the company can easily monitor the franchise activities by simply login in on the web base vendor management system, Brach monitoring Mang Inasal can communicate in their different braches even if some of does branches is located in difference place in the Philippines. 2.2.4 Shakey’s Restaurant Shakey’s Restaurant is one of the first founders of the pizza restaurant in the Philippines. The company is renowned and then began to have franchisees in just a couple of year. The main objectives of this company is to have a low cost of franchising investment, a good advertising and marketing services, financial system (Standardized) distribution and purchasing, and quality assurance when it comes in franchising software development. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 70 2.2.5 Adobo Connection The Adobo connection is a chain of restaurants that specializes in serving a variety of Adobo’s and other pinoy favorite dishes. Adobo connection currently has over 50 stores (16 of which are companies owned; 46 are open, 4 more are under construction). The main objectives of adobo connection are divided into four (4) good reasons. First, to maintain the traditional adobo of pinoy. Second, to satisfy the franchisers to enjoy the healthy and sustainable profit margins. Third, the adobo connection would like to be delight to help their costumer to find a good site. And the last thing is after they will be partners and have flexible franchise terns to close on the client’s needs. To actualize the objective of adobo connection, they are giving some incentives or franchise package for does clients who will continue the franchising fee of 5% of sales, 3% Royalties and 2% marketing fund. Their client can use the adobo connection Brand name, Logo and system. The company also includes the graphic design for marketing and store design. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 71 2.3 SYNTHESIS AND RELEVENCE TO THE STUDY (MATRIX – COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS) Vendor Management System becomes successful in and out of the country. It made a big improvement in any business using it, as well as the Restaurant business in terms of sales, staffs, transactions, reports,etc. The Proponents realized that it is possible to create a Vendor Management System that uplifts the performance of the company using it. 2.3.1 VMS and Foreign Synthesis and Comparative Analysis Vms Features Pitapit FMS Bee Line Berger King VMS Terms and Condition Franchise Advertising Franchise Monitoring Product Promotion Personalize Report (Timely Free format report generation or Report Customization Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 72 depending upon the user needs.) Personalize Screen or Interface depending to the user of VMS System Database(MS SQL as a huge storage and its import and Export of dataset capable of VMS) VMS Analytics or Graphical Report presentation for percentage, quantity or statistical Repot. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 73 2.3.2 VMS and Local Synthesis and Comparative Analysis VMS Max’s Mcdonals Mang Inasal Shakey’s Adobao Connection Features Terms and Condition Franchise Advertising Franchise Monitoring Product Promotion Personalize Report (Timely Free format report generation or Report Customization depending upon the user needs.) Personalize Screen or Interface depending to the user of VMS System Database(MS SQL as a huge storage and its Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 74 import and Export of dataset capable of VMS) VMS Analytics or Graphical Report presentation for percentage, quantity or statistical Repot. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 75 VMS RISK MITIGATION, MONITORING AND MANAGEMENT PLAN 1.0 INTRODUCTION Project team will undertake risk management plan. The proponents should monitor the risk constantly as well as the progress of the software development. Risk mitigation, monitoring and management is necessary to produce a good quality product which is the responsibility of the proponents and the client to monitor. 1.1 Scope and Intent of RMMM Activities The proponents aim is to develop software for Vendor Management System (VMS) where all areas and key functions are free from errors or defects, efficient and accurate, but bit is almost impossible to develop a system that is free of any defect because of the speed changes in technology. The proponent would like to have a risk management plan to counter any difficulties that may impact the development or the creation of the software. The project team goal is to assist every member in developing a strategy to deal with any risk. To achieve this aim, RMMM must be plan well and determine the possible potential risks in a generic sense. When all possible risks have been identified, the proponents will then be evaluated the possible risks to determine the risks and how will it affects the software Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 76 1.2 Risk Management Organizational Role. The project team members are involved in the software which has a certain obligation to manage the risks. The proponents should participate and paid close attention to mitigate, monitor and manage the risks. The proponents must monitor the progress of the tasks and schedules, cost estimations, scope analysis of the software, integration into other system and other possible present and future risks that might possibly affect the software as they occur. The project team can avoid the risks when they get the necessary details of the equipment that are accessible to the proponents. Risks can be avoided when the proponents will be responsible in all the changes before initiating request for the software. The client must give all the details needed as early as possible and sudden changes that must be added up or features that is wanted to occur in the software. Giving all the possible information in the software development with the help of the client can be avoided the risks. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 77 2.0 RISK DESCRIPTION This section is the definitions of different risks that might occur in the software development while it is on process. 2.1 Risks Tables This table shows the description of the risks and the possible problem that may encounter and can be affect the software. The following risks that may show are discussed as well as the probability and ways of its occurrences including the impact in the development process. 2.1.1 Description of the Risk m Business Impact Risks This is the risks where the concern is that not being able to come up or construct the product, where it leaves impact on the client’s business. If the product does not achieve the goals it will fails to help and contribute to the business progression. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 78 Customer Risk This risk refers to the cooperation and willingness of the client in helping software development with the project team to create a well-developed, quality assurance and effective software. If the client fails in giving the factual information needed for the business, the project might not be the one that helps the business. Development Risk This risk refers to the failure of the client to support and provide all necessary equipment for the development and the execution of the software which can cause the project to fail. On this scenario, project team must think another options or ways to continue the development of the product. Employee Risk This risk describes the caliber, potential and the willingness of the proponents to create operational and functional product like VMS. Coordination, interdependence and initiative are necessary for formulation of ideas, planning and development of the product. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 79 Financial Risk Financial risk refers to the budget or allocations in order to support the product or software development. It supports the procurement, development and requirements of the system. Process Risk It is about the excellence, quality and effectiveness of the product or software developed. To achieve this the project team will set a guidelines that might be used during the software development process. This will help the project team to meet the standard requirements of the client. Product Size It refers to the misjudgment between the client and project team. The project team must know the scope of the software development to avoid spending too much money or budget of the project. Technology Risk This risks involves of using technology that is soon to be stale. As the result of this risks the software developed will be functional for the short period of time. Since the Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 80 change of technology nowadays is rapidly the proponents and the client should keep eye for the current technology. Technical Risk This risk involves the configuration of the computer system, peripherals and the possible causes of accidents that might happen technically like shutting down of computer system, power interruptions and technical maintenance. 2.1.2 Probability and Impact for Risks m The following are sorted according to probability and impact of each categorized risks that might occur in developing VMS. Category Employee Risk Risk Lack of knowledge, Probability Impact 40% 1 training and experience Process Risk Low product quality 35% 2 Technology Risk Staling of technology. 