Componential analysis
advertisement

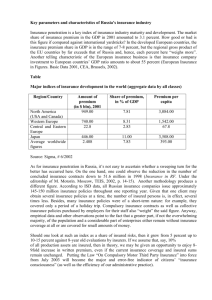
Term lesson 19 Componential analysis applied to terminology Terminology method componential analysis • a method of semantic analysis • modelled on phonology – isolating the smallest units • phonology : the phoneme (or phonetic feature) • semantics : the seme (or semantic feature) pioneered by POTTIER B. (1992), Sémantique générale. PUF Componential analysis for siège meuble pour s’asseoir accoudoirs dossier pour une personne chaise + - + + fauteuil + + + + canapé + + + - tabouret + - - + implications • Each semantic feature is made explicit • by presence (+) or absence (-) • The difference in meaning between words can be expressed by these features thus • Chair is a piece of furniture to sit on [the shared feature for all the words in the group] with a back, without arms and for one person [distinctive features] • Stool is a piece of furniture to sit on without a back or arms for one person etc… Problems? • language specific – can chairs have arms in English? • only works for certain semantic fields – footware, means of transport, etc. • therefore not a very comprehensive method of semantic analysis • but particularly appropriate for regulated fields (i.e. certain terminologies) Using componential analysis for terminology • Certain fields of terminology can be adequatedly analysed using componential analysis – Manufactured items – Tertiary fields where categories are often implicit • such as insurance Example: analysing the classes of life insurance • extract from a textbook used for first-year students in insurance in Australia Elements of Law and Insurance, Australian Insurance Institute Insurances of the Person There are three main types of cover which insure a person as distinct from a person's property. In principle, these types of insurance provide benefits in the advent of a person's retirement, death or loss of income resulting from an accident or illness. More specifically, the covers are as follows. Life Insurance The most basic contracts are: … “ Whole of life insurance • The policy benefits of whole of life insurance are payable on the death of the life insured whenever this occurs. Premiums are payable for the entire life or, upon payment of an extra premium. Premiums may cease at say 60 or 65 years, the age of retirement [sic]. Endowment insurance • This is a combination of term insurance and pure endowment, the policy proceeds being payable upon the death of the life insured within the specified period, or at the end of that period, say ten, 15, 20, 25 or 30 years, if the life insured survives until the end of the period. Pure endowment insurance • This is the same as endowment insurance except that no death cover is provided. In the event of the death of the person insured before the policy term expires there is usually a refund of premiums with interest. This cover is normally used for people who are not medically acceptable for a cover which includes death. Term insurance • Under a term insurance policy the benefits are payable upon the death of the life insured, provided that death occurs within a specified period. If the life insured survives to the end of the period the cover ceases and no benefits are payable. Confused…? • Each definition is drafted differently • Understanding one definition may depend on having understood the others • Which information is necessary to understand the difference between the four sorts of life insurance listed? • Which can be considered ‘background’ information? Solution ? • Componential analysis is your friend! – Extract each feature from the definitions – Find the common feature (which will be the hyperonym) – Find all the other features – Determine by comparison which are defining features and which are redundant. Features of term insurance • Under a term insurance policy the benefits are payable upon the death of the life insured, provided that death occurs within a specified period. If the life insured survives to the end of the period the cover ceases and no benefits are payable. – semes/features: • • • • a life insurance policy benefits payable on death of insured death must occur within specified period if not, no benefits! Features of whole of life insurance • The policy benefits of whole of life insurance are payable on the death of the life insured whenever this occurs. Premiums are payable for the entire life or, upon payment of an extra premium, premiums may cease at say 60 or 65 years, the age of retirement. – semes/features • a life insurance policy ? (not stated explicitly) • • • • benefits payable on death of insured death can occur at any time therefore there is always a payment of benefits age(s) when paying premiums may cease with componential analysis LifeA death spec p + Whole + Pure E + Endowm+ Term + + +/- + + +/- insured alive ? + +/- premiums medical ? ? Definitions derived from the table • Term insurance – life insurance (policy) which pays benefits on the death of the insured within a specified period endowment • life insurance which pays benefits if the assured dies within a set period or at the end of the same period if the insured is still alive pure endowment • life insurance which provides benefits at the end of a specified period, provided the insured is still alive whole of life • life insurance (policy) which pays benefits on the death of the insured, whenever this occurs Componential analysis • helps us to – understand the relations between concepts – identify additional information necessary to distinguish concepts – draft immediately comparable definitions – identify other features which may be relevant in other contexts • Eg. how and when premiums are paid for whole of life insurance Applying componential analysis to Whole of life insurance • Whole life insurance offers the policyholder a cash value account and tax-deferred cash accumulation and pays a death benefit directly to the named beneficiary. The policy is in effect during the lifetime of the insured and provides permanent security for all your dependents while building a cash value account. […] • There are several different types of whole policies. They are as follows: Single premium whole life • Single premium whole life policy is when the policyholder pays whole life premium in one lump sum. The only benefit to this policy is tax advantages. The regular life policy grows in response to the interest rate and the growth is then tax deferred. If a client wants to shelter some money and would want death benefits, the single premium would be an excellent choice. Continuous premium life Continuous premium life (aka straight life) policy is the most common whole life policies. This policy accumulates in cash value and provides lifetime protection with level premium payments up to the age of 100. This policy offers the lowest regular premium cost among the permanent policies. Limited pay • Limited-Pay policies are paid over a limited period of time. Each type of plan is named after the terms of the payment period (i.e., "20-Pay Life," or "Life Paid-up at 65"). The payment amounts are determined according to length of the payment period. In addition, the insurer must pay the full, insured amount to the beneficiary in the event that the policyholder dies, even if the insured has only made one payment to the policy. Current Assumption Whole Life Current Assumption Whole Life (aka Interest Sensitive Whole Life) premium payments fluctuate according to the current interest rates. The premiums are adjusted upon renewal of the policy. Preparing the analysis 1. All the forms of whole of life insurance inherit all the features of the hyperonym. 2. The sub-classes all have additional features. 3. Certain features distinguish the various sub-classes. 4. These features should be expressed as present or absent. Distinguishing feature • the premium – Sum paid by the policyholder to the insurer in return for cover Two features relative to the premium are mentioned… which ones ? When the premium is paid • in a lump sum • over the whole of the life • over a set period Is the premium constant or variable? for • single premium • continuous premium • limited pay – the premium is constant for • current assumption – the premium is variable Whole of life - features WoL lumpS WoL SetP single + continuous + limited p + current a + + - + +? + rate C + + - definitions • single premium whole life insurance – whole of life insurance for which the premium is paid in one lump sum • continuous premium whole life insurance – whole of life insurance for which the premium is paid over the whole period (or until the age of 100) • limited pay insurance – whole of life insurance for which the premium is paid over a period defined in the policy • current assumption insurance – whole of life insurance for which the rate of the premium is indexed on interest rates