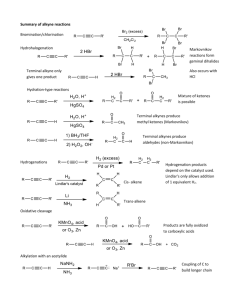
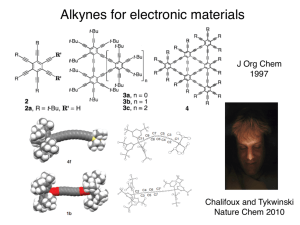
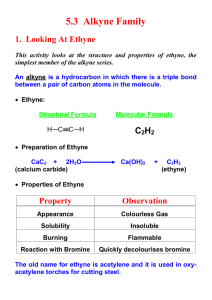
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
advertisement

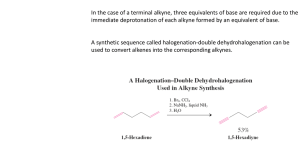
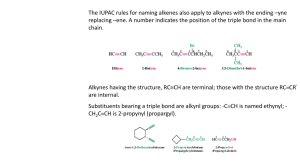
Alkynes I. Nomenclature and Properties A. Naming Alkynes 1) Carbon-Carbon triple bond, CnH2n-2 R C C 2) IUPAC a) Replace the –ene of an alkene with –yne b) Give the number where the triple bond occurs 3) Common Names: derivatives of acetylene CH3 Br H C C H Ethyne (Acetylene) 4) 5) Ethynyl CH3 C C CH3 2-Butyne Dimethylacetylene CH3 C C CHCH2CH3 4-bromo-2-hexyne R H3C C C C H CH3 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne Terminal alkyne has one unsubstituted C, Internal Alkyne does not As a substituent, an alkyne is named alkynyl C C H CH2 C C H 2-propynyl 6) Other examples: CH2 H C C C C H 2-propynylcyclopropane CH2 OH 2-propyn-1-ol trans-1,2-diethynylcyclohexane 7) 8) Molecule with double and triple bond is an alkenyne, C=C lowest # Molecule with triple bond and hydroxyl group is an alkynol OH CH3CH2CH=CH C CH 3-hexen-1-yne B. H2C CHCH2C 1-penten-4-yne CH 5-hexyn-2-ol Properties of Alkynes 1) Bonding a) Carbon-Carbon bond is made of on s (sp-sp) and 2 p bonds b) C—H s-bonds made of Csp and H1s overlap c) d) C-C triple bond DH = 229 kcal/mol (> double or single bond) C-H bond DH is 131 kcal/mol, stronger than alkene or alkane e) f) g) Weak p-bonds are the most reactive area C-C Bond length is shorter than alkene or alkane, as is C-H bond Linear geometry is result of sp hybridization 2) Boiling points are similar to alkenes and alkanes (fairly nonpolar) H C C H 3) Acidity a) Terminal alkynes are much more acidic than alkanes or alkenes b) sp hybridization makes C more electronegative than usual R C C H c) d) e) C. B: R C C Ethyne pKa = 25, ethene = 44, ethane = 50 Bases used to deprotonate alkynes: RMgBr RLi NH3(l) NaNH2 Resulting anion is called an Alkynyl Anion is a good nucleophile Spectroscopy 1) Proton NMR a) Alkynyl H are shielded by p-electron local magnetic field b) This is the opposite effect as seen in alkenes c) Geometry dictates the effect of the local field d) e) f) Local field opposes the NMR field at the H locations: shielded d = 1.7-3.1 for alkyne hydrogens Triple bond does transmit spin-spin coupling well. J = 2-4 Hz H R CH C C H Long Range 4-bond coupling 2) H C C H 71.9 3) 13C NMR a) Alkyne Carbons d = 65-95 ppm (alkenes = 100-150, alkanes = 5-45) b) Examples: H C C CH2CH2CH2CH3 68.6 84.0 18.6 31.1 22.4 14.1 CH3CH2 C C CH2CH3 81.1 15.6 13.2 IR a) C≡C—H = 3260-3330 cm-1 b) C≡C = 2100-2260 cm-1 (weak for internal alkynes) II. Stability of the Triple Bond A. Alkynes are high energy compounds Acetylene (ethyne) torches produce much heat for welding or cutting 2 CO2 + H2O H = -311 kcal/mol H C C H + 2.5 O2 B. Internal Alkynes are most stable 1) Heats of Hydrogenation to alkane a) 1-butyne = -69.9 kcal/mol b) 2-butyne = -65.1 kcal/mol 2) Hyperconjugation makes internal more stable III. Preparations of Alkynes A. Double Elimination 1) Alkenes can be prepared by E2 reactions with alkyl halides H X C C RO- 2) Alkynes can be prepared from a vicinal dihaloalkane base H X RO C C - X H Br CH3CH2CHCH2Br 3) 1. 3 NaNH2, NH3(l) 2. H2O CH3CH2 C C H Details: a. 3 eq. Base needed because alkyne will deprotonate when formed b. H2O re-protonates the alkyne c. NH3(l) boils away when reaction is done (b.p. = -33 oC) d. Stereochemistry of the Intermediate doesn’t matter H X C C X H - B anti elimination H B- X mixed intermediate “alkenyl halide” 2) Halogenation-Double Dehydrohalogenation Alkene to Vicinal Dihaloalkane to Alkyne Br Br2 1. 3 NaNH2, NH3(l) Br 2. H O 2 CCl4 Br B. Br Alkylation of Alkynyl Anions 1) Terminal Alkynes can be made into internal alkynes 2) Alkyl and Alkenyl Metal reagents don’t attack haloalkanes fast enough MgBr 3) + NO REACTION Br Alkynyl Anion can react with haloalkanes CH nBuLi (base) THF, HMPA C- Br SN 2 C HC CH 5) Secondary and Tertiary Haloalkanes give E2 products instead of SN2 a. Alkynyl anion is a strong base b. SN2 Reaction works much better with primary haloalkanes 6) Ethyne can be mono- or disubstituted nBuLi (base) THF, HMPA 7) HC C Br - SN 2 HC C nBuLi (base) THF, HMPA Br C SN 2 Alkynyl Anions can do other Nu reactions as well HC C - + O HC C OH OH CH3C CMgBr + O C CCH3 C