Table 4 Treatment-Emergent vital sign abnormalities Older Younger
advertisement

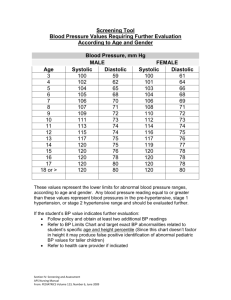
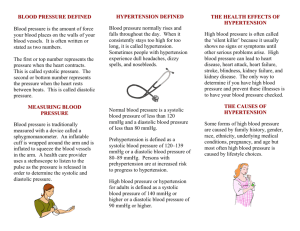
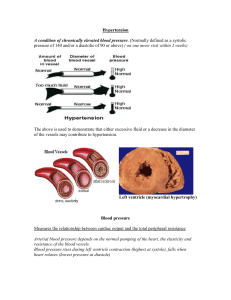
Table 4 Treatment-Emergent vital sign abnormalities Older p values Younger Treatment by age Placebo PCS Weight Duloxetine Placebo Duloxetine group interaction N* n (%) N* n (%) N* n (%) N* n (%) 92 3 (3.3) 102 0 153 0 128 1 (0.8) gain PCS Weight --92 0 102 6 (5.9) 153 1 (0.7) 128 2 (1.6) loss Sustained --84 2 (2.4) 95 1 (1.1) 140 2 (1.4) 121 3 (2.5) .37 82 0 91 0 135 1 (0.4) 116 0 --- 63 2 (3.2) 78 1 (1.3) 124 2 (1.6) 110 3 (2.7) .34 82 8 (9.8) 98 13 (13.3) 150 8 (5.3) 128 13 (10.2) .60 93 0 102 0 152 1 (0.7) 136 0 --- hypertension Diastolic hypertension Systolic hypertension Orthostatic hypotension Orthostatic tachycardia Definitions: N*, number of patients at baseline who were at risk for abnormality. PCS (potentially clinically significant) weight gain is ≥7% increase in body weight. PCS (potentially clinically significant) weight loss is ≥5% decrease in body weight. Diastolic hypertension is sitting diastolic blood pressure ≥ 85 mm Hg and increase from baseline of 10 mm Hg for at least 3 consecutive visits. Systolic hypertension is sitting systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mm Hg and an increase from baseline of 10 mm Hg for at least 3 consecutive visits. Sustained hypertension is having both diastolic and systolic hypertension for at least 3 consecutive visits. Orthostatic hypotension is a decrease of at least 10 mm Hg less than the supine diastolic blood pressure or the standing systolic blood pressure at least 20 mm Hg less than the supine systolic blood pressure. Orthostatic tachycardia is increase of ≥100 beats per minute upon standing.