35% 3 Technical Risk Unexpected 40% 2 30% 3 technical and power interruptions and computer configuration Financial Financial Risk budget to procure and support the Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 81 software development. Product Risk Estimation planning 30% 2 20% 3 10% 3 10% 3 might be erroneous. Development Insufficient resources. Risk Client Customer Risk might partake or fail to less involvement. Product may fail to meet Business Risk Impact the requirements of the business. Impact Values Description 1 Catastrophic 2 Critical 3 Marginal 4 Negligible The table is categorized the risks that might occur in the software development. In every risks categorized on the first column, the second column gives its concise description. The table also discussed the probability in percentage and the impact of the risk. The impact values assigned to each risks are described the section below the table. It is very convenient way to look at the risk and derive the information of the risk. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 82 3.0 RISK MITIGATION, MONITORING AND MANAGEMENT 3.1 Risk Mitigation for Risk m This is the section where we can find the for several different software development. This risk mitigation regards to the possible solution for every risks that might encounter, to maintain and keep the good quality of the software developed. Generally, the project team will mitigate plan in ascertaining the risks and scrutinized them during its existence. 3.1.1 Business Impact This section is the risk category wherein the quality of final product is being concerned. To avoid the identified risk, the project team must spend more time to understand the needs for the successful of the software development. The proponents must gather the factual information regarding to the vendor management system to meet the standard requirements of the client for the software development project. The proponents must understand the environment of the business that the client have. It will help the project team to create a system that suits to the requirements of the client. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 83 3.1.2 Customers Risk (client) Failure of the customer (client) is also the failure of the project team to create software that meets the client’s requirements. To prevent this kind of risks the user must participate during the software development stage. The customer must tell all the factual information needed by the project team for them to recognize the problem of the software. For the best partnership between the customer and the proponents there must have a regular communication to each other so that it result for the better understanding to the software that is being developed. 3.1.3 Employee Risk (project team) This is the risk that concerns for the knowledge and willingness of each project team members that develop a software that provides the necessities of the vendor. The proponents must have cooperation and coordination for every tasks done. Initiative is also must to avoid the overlapping of the tasks being assign to each project team members. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 84 3.1.4 Financial Risk This risk must exactly clear and classified, to know where the budget or allocation for the software development goes. The client and the proponents must coordinate to each other not only because the client gives the factual information regarding the software develop but as well as the monetary budget which is provided by the client. The proponent must report all the one-time, ongoing and outgoing cost where the fund spent. 3.1.5 Process Risk For achieving the good quality and quantity of the software, the client present a guidelines that must be follow by the proponents about the software. The guidelines state the dos and don’ts of the team member during the software development stage. For having this kind of strategy the team will surely create a software that will bring a good quality product and can also increase the level of success of the client’s requirement. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 85 3.1.6 Product Size Interviews are not enough as good source of information for the software development. Researches and surveys will also help to enhance the acquaintances of the proponents regarding the process of the business or vendor management that the project team will be needed to provide the solution that might encounter. By using this kind of way of gaining factual information, the proponents will estimate the financial statement of the software product. Knowing the scope of the VMS will also help to determine the product size of the software. 3.1.7 Technology Risk This refers to the archaic technology. The proponents must have an extra research on the latest technology to avoid this kind of risk. The project team has to make sure that the equipment requested is incumbent and not archaic in the near future. 3.1.8 Technical Risk This risk involves the configuration of the computer system, peripherals and the possible causes of accidents that might happen technically like shutting down of computer system, power interruptions and technical maintenance. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 86 3.1.9 Development Risk This risk refers to the failure of the client to support and provide all necessary equipment for the development and the execution of the software which can cause the project to fail. On this scenario, project team must think another options or ways to continue the development of the product. 3.2 Risk Monitoring for Risk m This is the section where the proponents can monitor the identified risk if the Risk m is suits to resist the different risks. 3.2.1 Business Impact The communication between the customer and the employee must not disrupt. The meetings of the employee must ongoing for the better maintained of the developed. Software for this kind of monitoring the customer can easily identify and determine the changes that may have to make the software for the better progression of their business. 3.2.2 Customer Risk The proponents will monitor and track the people attending the meetings conducted especially the client to ask or to insist the client’s suggestion and feedbacks. And for those clients that are not diligent to attend the meetings will be reminded. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 87 3.2.3 Employee Risk This is for monitoring and managing on how the team member interact to each other when exchanging and sharing knowledge. This is where team members gain information about the task, technique and using a particular tools that not familiar to team. Teaching – Learning technique is the best strategy to manage and monitor this risk. 3.2.4 Financial Risk This risk must exactly clear and classified, to know where the budget or allocation for the software development goes. The client and the proponents must coordinate to each other not only because the client gives the factual information regarding the software develop but as well as the monetary budget which is provided by the client. The proponent must report all the one-time, ongoing and outgoing cost where the fund spent. 3.2.5 Process Risk The best way to monitor this phase is to compare the previous work done to the other work. This would be help to overcome the problem that has been found. This Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 88 would also help for the team member if the guidelines that they’re follow is effective or not. 3.2.6 Product Size The proponents created the WBS which shows the scope and objectives of VMS. By using this, the proponents can used this as a basis to avoid the risk. 3.2.7 Technology Risk For monitoring this risk, during the software development the proponents and the client will keep eye on the latest technology to avoid the obsolete of the tools and equipment that are used to perform the software effectively. 3.2.8 Technical Risk This risk involves the configuration of the computer system, peripherals and the possible causes of accidents that might happen technically like shutting down of computer system, power interruptions and technical maintenance. 3.2.9 Development Risk This risk refers to the failure of the client to support and provide all necessary equipment for the development and the execution of the software which can cause the project to fail. On this scenario, project team must think Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 89 another options or ways to continue the development of the product. 3.3 Risk Monitoring for Risk m This is the section where the proponents can monitor the identified risk if the Risk m is suits to resist the different risks. 3.3.1 Business Impact The communication between the customer and the employee must not disrupt. The meetings of the employee must ongoing for the better maintained of the developed. Software for this kind of monitoring the customer can easily identify and determine the changes that may have to make the software for the better progression of their business. 3.3.2 Customer Risk The proponents will monitor and track the people attending the meetings conducted especially the client to ask or to insist the client’s suggestion and feedbacks. And for those clients that are not diligent to attend the meetings will be reminded. