Pathology of extrahepatic billiary tract and pancreas
advertisement

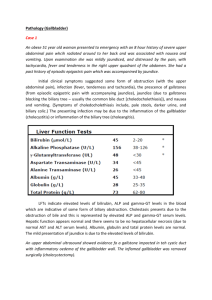
Pathology of extrahepatic biliary tract and pancreas MUDr. Helena Skálová Normal biliary tract Liver produces 1 liter of bile per day Storage of concentrated bile in gallbladder Release after meal Bile ducts are essential Gallbladder is not Pathology of biliary tract Inborn malformations Cholelithiasis Cholecystitis, cholangoitis PBC, PSC Tumors Inborn malformations Atresia of biliary ducts: - narrowing or total closure of the whole lenght of extrahepatic bile ducts or segmetally - ethiopathogenesis variable, often unknown (chromosomal defects, viral infections) - symptoms: cholestatis in days-weeks after birth, progresses to biliary cirrhosis - most frequent cause od death from liver disease in early childhood - therapy: surgery, liver transplantation Cyst of choledochus: - mostly females, up to 10 years old - tumor-like mass - symptoms: asymptomatic, pain, icterus - therapy: surgery Cholesterolosis Strawberry gallbladder Macrophages with cholesterol Clinically insignificant Cholelithiasis Bile stones in biliary tract 10-20% of adults in developed countries Risk factors: age, female, pregnancy, obesity, bile stasis, hyperlipidemia, biliary infection Cholesterol stones Pigment stones Mixed stones Cholesterol stones 80% of bile stones Pathogenesis: - supersaturation of bile with cholesterol - slow motility of gallbladder - nucleation into cystals - aggregation into stones in mucous Yellow - white, transparent Solitary / a few Pigment stones Pathogenesis: - inflammation (↑ acidicity) - hemolysis (overload with bilirubin) Black, hard or brown, soft Factes, multiple Mixed stones Cholesterol core, pigmented surface Solitary / multiple Location Cholecystolithiasis, hepaticolithiasis, choledocholithiasis Cholecystolithiasis Most common 70% asymptomatic Cholecystitis, hydrops Carcinoma of gallbladder No icterus Stools and urine normal ! Choledocholithiasis Intrahepatic cholestasis Obstructive icterus Pale stools Dark urine Bile colic / strong constant pain Long-term → secondary biliary cirrhosis Complications of cholelithiasis Acute / chronic cholecystitis, cholangoitis Hydrops of gallbladder Empyema of gallbladder Decubital ulcers Perforation, peritonitis Fistula to duodenum, colon Biliary ileus Obstructive icterus (conjugated hyperbilirubinemia) Biliary cirrhosis Pancreatitis Carcinoma of gallbladder Acute cholangoitis Suppurative inflammation Infection + stones or tumor May spread to intrahepatic ducts → cholangiogenic abscesses → sepsis Obstructive icterus Therapy: restore bile drainage, atb Chronic cholangoitis Chronic inflammation accompanying obstruction of bile ducts Prominent fibrosis Stenosis Attacks of icterus, sepsis Secondary biliary cirrhosis Acute cholecystitis Calculous (90%): - obstruction of gallbladder neck or ductus cysticus → ischemia, toxic agents from bile → aseptic inflammation → infection (E.coli) - rarely primarily bacterial (Salmonella typhi) - older women Acalculous: - severly ill patients (surgery, trauma, burns …) - ischemia Suppurative (empyema) Decubital necrosis, ulcer Gangrenous Complications: rupture (esp. acalculous), peritonitis Chronic cholecystitis Very common Traumatization by bile stones, repeated mild acute cholecystitis, mild infection Wall thicker (fibrosis, hypertrophy of mucosa) or thinner (atrophy) Mucosa – metaplasia (gastric, intestinal), dysplasia (low / high grade) Hydrops – chronic obstruction, atrophy, fibrosis, clear secretion Porcelain gallbladder – calcified Decubital necrosis RF for carcinoma of gallbladder Symptoms of cholecystitis Acute: Chronic: Sudden onset Milder course Pain Recurrent atacks of steady Signs of sepsis Nausea, vomiting Subsides in 1-10 days Relapses more intensively Therapy: cholecystectomy or colicky pain Nausea, vominting Intolerance for fatty food Therapy: cholecystectomy Icterus – present ONLY if the inflammation spreads to choledochus or common hepatic duct and obstructs them Diseases involving intrahepatic bile ducts Primary biliary cirrhosis Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PBC): (PSC): Autoimmune nonsupurrative destruction of small and medium-sized intrahepatic bile ducts, portal inflammation Etiopathogenesis unknown Association with IBD (70% of patients have UC) Fibrosis, biliary cirrhosis Inflammation and obliterative fibrosis of intra- and extrahepatic larger bile ducts Middle-aged women Dilatation of preserved segments Biliary cirrhosis Middle-aged men Tumors of gallbladder Adenoma: - tubular, vilous, tubulovilous - low / high grade dysplasia Adenocarcinoma: - 7th decade, slightly more women - 80% associated with gallstones (chronic inflammation) - Asia: higher % of pyogenic and parasitic diseases (without gallstones) - infiltrating (scirrhotic) / exophytic - fundus, neck - invades directly into bile ducts, liver, peritoneum, LN - metastases: LN, peritoneum, GIT, lungs - symptoms: similar to cholecystitis - diagnosis: late, after cholecystectomy Adenocarcinoma of extrahepatic bile ducts Uncommon Older age, slightly more men 30% associated with gallstones RF: PSC, UC, choledodal cyst, fluke infection (Asia) Symptoms: painless, progressive jaundice, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, hepatomegaly, palpable gallbladder Diagnosis: early, but tumor is usually not resectable Spreads along bile ducts, metastases in LN Klatskin