Evaluating Three Alternative Inventory Methods Based on Income
advertisement

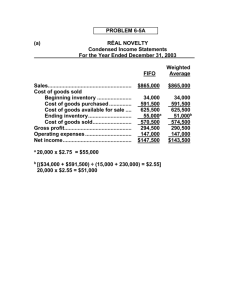
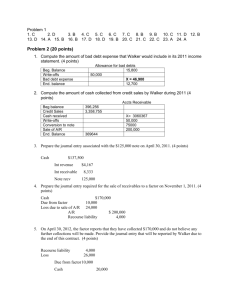
Evaluating Three Alternative Inventory Methods Based on Income and Cash Flow The records of MEMBA Company showed the following for a particular item that sold for $11 per unit: Transactions Units Amount Inventory, January 1, 2013 Sale, January 10 Purchase, January 12 Sale, January 17 Purchase, January 27 400 (400) 600 (400) 500 700 (500) 500 (500) 200 400 $2,400 Inventory on hand, January 31 Sale, February 5 Purchase, February 10 Sale, February 18 Purchase, February 26 Inventory on hand, February 28 $4,200 $4,000 ??? $4,500 $2,000 ??? Required: 1. Compute the following amounts, assuming the application of the FIFO, LIFO and Weighted Average inventory costing methods. Assume a periodic inventory system. Show calculations and round ending inventory ‘s unit cost to two decimals. Ending Inventory Units Dollars Cost of Goods Sold Units Dollars January, 2013: FIFO Weighted Average LIFO February, 2013: FIFO Weighted Average LIFO 2. Prepare a summarized income statement through gross profit under each inventory costing method. FIFO January, 2013: Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit Weighted Average LIFO February, 2013: Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit 3. Of FIFO and LIFO, which method would result in the higher pretax income? Explain. 4. Of FIFO and LIFO, which method would result in the lower income tax expense? Explain, assuming a 20% average tax rate. 5. Of FIFO and LIFO, which method would produce the more favorable cash position? Explain. 6. Compute the following amounts, assuming the application of the FIFO or LIFO inventory costing methods. Assume a perpetual inventory system. Show calculations and round ending inventory ‘s unit cost to two decimals. Ending Inventory Units Dollars Cost of Goods Sold Units Dollars January, 2013: FIFO LIFO February, 2013: FIFO LIFO 7. Prepare a summarized perpetual income statement through gross profit for each inventory method. FIFO January, 2013: Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit February, 2013: Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit LIFO