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 90 3.3.3 Employee Risk This is for monitoring and managing on how the team member interact to each other when exchanging and sharing knowledge. This is where team members gain information about the task, technique and using a particular tools that not familiar to team. Teaching – Learning technique is the best strategy to manage and monitor this risk. 3.3.4 Financial Risk This risk must exactly clear and classified, to know where the budget or allocation for the software development goes. The client and the proponents must coordinate to each other not only because the client gives the factual information regarding the software develop but as well as the monetary budget which is provided by the client. The proponent must report all the one-time, ongoing and outgoing cost where the fund spent. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 91 3.3.5 Process Risk The best way to monitor this phase is to compare the previous work done to the other work. This would be help to overcome the problem that has been found. This would also help for the team member if the guidelines that they’re follow is effective or not. 3.3.6 Product Size The proponents created the WBS which shows the scope and objectives of VMS. By using this, the proponents can used this as a basis to avoid the risk. 3.3.7 Technology Risk For monitoring this risk, during the software development the proponents and the client will keep eye on the latest technology to avoid the obsolete of the tools and equipment that are used to perform the software effectively. 3.3.8 Technical Risk This risk involves the configuration of the computer system, peripherals and the possible causes of accidents that might happen technically like shutting down of computer system, power interruptions and technical maintenance. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 92 3.3.9 Development Risk This risk refers to the failure of the client to support and provide all necessary equipment for the development and the execution of the software which can cause the project to fail. On this scenario, project team must think another options or ways to continue the development of the product. 4.0 Special Conditions This section discussed the special condition associated with HRMS software and these are the following: Technical Training The user of the software must be trained to be literate on using the software. But before of the software usage, the user must know or has the knowledge on using computers. Of course, the client or the user are very excited to use a new process intertwined with the technology, but it very necessary to train them first in computer configuration as discussed to technical risk. The Branch Manager and the Administrator must spent their time to scheduled training and provide new knowledge and skills for them. The users must know basically the operation of computer units, the technicalities might occur until they reach the training on using the software. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 93 VMS SOFTWARE CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT PLAN 1.0 Introduction This section is about the changes coming from the original plans that are not good enough to meet the developments that are needed. Software Configuration Management Plan lists all the changes that are feasible to make the software development effective. 1.1 Scope and Intent of SCM Activities The main reason of having SCM is to make, track and report of changes that are made from the original software development rather than the original software developed. It also helps to reduce the mistakes done by the developed software. The project team should keep eye to the developed software for them to easily identify what changes should be made. The following are the SCM Activities: Recognize change Improve the change Manage the change Make sure that the change made is properly implemented. Document the change Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 94 1.2 SCM Organizational Role Since the proponents are compose of 5 members, each member has their own corresponding task to make. The proponents are responsible the o monitor and report any changes that might occur. If one of the project team reports a change, the other member will take up the job to authorize the change. Some changes occur are come from the suggestion of the proponent that may help for the proponents that may help for the progression of the VMS process vice versa with then client that aims for the improvement of the software that are necessary for the business. 2.0 SCM Tasks This is about the detail and list of tasks of SCM and the assign responsibilities of each proponents. SCM tasks is not only for the knowledge of the proponents but the client as well. It would be discussed and be informed by the assigned member of the project team during the meetings. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 95 2.1 Identification In this section, the proponents will discuss how software configuration item will be identified for SCM Plan 2.1.1 Description Recognize change If one of the project team member suggests a change regarding the software, the entire project team will discuss and the change that is being suggest and figure out if the change is necessary for software development with the approved of the client if it is suits for the business. Improve the change The changes that are approve to be change must be improve according to the process and features. The changes that are made for the software might be used to avoid the risks and must effectively to progress the business process. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 96 Manage the change The project team will control the changes made to the software. If one of the proponents thinks any change, the other proponent should know the change that is being suggest implementing it. before It can creating cause and technical problems to the software if the change will not properly control. The project team will create a rule that manage the changes, for every change that the proponent identified the entire project team should know the changes. The proponents who’s not abiding the rule has a corresponding punishment. Make sure that the change is properly implemented. Since the entire project team has their own task, there is the possibility that the change for the software is not correctly implemented. To assure the correct implementation for the software, the project Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 97 team will make a routine to look over the change for properly implementation. Document the change Every changes made for the software development should be documented. It helps the project team and the client to know what part of the software development is being changed and why is it changed. This serves as a record for the changes that are made. 2.1.2 Work Products and Documentation Recognize the change Once the change is identified and listed the project team will be study and analyze it and discussed it to the client to know if the client will approve it. Improve the change After analyzing and discussing the change, it must be improve base on the level of necessity for the progression of the process. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 98 Manage the change After scrutinizing, the change will be made. Ensure that the change is properly implemented. Document the change Once the change is approve the project team will document the change. 2.2 Configuration Control 2.2.1 Description Human procedures and automated tools are the necessary thing use to control the change. Here are the steps. Identify the Change Study and Analyze the Identified change Evaluation of Change Final Decision making for the Change If Change approved: Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 99 1. Define Constraints 2. Purpose of Change 3. Remake the Software 4. Implementation 5. Effect of the Change 2.3 Version Control 2.3.1 Description As a result of change, as is it implemented the version number will increased accordingly. The proponents will be used the universal version number system for all the change might occur. The proponents will also have a final version of the entire product. The revised or additional features of the documentation will also have version number. 2.3.2 Increasing Version Number When a change request is filed, a change will be created. It is important to report and record all the changes that might occur and improve to the software development that serves as a reference. After finalizing the change, it will be documented. The Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 100 project team will be using a decimal point version number system. <Minor Update><Major Update><Bug Fixing><Software Features> System Features The clients increases its needs as it firm became huge and border. The software will also adjust to those needs. That’s why the client wants to change or innovate the features of the software of inputted to and the proponents must deal with the request to of the clients. Bug Fixing Bug fixing is more likely as a maintenance. It is necessary for the software to fixed the logical and code errors that might be encountered during the implementation stage. The more bug fixes have been made, the bug fix will also increase, and the increase version must follow. Major Update Having a major update for the change will undergo to the major revision of the software. As the major update will imposed, increase of version will be Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 101 made. The increase of version will be labeled as version 2.0. Minor Update Minor update includes the changing of the design and interface that will increase the userfriendliness and performance but doesn’t change the function or interface work. It also cause to increase the version number. 