tumor: - slowly growing sclerotizing tumor from large ducts at liver hilus, rare metastases Carcinoma of the ampula of Vater: - origin may be also in pancreas or duodenum Normal pancreas Exocrine component (80%): - Acinar cells – cca 20 digestive enzymes (trypsin, chymotripsin, aminopeptidases, lipasis, amylasis, fosfolipasis …) - Ductules, dutcs – bicarbonate - Regulation by secretin and cholecystokinin (produced by duodenal mucosa) and n. vagus - 1-3 l of pancreatic juice / day - Protective mechanisms (inactive precursors, inhibitors) Endocrine component: - Langerhans islets (insulin, glucagon, somatostatin) Inborn malformations Agenesis - rare, associated with widespread malformations Pancreas divisum - common, failure of fusion of dorsal and ventral part Annular pancreas - ring around duodenum Ectopic pancreas - common in stomach, duodenum Inborn cysts – solitary, multiple Polycystosis – kidney, liver, pancreas Cystic fibrosis = mucoviscidosis, cystic pancreatofibrosis White rase, incidence in CR 1:2500 AR, mutation in CFTR gene 2-5% of people are heterozygots (carriers) Defective ion (chloride) transportation Highly viscous mucous → obstruction of ducts in exocrine glands → dilatation of terminal ducts and acini (cysts) → atrophy → fibrosis Symptoms of cystic fibrosis Pancreas: malabsorption, steatorrhea, hypovitaminosis, DM (10%) Intestine: meconium ileus in newborns Bile ducts: cholestasis, biliary cirrhosis Salivary, lacrimal glands: xerostomia, xerophtalmia Epidydimis: infertility Skin: salty sweat (diagnostic) Cystic fibrosis in lungs Most severe changes (90% of deaths) Retention of viscous mucous in respiratory tract Squamous metaplasia Chronic bronchitis → bronchiectasias → repeated bronchopneumonia → lung abscesses → fibrosis Staphylococcus aureus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Burkholderia cepacia Cor pulmonale chronicum Cystic fibrosis Therapy: - substitution of pancreatic enzymes - vaccination, atb, NSAID - mucolytics, oxygenotherapy - lung transplantation Prognosis: - without therapy death in childhood - with advanced therapy between 30-40 years Acute pancreatitis Common (Western countries) Etiology: Biliary diseases Alcoholism (exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis) Others: obstruction of pancreatic ducts, drugs, infections, parasites, ischemia, trauma, genetics Types of acute pancreatitis: Intersticial nonsuppurative – accompanies systemic infections (e.g. endemic parotitis) Intersticial suppurative – after hemorrhagic necrotizing, hematogenous Hemorrhagic necrotizing Pathogenesis and morphology of acute hemorrhagic necrotizing pancreatitis Obscure Key role of activation of tripsinogen, which then activates other enzymes Autodigestion – necrosis and liquefaction of pancreas Lipase – fatty tissue necroses Hypocalcemia – precipitation of Ca soaps in fat necroses Elastase – vascular destruction, hemorrhage Coagulative cascade – DIC Enzymes enter blood circulation: - Lipase - fatty tissue necroses in distant sites - Phospholipids – surfactant destruction, ARDS Loss of blood volume, electrolyte disturbance, release of cytokines, vasoactive factors - shock Symptoms of full-blown acute hemorrhagic necrotizing pancreatitis Severe constant abdominal pain, vomiting Rapidly progresses to shock and circulatory failure, DIC, acute tubular necrosis, ARDS Lab: ↑ amylase, lipase in plasma, leucocytosis, hypocalcemia 20% mortality Therapy: total restriction of food and fluid, supportive therapy Consequences in surviving patients: - pancreatic abscess (G- bactieria) - pancreatic pseudocyst - scarring Chronic pancreatitis Etiology: - alcoholism (most common) - chronic obstruction of pancreatic ducts (pseudocyst, concrements, tumor…) - hereditary - autoimmune - tropical (malnutrition, Africa, Asia) - idiopathic Chronic inflammation, fibrosis, duct dilation, destruction of exocrine and much later also endocrine parenchyma Irreversible destruction and decrease of function Chronic pancreatitis - Symptoms: attacks of pain maldigestion jaundice malabsorption, weight loss, hypoalbuminemic edema diabetes mellitus pseudocyst RF for pancreatic carcinoma - Tumors Pseudotumors: - Congenital cyst - Pseudocyst Benign tumors: - Serous cystadenoma Tumors of variable behaviour (low, high grade dysplasia, malignant): - Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN) - Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) Malignant tumors: - Carcinoma Precancerous lesions Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN): - Low grade (PanIN 1) - Intermediate grade (PanIN 2) - High grade (PanIN 3) Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN) Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) Pancreatic carcinoma 6. – 8. decade, slightly more common in black race Association with smoking, chronic pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus High mortality Ductal adenocarcinoma with abundant desmoplastic stroma Symptoms - late: - long-term silent - 60% in head → obstructive jaundice (tail, body without jaundice) - weight loss, weakness, anorexia, cachexia - thrombophlebitis migrans - pain (perineural spread) Metastases: LN, liver, lungs, bones Dif. dg.: chronic pancreatitis Summary: Consequences of cholelithisis Acute cholangitis Biliary cirrhosis Chronic cholangitis Cholelithiasis Acute cholecystitis Chronic cholecystitis Carcinoma of gallbladder Acute pancreatitis Chronic pancreatitis