Why do Financial Markets Exist Anyway?
advertisement

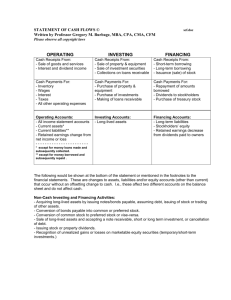
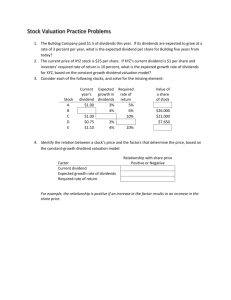
Raising Money to Grow a Business Lesson 2 Issuing Stock How Companies Expand Aim: What are the pros and cons of issuing stock? Do Now: What would be the pros and cons of having a rich retired relative invest a lot in your business and receive half ownership in return? How Companies Expand Do Now answers: 1. Pro: You now have a significant amount of money to grow the business. 2. Con: Your rich relative is now officially an equal owner to you. He or she may not agree with you how to best run the business. Frizzle, Inc. Ice cream and restaurant. Opening new Frizzle’s around the world for the past five years. One of the most popular ice cream restaurants in the United States and Europe. 20% market share. 25,000 employees in multiple locations in the United States and Europe. Headquartered in New York, NY. Looking to expand to China or Russia. Needs $500 million in order to expand. Financial statements indicate a healthy, profitable company. Issuing Stock (aka Equity) What is (common) stock? An investment representing ownership Each unit is known as a share. Stockholders gain more ownership as they buy more shares The more stock a company issues, the less ownership percentage the founders will retain Easy to buy shares once a company “goes public” (ie: sells its shares to the outsiders for the first time) Stockholders Shares of stock Cash Company Cash Shares of stock Benefits of Owning Stock 1. As mentioned earlier, the right to vote for members of the Board of Directors 2. The right to receive dividends (discussed next) if the Board believes the company can afford to pay them. 3. Of course, to profit if the share price goes up! Issuing Stock Dividends Portion of company profit distributed to stockholders because its not needed When companies are secure and stable, they usually pay dividends Board of Issuer, or Frizzle, Inc., can elect not to pay dividends, especially when it is in expansion mode Timing and the amount of the dividends are uncertain, although once a company begins paying a dividend, it likes to continue paying it Issuing Stock Stock Cash Flow Dividend 0 Dividend 1 Dividend 2 Dividend 3 Dividend 4 5 Perpetuity Year Perpetuity – A constant stream of identical cash flows with no end Issuing Stock Stock Cash Flow (continued) Dividends may be received in perpetuity (ie: never end) because stock does not have an expiration date! Because there’s no end, the company doesn’t ever pay the shareholder back for his or her stock. When the shareholder no longer wants to own it, he or she sells it to another investor to receive the “final cash flow”, so to speak. Downsides of Owning Stock If a company fails and must sell (ie: liquidate) its assets, common stockholders are the last to get their investment back. $ $of$Company “X” $ $ Liquidation $ $ $ $ Bondholders and those who have loaned the company money are entitled to be paid back everything before common shareholders get anything! Common stockholders are also known as “residual” owners, because they only get what’s left after all debts have been paid! Issuing Stock Liquidate When a company sells all of its assets in the process of going out of business. It tries to get as much as possible so it can pay back its investors Issuing Stock (vs. Borrowing) Advantages Disadvantages Company can raise a lot of money from external investors Money does not have to be paid back Company won’t have to borrow money from the bank and pay back at a high interest rate Founders are giving up some control by sharing ownership of company (and the right to profits) with other stockholders This effect is called dilution because the founders’ ownership is watered down with each new share sold to other investors The Best of Both Worlds? Common stock and Bonds have their advantages and disadvantages from the both the issuer’s side and the investor’s side. What to do? Create an investment that has some of the traists of common stock and some of bonds Because it takes from both, it’s known as a hybrid security Its name is Preferred Stock While every publicly traded company has common stock, most do not offer preferred stock Preferred Stock Equity in a corporation, to a limited degree Little or no voice in the decisions of how a company should be managed because there are no voting rights Get paid fixed dividends that will not increase even if company profits are increasing and the common stock dividend has been increased Company must pay the preferred stockholders their dividend first before common stockholders If a company liquidates, they are the first of the stockholders to get their money back The Complete Liquidation Payback Order Liquidation of Company “X” that has previously issued bonds, preferred stock $ $ stock $ $ $ $ $ $ and$common 1st Bondholders 2nd Preferred Stockholders 3rd Stockholders Lesson Summary 1 of 2 1. What is another name for ownership? (Hint: begins with E) 2. What do we call a unit of ownership? 3. What do we call the first time a company issues stock to outside investors? 4. What are the major benefits of owning stock? 5. What do we call the effect of ownership being watered down as a company raises money by issuing new shares to the investing public? Lesson Summary 2 of 2 6. What do company founders risks when the company sells new shares to the investing public? 7. What do we call the selling of assets as part of going out of business? 8. What type of investment has traits of both common stock and bonds? 9. What are the pros and cons of issuing stock? Web Challenge #1 • Challenge: Research three companies that are planning to go public. Answer: – How long have they been in business? – Are they currently making profits? – Which investment bank is in charge of the Initial Public Offering (IPO)? – How much money does the company intend to raise? Web Challenge #2 Q: How much can an investor benefit from receiving dividends? • A: A lot! Some companies pay sizable dividends when compared to the price of the stock (which is what investors must pay for the right to receive the dividend). • Challenge: Search using “dividend growers” or “rising dividends” for three companies that have raised their dividends year after year. How much have they risen? Which company holds the record for most consecutive increases? Web Challenge #3 • Challenge: Some company founders are very interested in raising money and also keeping control of their businesses. Two such companies are Facebook and Google. Research what each company did when issuing shares and raising money to ensure that the founders would retain control!