2.3.3 Work Product and Documentation The single document titled Version Revision History will be the reference of all revisions made on the software. 2.4 Configuration Status Accounting There are different ways that can be used to communicate the project team members and to inform clients regarding to the changes concern. 2.4.1 Description Online Help desk This tool will be used to help team to communicate with the clients. Client can submit Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 102 enhancement report revision report by means of online help desk. In response to the submitted report the project team can post the development to each items that have been submitted to the help desk. Verbal communication Sincethe project team has a small number of member and all team members are all in constant touch with each other it would be better to communicate verbally. 2.4.2 Work Products and Documentation 3.0 Online help desk Verbal communication Software Quality Assurance Overview This regards to the Software Quality Assurance description that will be elaborate the Software Quality Assurance Plan (SQA). SQA focused and discussed the management issues and the process activities to ensure the right way of using the software Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 103 at the right time. SQA plan will be serve as a guidelines for manipulating the software quality assurance. Scope and Intent of SQA Activities The main reason of having SCM is to make, track and report of the changes that are made from the original software development plan. This change would make the better development rather than the original software developed. It also helps to reduce the mistakes done by the developed software. The project team should also keep eye to the development of the software for easily identify the change. A quality management approach Effective software engineering guidelines Formal Technical Reviews A Multi-Testing strategy Control for the software documentation Software Development Standards Compliance Reviews and Audits The Formal Technical Review (FTR) is a software quality assurance activity that is performed by software engineers. The objectives of the FTR are: Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 104 1. To uncover errors in function, logic and implementation for any representation of the software. 2. To verify the software under reviews meets its requirements. 3. To ensure that the software has been represented according to the predefined standards 4. To make the better software manageable, effective, accurate and maintained. 3.1 Generic Reviews Guidelines ISO 9001 is the quality assurance standard that applies to software engineering. The following are the 20 requirements delineated by them. The proponents will try to follow the standard assurance plan. Management Responsibility Quality System Contract Review Design Control Document and Data Control Purchasing Control of Customer Supplied Product Product Identification and Trace Ability Process Control Inspection and Testing Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 105 Control of Inspection, Measuring and Test Equipment Inspection and Test Status Control of Nonconforming Product Corrective and Preventive Action Handling, Storage, Packaging, Preservation, and Delivery Control of Quality Audits Training Servicing Statistical Techniques 3.1.1 Conducting of Review Two kinds review will be held, review cases with the client and review cases with the proponents. The project team should agree keep and a good record of the software before and after the change, this change helps to enhance the client’s performance when using the software. 3.1.2 Roles and Responsibilities It consist of the project team members including the roles and responsibilities: Project Manager: Juvelyn F. Seno Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 106 Business Analyst: Jennifer V. Quibuyen System Analyst: Khristine T. Escovidal Document Specialist: Jeseca V. Bodollo Lead Programmer: May-ann L. Caguindagan 3.1.3 Review Work Product The proponents have a weekly meeting with the adviser, Mr. Andrew U. dela Cruz that guide the project team throughout the project. The adviser is the one who gives feedback about the documentation progress and will also advice or discuss the process of your system development. The adviser can also give some idea that will help the project team to improve the knowledge about the project that is being made. It is not about the proponents and adviser interactions but it is also about the unity of each project team of every sub-system that is needed to compose the entire Restaurant Management System. Each project team of each sub-system will update each other about the changes and progress happen to the sub-system, assigned to each team. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 107 All the past works done of each project team members should be documented in the project timeline. 3.2 Formal Technical Reviews Here are the FTR conducted during the software development process. - Software Inspection - Consultation Each interface that will be designed by the proponents should undergo in testing method. The proponents will set a meeting for the entire member and the client and will conduct an open forum that look for any suggestions and feedbacks. Description of the Software Inspection Review This is about the developed software if it is correctly, effectively and manageable. It is the integration of the design parts such as interface, forms, and database of the system.it also focuses on the correctness of the parts that will be design. Description of Consultation Consultation refers to the suggestions and feedbacks of the proponents regarding to the software development. If Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 108 the changes occur, the client and the proponents will scrutinize the change to make. 3.2.1 System Review Specification System specification of VMS is fixed and constant especially to the database which is MS SQL and platform for the software development which is Java Language. For further information regarding the software specification please see the document System specification. 3.2.2 Software Project Plan Review The purpose of this plan is to look over the entire project. For further explanation regarding to this section please the Project Plan section. 3.2.3 RMMM Review RMMM, is the risk mitigation, monitoring and management which is use as a guide to monitor and to control the risk that may occur to the software. For more information please read the RMMM section in chapter 3. 3.2.4 Requirement Reviews (Models, Specification) Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 109 This section is composed of the data requirement and specification of the software. Please see the “Software Requirements Specification”. 3.2.5 Data Design Review This section is about the data flow between each interface (form) to the database. Data design can be found on the document titled “Software Design Specification” 3.2.6 Architectural Design Review Architectural design refers to the entire design, layout and dataflow of the software. For more information regarding Architectural Design, please see the section for Architectural Design. 3.2.7 Interface (GUI) Interface is still on the process and not yet finalized. The interface of the Vendor Management System must have resemblance to the other sub-system. This includes the procedures and the process of the VMS as the part of the entire system. The front-end of the software is Java Netbeans Platforms. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 110 3.2.8 Component Design Review VMS is still on the design phase. The project team will be having an integration and online help desk after the software is already finalized and ready for implementation. 3.2.9 Code Review Not yet applicable. 3.2.10 Test Specification Review Please see “Test Specification” but not yet applicable. 3.2.11 Change Control review and Audits Not yet applicable. 3.3 SQA Audits Project team members will have a weekly meeting to their adviser to the report about the past works done for the past week. Any problems, question, regardless to the documentation of the software development will be noted and every tasked done by the proponents will be documented on the project timeline. Any changes that will be happen or occur on the software development must be discussed to the other members of the project team together with the client. Minor or major changes Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 111 should be consulted to the persons involve in the project development. 3.4 Problems Reporting and Corrective Action/Follow-up This section will describe problem reporting mechanisms that occur as a sequence of the FTRs that are conducted and the means for corrective action and follow-up. 3.4.1 Report Mechanism As a report mechanism, the proponents used a method of follow-up meetings to inform each member about the progress and changes of the software development. 