Financial Management – Evaluating Assets
advertisement

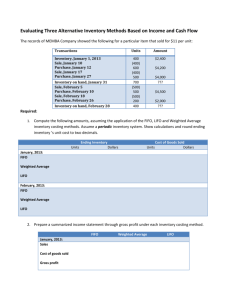
Financial Management – Evaluating Assets Předmět Tematická oblast Autor Škola Anglický jazyk Odborná angličtina - obchodní, ekonomická a ICT Ing. Stanislav Kindl, MBA Hotelová škola, Obchodní akademie a Střední průmyslová škola, Teplice, Benešovo náměstí 1, příspěvková organizace Kód VY_32_INOVACE_JAA_849 Datum 21.01.2013 Zadání: Pracujte s textem a připravenými úkoly či otázkami. Podtrhněte si neznámé pojmy. Financial Management Course IV 1 Financial Management IV – Evaluating Assets TASK 1 – Open your Financial Accounting PDF and read “Reporting on Business Activities” up to page 1-12 ending with IFRS Insight : Balance Sheet Presentation and IFRS. Do you have any questions to the reading? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Pay extra attention to page 1-11 and study the exhibit “Relative Proportion of Short-Term and Long-Term Assets”. Why do you believe are we witnesses of such a variance of assets structure? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ TASK 2 – Please, have a look at the balance sheet on page 2. What can you tell me about the asset structure? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Financial Management Course IV 2 And what would you say to the year-on-year development? What drives the Total Assets in 2010? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ TASK 3 – Regarding the balance sheet above, try to fill in the missing words in the text to make it a meaningful comment of the MicroDrive’s Inc. assets. Cash, short-term investments, __________, and inventories are listed as __________ assets because MicroDrive is expected to convert them into __________ within a __________. All assets are stated in dollars, but only __________ represents actual money that can be spent. Some marketable securities __________ very soon, and these can be converted quickly into cash at prices close to their __________ values. Such __________ are called “cash equivalents” and are included with cash. Therefore, MicroDrive could write checks for a total of $__________. Other types of marketable securities have a longer time until maturity, and their market values are __________ predictable. These securities are classified as “__________ investments”. When MicroDrive sells its products to a customer but doesn’t demand immediate __________, the customer then has an obligation called an “account __________”. The $375 million shown in account receivable is the amount of sales for which MicroDrive has not yet been __________. Inventories show the dollars MicroDrive has invested in raw __________, work-in-process, and finished goods available for sale. MicroDrive uses the FIFO (first-in, first-out) method to Financial Management Course IV 3 determine the inventory value shown on its balance sheet ($__________ million). It could have used the LIFO (last-in, last-out) method. During a period of raising prices, by taking out old, low-cost inventory and leaving in new, high-cost items, FIFO will produce a higher balance sheet inventory value but a lower cost of __________ sold on the income statement. [This is strictly used for accounting purposed; companies actually use older items first.] Because MicroDrives uses FIFO and because inflation has been occurring: (1) its balance sheet __________ are higher than they would have been had it used LIFO, (2) its cost of goods sold is lower than it would have been under LIFO, and (3) its reported __________ are therefore higher. In MicroDrive’s case, if the company had elected to switch to LIFO, then its balance sheet would have inventories of $585 million rather than $__________; and its earnings would have been reduced by $18 million. Thus, the inventory valuation method can have a significant effect on financial statements. Rather than treat the entire purchase price of a long-term asset as an expense in the purchase year, accountants “spread” the purchase cost over the asset’s useful __________. The amount they charge each year is called the __________ expense. Some companies report an amount called “gross plant and equipment”, which is the total cost of the longterm assets they have in place, and another amount called “accumulated depreciation”, which is the total amount of depreciation that has been charged on those assets. Some companies, such as MicroDrive, report only __________ plant and equipment, which is gross value less depreciation. TASK 4 – Make sure you understand both the FIFO and LIFO methods. What is the key difference? And what other methods might be applied in accounting? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ Hint: Use additional reading; e.g. http://amgstr.blogspot.com/2009/05/lifo-and-fifofundamentals-of.html - Will you be able to describe the graphs? Hint 2: Concerning the inventory accounting methods, I would highly recommend you to read the following text. http://financial-education.com/2007/03/05/inventory-accountingmethods-lifo-fifo-weighted-average-and-specific-identification/ Do you have any questions to FIFO, LIFO, or WA? [Note: We will not talk about SI.] Financial Management Course IV 4 TASK 5 - News This time, I wish you discussed the following item. What are the key expectations for the Czech economy in 2012? And what factors may determine whether the forecasts come true? What is your view of the national 2012 economy? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ CZECH ECONOMY TO STAGNATE IN 2012 Employers associations expect the Czech economy to stagnate in 2012. “Czech GDP will not grow by more than one percent, while unemployment will rise moderately and real wages will decrease, Milan Mostýn, spokesman of the Czech Confederation of Industry said. Key issues for Czech firms will be the development of the German economy, a solution to the debt crisis in the euro-zone and the willingness of banks when it comes financing companies.. "Our basic scenario counts with a slow-down of economic growth to a rate of 0.3 to 0.8 percent year-on-year," Mostýn stated. "Nevertheless, recent economic indicators as well as the unresolved debt crisis in the eurozone force us to prepare also for a negative growth rate of between zero and minus one percent at least. And we are not even taking into account possible developments towards an increasing instability in the euro zone," Mostýn added. Further will the economic development contribute to a rise of unemployment. "Our estimates move between 7 and 7.5 percent with an upward risk," Mostýn said. The Confederation of Industries also expects2012 also a fall in real wages, especially in companies without signed tariff agreements, he remarked. Agreements on wage growth in the order of several percent were signed in many companies at the turn of 2009 and 2010 when the economy grew quite dynamically. However, the agreed growth between 3 and 6 percent is now quite unrealistic. This concerns many large companies, Mostýn added. Chances of diverting the 2012 slow-down of the Czech economy are small: "The source of our problems is not in the Czech Republic and we can divert them only partly. Lower volume of orders will cause troubles and signals are already appearing that banks will start to reduce access to loans," Mostyn said. Financial Management Course IV 5