Hypertension
advertisement

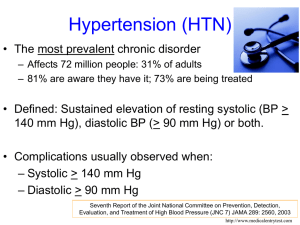
DR.SYED FASIH AHMED HASHMI FCPS HEAD OF CARDIOLOGY DEPARTMENT, LUMHS CARDIOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF LUMHS HTN contributes to all CV comorbidities like: CAD MIs CVA Systolic HF Diastolic HF PVD. Hypertension is the most common primary care diagnosis worldwide. It affects about 1 billion people around the world. HTN is associated with increased total mortality among men and women of all ages and ethnic groups regarless of CVD. Definition: It is a sustained elevation of blood pressure more than 140 mmHg systolic and more than 90 mmHg diastolic. OR The need for antihypertensive medicine. Primary Secondary Also known as essential Hypertension Account to 5% - 10% cases Account to 90% – 95% cases Secondary to other potential rectifiable causes Cause not known •HTN is a complex disease modified by •Genetic and •Environmental factors GENETIC: HTN does not follow classic Mendalian rule of inheritance however variation in the genes that control various components of renin-angiotensinAldosteron system, the kilikerin-kinin system and the sympathetic nervous system are potential causes of HTN. Environmental Factors: Excessive Sodium intake Excessive Alcohol intake Abnormal Renal function Abnormal Vascular function Dysfunction of Renin angiotensin system Insulin resistance There are number of diseases that cause secondary Hypertension: Renal Disease (Account for over 80% of cases) Diabetic nephropathy Chronic glumerulonephritis Adult polycystic disease Chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis Renovascular Disease (Continue) Endocrine Disease Conn’s syndrome Adrenal hyperplasia Acromegaly Pheochromocytoma Drug & Toxins OCPs Corticosteriod NSAIDs Sympathomimetic Vascular Disease Coarctation of aorta Vasculitis Pregnancy Induced Hypertension MRFIT(11.6 yr follow up-361,000 subjects) 40% more deaths in stage 1 HTN! Relationship was stronger for systolic than diastolic HTN Mortality can be decreased by 36% by primary prevention of HTN in general population Mostly asymptomatic, it usually takes several years for high BP to cause noticeable symptoms and even when it does cause problems, the symptoms are often mild and non-specific(i.e, they could be caused by several different conditions) May be Dizziness Blurred or double vision Headache Nose bleeds Flushed face Palpitations SOB BP must be measures in a standardized manner with equipment that meet certification criteria 1. Sits in a chair with back supported and arms bared and supported at heart level 2. refrain from smoking and caffeine 30 min prior to the measurement 3.at least 5 min of rest 4.appropriaate cuff size must be used 5. Hg sphygmomanometer is preferable 6. First appearance of sound is systolic BP the disappearance(and not muffling) of sound is diastolic BP 7. Two or more readings separated by 2 min should be averaged. Blood pressure measurement particularly when performed by a doctor, can cause an unrepresentative surge in blood pressure which is termed as white coat or office hypertension. As many as 20% of patients with apparent hypertension in the clinic may have a normal blood pressure. In such cases automated ambulatory blood pressure(IABP) measurements obtained over 24 hours or longer provides a better profile. Usually unrewarding Fundoscopic Examination Examination of Neck Heart: for rate rhythm increased size precordial heave murmur and S3 and S4 Lungs: ◦ Rales and broncospasm Abdomen; Kidneys and bruits and abnormal aortic pulsation Examination of extremities Neurological Examination to identify known cause of HTN to assess the presence or absence of end organ damage and CV disease ,the extent of the disease and response to therapy to identify other CV risk factors or concomitant disorders that may define prognosis and guide treatment Cardiovascular Ventricular hypertrophy, dysfunction and failure. Arrhythmias Coronary artery disease, Acute MI Arterial aneurysm, dissection, and rupture. CNS Stroke, intracerebral and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cerebral atrophy and dementia Effects On Eye Retinopathy, retinal hemorrhages and impaired vision Vitreous hemorrhage, retinal detachment Neuropathy of nerves leading to extraoccular muscle paralysis and dysfunction Effects On Kidney Glomerular sclerosis leading to impaired kidney function and finally end stage kidney disease Ischemic kidney disease especially when renal artery stenosis is cause of HTN. In all patients, CBC Urine analysis Serum urea and creatinine Serum Electrolytes especially potassium Fasting blood sugar Lipid profile Serum uric acid ECG X-Ray Chest Echocardiography Category SBP (mm Hg) DBP (mm Hg) Optimal <120 80 Normal 120-129 80-84 prehypertension 130-139 85-89 Stage 1 140-159 90-99 Stage 2 ≥160 ≥100 Hypertension Life Style Modification Weight reduction Reduction in alcohol consumption Stop cigarette smoking Salt restriction Avoid stress DASH diet( dietary approach to stop hypertension) It recommends: o more fruits, vegetables, whole grain fruits, lower fat dairy, fish, poultry, nuts, eat less red meat, saturated fats and sweets. Diuretics Beta Blockers Calcium channel blockers ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Alpha adrenergic blockers Mechanism Of Action It is often 1st drug of choice, if diet and exercise changes are not enough Also called the water pills Help body to shed excess sodium and water to lower the BP. Side Effects Deplete body potassium leading to muscle weakness, leg cramps and fatigue Increase blood sugar Erectile dysfunction less common. Mechanism Of Action It act by causing the arteriolar vasodilatation Side Effects Headache Palpitation Peripheral edema Bradycardia Constipation Heart block Mechanism Of Action Act by blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II (a vasoconstrictor) Produce arterial and venous vasodilatation Side Effects Dry cough Skin rashes Dizziness Hyperkalemia Mechanism Of Action It act by relaxing the smooth muscles Decreases the peripheral vascular resistance These are drug of 1st choice if patient has benign prostate hypertrophy along with hypertension because it reduces the symptoms of prostatism. Side Effects Headache Dizziness Fatigue Insomnia Mechanism Of Action Block receptors for angiotensin ARBs takes several weeks to become fully effective Side Effects Insomnia Dizziness Muscle cramps Hyperkalemia Mechanism Of Action Slows the heart rate Inhibit the renin Side Effects Insomnia Dizziness Fatigue Cold hands and feet Erectile dysfunction Patient should return for follow-up and adjustment of medications until the BP goal is reached More frequent visits for stage 2 HTN or with complicating comorbid conditions Serum potassium and creatinine monitored 1-2 times per year After BP at goal and stable, follow up visits at 3 to 6 month intervals Co-morbidities such as Heart failure associated diseases, diabetes, etc need laboratory tests influence the frequency of visits.