3.4.2 Responsibilities Each member of the project team has a corresponding position to handle. Since there is a project manager who is responsible for leading and managing the project team members to make sure that the project flows is into the right direction according to the schedule of each task, it doesn’t mean that all of the decision making process will be made by only one person. Every decision making Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 112 needed must be decided by all of the member, by this coordination and cooperation is shown. Project Manager: Juvelyn F. Seno Business Analyst: Jennifer V. Quibuyen System Analyst: Khristine T. Escovidal Document Specialist: Jeseca V. Bodollo Lead Programmer: May-ann L. Caguindagan 3.4.3 Data Collection and Valuation To properly conduct software quality assurance, data about the software engineering process should be collected, evaluated, and disseminated. Statistical SQA helps to improve the quality of the project and the process itself. During each meeting, the proponents will present a drafted of the possible design of the software to the client. The proponents will undergo a defense that will criticize the project done by the proponents. The client will give an additional idea, suggestion and feedback about the software development. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 113 VMS SOFTWARE QUALITY ASSURANCE PLAN 1.0 Introduction The project team gives the general overview of the Software Quality Assurance Plan (SQA) regarding to the sub-system entitled Vendor Management System (VMS). 1.1 Scope and Intent of SQA Activities The following are the objectives of the SQA: A quality management plan Effective software engineering guidelines A procedure to assure compliance to meet the client’s requirement. Formal Technical Review Control for manipulating the software documentation and the changes made to it. 1.2 SQA Organizational Role The proponents are relatively small team. It compose of 5 members. The project team members has a corresponding role. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 114 VMS Organizational Structure Business Analyst lead Programmer Project Manager System Analyst Document Specialist Project Manager: Juvelyn F. Seno Business Analyst: Jennifer V. Quibuyen System Analyst: Khristine T. Escovidal Document Specialist: Jeseca V. Bodollo Lead Programmer: May-ann L. Caguindagan The project team assigned to a position according to the abilities and skills to handle the role appoint to each member. Here are some advantages and disadvantages facing off by the project team. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 115 The advantages are: Easy communication for the proponents. Better distribution of tasking among members. Better understanding about the issues might happen to the team. The disadvantages are: Having a small number of member might bring the financial stability. Hard time to finish the task appoint to the proponents on the set date. Overlapping of tasking assigned to each project member. Initiative, cooperation, and coordination are necessary for each member of the project team. For be able to finish the task that is being needed to the software development. Quality assurance plan helps the proponents to track the errors during the requirements, planning and designing phase. Since the project team does not have any extra personnel to spare, the proponents will invite a member from the client to monitor if the testing is effective, correct, and maintainable for the software development. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 116 2.0 SQA Tasks The following are the task that the proponents used as a guide to have Software Quality Assurance. Contact with the Client Requirements Review Subject Research Universal Design Details 2.1 Task Overview The proponents will describes the tasks that covers the product quality, control, saving design time and cost, minimizing errors and problems and data flow. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 117 2.2 Standard, Practices and Conversation (SPC) Pre-Arrange Method The project team are grouped into Five(5) members. Each member are appointed according to its knowledge and capabilities. But the proponents ensure that the tasks are equally distributed to avoid the unfairness among the members. Each of the members has the suggest, to decide and to lead. Each of the members are given the authority to provide insight, inputs and proposition in order to develop a Vendor Management System. Contact with the client Aside from the initial and follow-up interview, the proponents contact the client if there is a necessary requirements, problems, information and changes regarding to the software development project especially for vendor management system. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 118 Meeting Date Discussions / Subjects Company Time Interview: Company overview and Background. Details of the Company July 7, 2014 Vendor Chesa Bianca Management Restairant 3:00pm 5:00pm Procedures. Initial problem Vendor in Management System. Features and requirement. Research: The proponents go to other Aug Libraries / QCPU BCP Library Universities to find out SB Library 10:am what UP Library 5:00pm are the other Features that may be Q.C Hall Public include in the Vendor Library Management System. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 119 Research: The proponents do Jollibee some Bench Marking McDonalds in Different Restaurant Max’s near the school for Chowking other suggestion of the Mang Inasal client regarding to the Janet’s Vendor Management System. Requirements Review Reviewing the client’s requirements upon the software development is the basic information needed by the proponents. It is the initial guidelines of the proponents to know if the proponents understand the necessities of the software development upon the client’s request. Subject Research Lack of knowledge is the major problems of the proponents when it comes to the vendor management system information. The proponents might do some research, surveys and interviews for be able to gain a Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 120 factual information needed by the proponents to improve VMS. The other references that the proponents can use for the research are the related literature and the project study or the thesis of the other project team done in the past that composed the necessary information needed to fulfill the satisfaction of the proponent’s knowledge about the software development. Universal Design Detail After reviewing the factual information of the proponents regarding to the software development, it gives idea to the project team about the design that can be apply to achieve the design that the proponents wanted to create. 2.3 SQA Resources May or not be applicable as of now. 3.0 Reviews and Audits The Formal Technical Review (FTR) is a software quality assurance activity that is performed by software engineers. The objectives of the FTR are: Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 121 1. To uncover errors in function, logic and implementation for any representation of the software. 2. To verify the software under reviews meets its requirements. 3. To ensure that the software has been represented according to the predefined standards 4. To make the better software manageable, effective, accurate and maintained. 3.1 Generic Review Guidelines 3.1.1 Conducting Reviews Two kinds review will be held, review cases with the client and review cases with the proponents. The project team should agree keep and a good record of the software before and after the change, this change helps to enhance the client’s performance when using the software. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 122 3.1.2 Roles and Responsibilities It consists of the project team members including the roles and responsibilities: Project Manager: Juvelyn F. Seno Business Analyst: Jennifer V. Quibuyen System Analyst: Khristine T. Escovidal Document Specialist: Jeseca V. Bodollo Lead Programmer: May-ann L. Caguindagan 3.1.3 Review Work Product The proponents have a weekly meeting with the adviser, Mr. Andrew U. dela Cruz that guide the project team throughout the project. The adviser is the one who gives feedback about the documentation progress and will also advice or discuss the process of your system development. The adviser can also give some idea that will help the project team to improve the knowledge about the project that is being made. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 123 It is not about the proponents and adviser interactions but it is also about the unity of each project team of every sub-system that is needed to compose the entire Restaurant Management System. Each project team of each sub-system will update each other about the changes and progress happen to the sub-system, assigned to each team. All the past works done of each project team members should be documented in the project timeline. 3.2 Formal Technical Reviews Here are the FTR conducted during the softwaredevelopment process. - Software Inspection - Consultation Each interface that will be designed by the proponents should undergo in testing method. The proponents will set a meeting for the entire member and the client and will conduct an open forum that look for any suggestions and feedbacks. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 124 Description of the Software Inspection Review This is about the developed software if it is correctly, effectively and manageable. It is the integration of the design parts such as interface, forms, and database of the system.it also focuses on the correctness of the parts that will be design. Description of Consultation Consultation refers to the suggestions and feedbacks of the proponents regarding to the software development. If the changes occur, the client and the proponents will scrutinize the change to make. 3.2.1 System Review Specification System specification of VMS is fixed and constant especially to the database which is MS SQL and platform for the software development which is Java Language. For further information regarding the software specification please see the document System specification. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 125 3.2.2 Software Project Plan The purpose of this plan is to look over the entire project. For further explanation regarding to this section please the Project Plan section. 3.2.3 RMMM Review RMMM, is the risk mitigation, monitoring and management which is use as a guide to monitor and to control the risk that may occur to the software. For more information please read the RMMM section in chapter 3. 3.2.4 Requirement Reviews (Models, Specification) This section is composed of the data requirement and specification of the software. Please see the “Software Requirements Specification” 3.2.5 Data Design Review This section is about the data flow between each interface (form) to the database. Data design can be found on the document titled “Software Design Specification”. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 126 3.2.6 Architectural Design Review Architectural design refers to the entire design, layout and dataflow of the software. For more information regarding Architectural Design, please see the section for Architectural Design. 3.2.7 Interface (GUI) Interface is still on the process and not yet finalized. The interface of the Vendor Management System must have resemblance to the other sub-system. This includes the procedures and the process of the VMS as the part of the entire system. The front-end of the software is Java Netbeans Platforms. 3.2.8 Component Design Review VMS is still on the design phase. The project team will be having an integration and online help desk after the software is already finalized and ready for implementation. 3.2.9 Code Review Not yet applicable. 3.2.10 Test Specification Review Please see “Test Specification” but not yet applicable. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 127 3.2.11 Change Control review and Audits Not yet applicable. 3.3 SQA Audits Project team members will have a weekly meeting to their adviser to the report about the past works done for the past week. Any problems, question, regardless to the documentation of the software development will be noted and every tasked done by the proponents will be documented on the project timeline. Any changes that will be happen or occur on the software development must be discussed to the other members of the project team together with the client. Minor or major changes should be consulted to the persons involve in the project development. 4.0 Problems Reporting and Corrective Action/Follow-up This section will describe problem reporting mechanisms that occur as a sequence of the FTRs that are conducted and the means for corrective action and follow-up. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 128 4.1 Report Mechanism As a report mechanism, the proponents used a method of follow-up meetings to inform each member about the progress and changes of the software development. 4.2 Responsibilities Each member of the project team has a corresponding position to handle. Since there is a project manager who is responsible for leading and managing the project team members to make sure that the project flows is into the right direction according to the schedule of each task, it doesn’t mean that all of the decision making process will be made by only one person. Every decision making needed must be decided by all of the member, by this coordination and cooperation is shown. Project Manager: Juvelyn F. Seno Business Analyst: Jennifer V. Quibuyen System Analyst: Khristine T. Escovidal Document Specialist: Jeseca V. Bodollo Lead Programmer: May-ann L. Caguindagan Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 129 4.3 Data Collection and Valuation To properly conduct software quality assurance, data about the software engineering process should be collected, evaluated, and disseminated. Statistical SQA helps to improve the quality of the project and the process itself. During each meeting, the proponents will present a drafted of the possible design of the software to the client. The proponents will undergo a defense that will criticize the project done by the proponents. The client will give an additional idea, suggestion and feedback about the software development. 4.4 Statistical SQA May or may not yet applicable. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 130 5.0 Software Process Improvement Activities Determining the factor for Software Quality and Organizational effectiveness. Franchisor Client Technology Software Development Vendor Management System Process Franchising Organizational Condition Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 131 5.1 Goals and Object of SPI 1. All errors and defects are categorized by its origin. (e.g. flaw in design and system specification, flaws in logic, and non-compliance to the standard) 2. Records the errors and defects of the software. 3. Errors and defects are categorized according its severity. 4. Plans are developed to modify the intent of eliminating or reducing the frequency of the occurrences of errors and defects that is costly. Fields Reason % None of the member have any experience on Logic 30% doing a project in this size, nor the experience on the project in this degree of difficulties This is the area where the user interacts with Interface 25% the software. It is very important to design an interface according to the level of understanding of Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 132 the proponents. This project involved a lot Data handling 15% of data accessing/storing, data flow each between interfaces. It’s not easy to keep track of them. And the queries that the database used are pretty much outdated. The proponents practically proud of this size and the experience that the proponents had Error checking 10% in this field should get a higher error percentage. Since the project team have a very close contact with the client, and have done an exceptional work on research and study the old version. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 133 The proponents believed that the team can keep the field under 10%. Since the proponents have no experience such as degree of project, so Standard 10% other errors might be uncover, but the project team optimist to make a pretty good research on the project, and spent many times on designing phase before any actual coding. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 134 Error Graph 5.2 SPI Tasks and Responsibilities Since the proponents have only 5 members, each members will be having the responsibility of the SPI activities. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 135 6.0 Software Configuration Management and Overview This is about the changes coming from the original plans that are not good enough to meet the development that are needed. Software Configuration Management Plan listed all the changes that are feasible to make the software developed effective. For further information regarding SCM plan please see the document entitled “Software Configuration Management Plan”. 7.0 SQA Tools, Techniques and Methods The proponents will be using software review, logic and coding error tracking, and follow the standard organizational structure, responsibilities, procedures, process and resources for implementing quality management plan. But the truth is, limited time and the project team is results to overlapping of the tasks given to the proponents, still the proponents can finish the task though it is out of the schedule. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 136 VMS SYSTEM SPECIFICATION 1.0 Introduction Vendor Management System (VMS) is a part of Restaurant Management System. The purpose of VMS is to help the entire process of the software. It acts as a mechanism for business to manage and procure staffing services-temporary, and in some cases permanent placement services. It also include order distribution, consolidated billing and significance enhancement in reporting capability that out performs manual systems and processes. 1.1 Goals and Objectives The goal of the VMS is to manage the franchised product of franchisor and the services they deliver in order to ensure the organization gets the best value from each franchisor throughout the lifecycle of the relationship with the franchisor. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 137 1.2 System Statement and Scope This section contains a general description of the software functionality followed by detailed requirements that will be seen throughout the project. Before someone could access the Vendor Management System that the proponent proposed, the designated personnel will be required to enter their username and password. There are a maximum of five (5) persons that can create an account and to serve as the Administrator to use or access the system. Here, the proponent limits the number of persons that can create an account to secure the data and information of the restaurant inside the system. They are the only persons allowed to view, edit and update all the information seen in the system. Each of them can only have three (3) attempts in logging into system. This also covers the security of data and information of the previous transaction done by: - The Branch, their previous transaction will be saved in the database of the stand-alone system in their restaurant. