Ester & Lactone Formation: Synthesis, Sources & Applications
advertisement

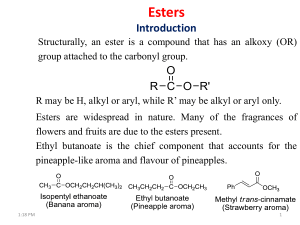
Title Formation of ester and Lactone Objectives Sources of esters Different method for preparation of ester Applications of esters Methods of lactone formation Applications of lactones Sources of ester Ester occur naturally Low molecular weight esters are fairly volatile The characteristic fragrances of many flowers and fruits are primarily due to esters. The aroma of oranges for example, contains 30 different esters along with 10 carboxylic acids 34 alcohols, 34 aldehydes and ketones, and 36 hydrocarbons. Esters of carboxylic acids have pleasant odors and flavors: Preparation of ester Ester can be prepared by following methods: 1. Esterification Carboxylic acids react with alcohols to form esters through a condensation reaction known as esterification. It is also known as Fischer esterification. General reaction Mechanism Examples From acyl chlorides The reaction of acyl chlorides with alcohols is one of the best ways to synthesize an ester. Pyridine is often added to the reaction mixture to react with the HCl that forms. (Pyridine may also react with the acyl chloride to form an acyl pyridinium ion, an intermediate. Mechanism In the conversion of an acyl chloride into an ester, the nucleophilic alcohol attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acyl chloride Examples Applications The chemical industry uses esters for a variety of purposes. Ethyl acetate, is a commonly used solvent. dialkyl phthalates are used as plasticizers to keep polymers from becoming brittle.