Chromatography I: Paper - University of North Carolina Wilmington
advertisement

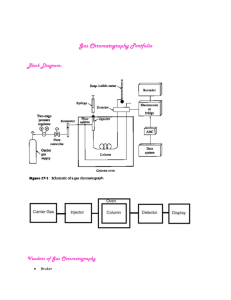
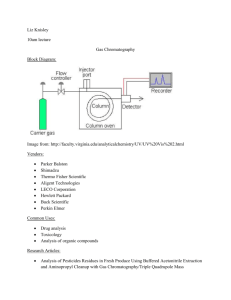
CHM 101/102 Chromatography I: Paper General Chemistry 101/102 Laboratory Manual University of North Carolina at Wilmington Laboratory Manual CHM 101/102 Chromatography I: Paper • Purpose Use the technique of paper chromatography to separate a homogeneous mixture into its individual components. • Safety Considerations Butanol and ammonia (both liquid and vapor) are toxic and are strong skin and eye irritants. Keep the ammonia in the hood and cover all butanol and ammonia solutions. Dispose of butanol in the waste container in the hood. Laboratory Manual CHM 101/102 Chromatography I: Paper • Procedure Place 25 mL of solvent in a 600 mL beaker. Cover the beaker and set it aside. Obtain a piece of chromatography paper and draw a line 1 cm from the bottom with a pencil. Place a small spot of each indicator on the line. 2 mm 1 cm Laboratory Manual 25 mL CHM 101/102 Chromatography I: Paper • Procedure Spot and label each of the four indicators and one of the unknowns. The spots should be about 2 cm apart. When the spots have dried, re-spot each one. 2 cm Laboratory Manual CHM 101/102 Chromatography I: Paper • Procedure When the spots have dried, form the paper into a cylinder with the spots facing out. Staple the edges together being careful to keep them straight and not allowing them to touch. Place the cylinder into the 600 mL beaker and replace the cover. Be sure the cylinder is not touching the sides of the beaker. Laboratory Manual CHM 101/102 Chromatography I: Paper • Procedure Let the chromatogram develop until the solvent is 2 cm from the top of the paper. Remove the chromatogram from the beaker and immediately mark the solvent front with a pencil. Allow the chromatogram to dry before going to the next step. Laboratory Manual CHM 101/102 Chromatography I: Paper • Procedure Take the chromatogram to the hood and lightly mist it with water. Place it in the ammonia chamber. Remove the cylinder from the ammonia chamber and unroll it. Immediately circle the colored regions with a pencil. Laboratory Manual CHM 101/102 Chromatography I: Paper • Procedure Determine the RF values for each colored spot in the knowns and the unknown. RF(a) = a d Use your computed RF values to identify the components of your unknown. Laboratory Manual d c b a