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 138 - The Administrator, the previous successful transaction by every branch they are monitoring will be also saved in the database of the online system. These designated personnel authorized by the system are the only persons who can access the viewing of the data and information’s inside the system. When there is a new franchise that is approved by the Board of Directors, and all things are settled before them and the restaurant will be operating, they have to register in the Vendor management system so they can be part of the monitoring branch. Here, we made the monitoring of every branch easier for the Main office. The branch that would make a borrow request transaction will just have to fill up the transaction form in the stand-alone system in their restaurant and send it to the online system of the Administrator. And the Administrator is responsible to contact other branch to confirm the availability of the product that is borrowing by the other branch. They can also be easily identify the availability of borrowing product in a specific branch because the Vendor Management System is enable to send email to every Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 139 branch for confirmation of the availability of the products. And every system is capable of receiving email coming the Administrator and also sending back email going to Administrator. And every successful transaction between branches will be saved in the database of the system. This monitoring will be more efficient and accurate. Promotion of new Products is a responsibility of the Administrator. Since he is monitoring every branch, he is also responsible to promote the new product of Max’s in each of them. The Administrator is capable of putting all information in the Vendor Management System about the product to be launched as well as its ingredients and process of cooking/making. The Administrator is capable of sending this information’s through internet that can be received by every branch. This process is easier than the process they’re doing before. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 140 The Proponents proposed a Vendor Management System that would help The restaurant in advertising their franchising to the market with use of Internet connection. The Administrator can put information’s about franchising of Restaurant and it will be seen by the internet users, so that interested entrepreneurs can easily be informed about the restaurant franchising. They can also avail a downloadable form than can be fill up and just send via email. This Vendor Management System can be able to generate and print personalize reports. This also answers the problem by the restaurant nowadays. The typographical errors is the main problem of every report of their previous transactions, the transaction are not risky from error because we will be implementing a Vendor Management System with the transaction form that will not be needing any typing. With the use of drop down buttons, Branch managers can choose the forms without doing any typing and making errors from it. The reports will be accurate and easier to monitor. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 141 1.2.1 General Requirements The following below are the general requirements for VMS: A way in which the company could easily generate contract for the vendor (franchisor). A way in which the company can promote the business and products. A way to search an existing facility. To ensure the high quality of products and services offered to the franchisor, according to the technical and qualitative standards based on the market needs. To constantly improve the high quality and characteristics of the products and services offered. Provide products and services that satisfy the customer’s needs, expectations of quality, safety, reliability and services. To establish and manage a constructive relationship with the franchisor. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 142 Interface Enhancement The staff or vendor of the restaurant and vendor management department had requested a lot of interface enhancements that will positively augment the capability of the propose system for the end user. Database Administrative Interface Provides a structure to manage all the vendor information from the portal data to paper bills for all accounts that will manage the changes proactively with interface updates to standardize and centralize into a uniform format for processing reconciling and reporting. Training Vendor management staff are also requested to have a seminars or training to precisely use of the software. 1.3 System Context The database application that the proponents will used is the MSSQL. As a database, it is a software product whose primary product is store and retrieve data as requested by the other software application. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 143 1.4 Major Constraints Time The proponents actually out of the schedule and the time is not enough to fulfill the task assigned to each member because the project team is compose of only 5 members having a lot of task. Cost Financial stability is one of the problems that the proponents can have. The proponents listed all the expenditures that the software development can cost. 2.0 Functional Data Description This section will discuss the overall system function and the information included on this: Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 144 2.1 System Architecture 2.1.1 Architectural Model Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 145 2.1.2 Current Subsystem Overview 2.2 Data Description 2.2.1 Major Data Objects 2.2.2 Relationships Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 146 2.3 Human Interface Description Human interface is the environment where the user can communicate and interact to the software. The front-end of the software is create on the Java Netbeans, the Java Netbeans makes the interfaces more user-friendly, accurate, effectively and maintainable. The interface of VMS is compose of 2 modules which is franchising and catering based on the work breakdown structure developed by the proponents. Franchising This are the following activities that composed of the Process: Franchising Application Qualification Detailed personal information In this section of VMS objectives is including all contact information and other biographical basic information and character background. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 147 Business interests This is a part of franchising qualification that the franchisor want to know if the franchisee have ever owned a business, have been involved in any kind of litigation/arbitration, or have any partners. Location preferences In this section will usually ask for cities/territories you're interested in and any alternates you would consider as well as if you are open to relocation. Detailed Employment history This is the part of objective where the franchisee state their pass worked, what the franchisee did, for how long, and annual compensation. Educational Background This is the part of objective where the franchisees state the other pertinent training/experience. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 148 Personal Financial Statement This is the part of objective where the franchisees is required to state the Assets, liabilities, net worth, source income, and total income. General Inquiry The franchisors will want to know what the franchisees know about them, their franchise opportunity, and why the franchisees are interested. Franchising Interview Transaction selection This is about identifying appropriate acquisition or new development opportunity based on availability. Operation interview It refers to the interview with the respective person in the company, candidate submits business plan for review and approval, determine training requirements Transaction approval Transaction approval refers to the Capitalization Plan and Financial Review. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 149 Final approval Franchisee transactions must result in well capitalized, growth oriented buyer groups which help to optimize, and strengthen the markets they enter. Franchising Terms and Condition Agreement The franchise agreement is essentially a legal document between the franchisor and franchisee. It is a legal binding agreement. It explains in detail what the franchisor expects from franchisee, in the way franchisee operate every facet of the business. There is no standard form of franchise agreement because the terms, conditions, and the methods of operations of various franchises vary widely depending on the type of business. Every franchisee is required to sign the franchise agreement, and the franchisor will also sign the document. Location/Territory The franchise agreement will designate the territory in which you will operate and outline any exclusivity rights you may have. Operations This section details how franchisees are expected to run their units. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 150 Training and Ongoing Support Franchisors offer training and training programs for franchisees and their staff. Training may take place at corporate offices or out in the field. All ongoing administrative and technical support will also be outlined in the agreement. Duration The document will detail the length of the duration of the franchise agreement. Franchise fee/investment There will generally be an upfront initial franchise fee that grants the franchisee the right to use the franchisor's trademark and operating system. Those costs will be clearly outlined. Royalties/ongoing fees In this section the franchisee will find the details of the franchisor's royalty structure. Most franchisors require franchisees to pay An ongoing royalty, usually a percentage of total sales, which is often paid on a monthly basis. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 151 Trademark/patent/signage This section will outline how a franchisee can use the franchisor's trademark, patent, logo and signage. Advertising/marketing The franchisor will reveal its advertising commitment and what fees franchisees are required to pay towards those costs. Renewal rights/termination/cancellation policies The franchise agreement will describe how the franchisee can be renewed or terminated. Some franchisors include an arbitration clause. This requires, in the event of any legal action, that an arbitrator review the case before it goes to court. Exit strategies. Every franchise has its own resale policy The franchise agreement will describe how the franchisee can be renewed or terminated. Some franchisors include an arbitration clause. This requires, in the event of Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 152 any legal action, that an arbitrator review the case before it goes to court. Types of Franchising Single Unit Franchising In a single-unit franchise system, one person buys a store from the main company and operates it according to the company's rules. Operating one store at a time is a good choice for new business owners. Some successful operators of one store eventually buy more stores. Multi Franchising Area Development Area developer franchises allow a business owner to own all franchises within one location. The location can include a city or neighborhood. The franchisee often has to open a certain number of businesses within a specific time period or follow other stipulations set by the parent company or franchisor. Area development contracts typically require development in an area within five years. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 153 Master Franchising The master franchise is a popular way to spread American businesses to international territories. This method allows one entity to find many franchisees in an overseas area. The master franchisor is responsible for training and providing support to the new franchisees within the large area, which can include an entire country. Master franchisers often establish training centers for new franchisees. Franchise Monitoring Adding new Branch All granted franchisees must register to the Vendor Management system (VMS) So that the franchisor main office can monitor their Branch. Branch Profile This section will contains a updating of their file or franchise renewal and borrowing supplies. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 154 3.0 Subsystem Description 3.1 1.0. Subsystem Flow Diagrams Enhanced Interface Prototyping 1.1. Prototyping Requirements The proponents develop a software which is VMS to minimize the process that the Branch Manager experiences. The main goal of the proponents is to make the interface Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 155 more flexible and easy to use for the future users of the software. To create a prototype of VMS, the proponents will be use a Java Programming Language for the front end, particularly to Java Netbeans application which is the specific software to create VMS. Java language is a 4 th generation language which widely uses on creating software, games, apps and applications. Product Version: NetBeans IDE 7.3 (Build 201302132200) Java: 1.7.0_21; Java HotSpot(TM) Client VM 23.21b01 Runtime: Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment 1.7.0_21-b11 System: Windows 7 version 6.1 running on x86; Cp1252; en_US (nb) Another application is MS SQL Server to create the back-end of VMS and serves as the database for the stored information it will acquired. It is a powerful and reliable free data management system that delivers a rich and reliable data store for lightweight Web Sites and desktop applications. Designed for easy deployment and rapid prototyping, this download includes support for System, Microsoft's System Preparation Utility for Microsoft Windows operating system deployment. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 156 VMS SYSTEM REQUIREMNTS SPECIFICATION 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Goals and Objectives The goal of the VMS is to manage the franchised product of franchisor and the services they deliver in order to ensure the organization gets the best value from each franchisor throughout the lifecycle of the relationship with the franchisor. 1.2 System Statement Scope 1.2.1 General Requirements The following below are the general requirements for VMS: A way in which the company could easily generate contract for the vendor (franchisor). A way in which the company can promote the business and products. A way to search an existing facilities. To ensure the high quality of products and services offered to the franchisor, according to the technical and qualitative standards based on the market needs. To constantly improve the high quality and characteristics of the products and services offered. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 157 Provide products and services that satisfy the customer’s needs, expectations of quality, safety, reliability and services. To establish and manage a constructive relationship with the franchisor. Interface Enhancement The staff or vendor of the restaurant and vendor management department had requested a lot of interface enhancements that will positively augment the capability of the propose system for the end user. Database Administrative Interface Provides a structure to manage all the vendor information from the portal data to paper bills for all accounts that will manage the changes proactively with interface updates to standardize and centralize into a uniform format for processing reconciling and reporting. Training Vendor management staff are also requested to have a seminars or training to precisely use of the software. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 158 1.3 System Context The database application that the proponents will used is the MSSQL. As a database, it is a software product whose primary product is store and retrieve data as requested by the other software application. 1.4 Major Constraints Time The proponents actually out of the schedule and the time is not enough to fulfill the task assigned to each member because the project team is compose of only 5 members having a lot of task. Cost Financial stability is one of the problems that the proponents can have. The proponents listed all the expenditures that the software development can cost. 2.0 Functional Data Description This section will discuss the overall system function and the information included in Vendor Management system. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 159 2.0 Usage Scenario 2.1 User Profiles The following definitions describe the levels of the actors in the System. Administrator An Administrator has an ability to handle transaction of every branch regarding the borrowing of the products and supplies. The Administrator has an unrestricted access to the vendor management system including the viewing list of branches, list or the History of transaction of the borrowing request, Contract other branch editing branch information, confirming availability if products and waiting for status confirmation. Also for the administrator can view the reports, sends new product promotion to every branch via email and displays information on the website regarding the happenings in restaurant. The Administrator can also unrestrict to the changing of the password. Branch Manager A Branch Manager has the responsibility to make a transaction on borrowing products and supplies for the continuous operation of the restaurant. A Branch Manager can also view transaction list done by the restaurant and confirm the borrowing status. The branch manager can also restrict to change their username and password. Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 160 2.2 Use-Cases The following use-case is typical interaction between the external environment and the external software system. Each use-case is described in this section. Branch Manager log onto system Borrow Request View Transaction List Confirm borrowing status Receives new product promotions Administrator log onto system View List of branch Edit branch Information View Transaction List Contact every Branch Confirm availability of products and supplies Wait for status confirmation View Reports Send new product promotion Display information on website - Franchising - Advertisement Display transaction list Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 161 3.0 Data Model and Description 3.1 Data Description 3.1.1 Data objects and Dictionary Add User Accounts 1. User_ID: Unique ID number of an employee. 2. User_Lname: Employee’s last name. 3. User_Fname: Employee’s first name. 4. User_Fname: Employee’s middle name. 5. User_Type: Employee’s type of accounts. 6. Username : Employee’s username. 7. Password: Employee’s password use to log in to the system Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 162 Restaurant Management System – Vendor Management System 163