HSP3M Introduction to Anthropology, Psychology & Sociology
advertisement

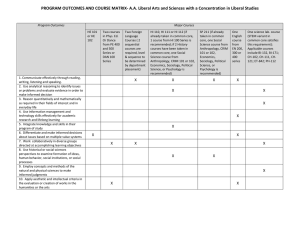
All truths are easy to understand once they are discovered; the point is to discover them. Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642) - Social sciences are disciplines that use research and analysis to examine human behaviour - To understand human behaviour social scientists: - Collect and analyze “statistics” - Conduct experiments - Examine the writings and creations of humans - Social sciences consist of a variety of different areas of study including: - Anthropology Economics Geography History Politics Psychology Sociology Why study the social sciences? • We can understand the basis of human behaviour and various links and relationships • For example: – By studying history, we can understand the relationships between Aboriginals and nonAboriginals – By studying economics, we can understand the connection between lower taxes and job creation – By studying geography we can balance economics with protecting the environment Anthropology • Anthropology is the study of the customs and culture of humans • Anthropology consists of several subdisciplines such as: – Linguistics – Cultural anthropology – Physical anthropology – Archaeology Psychology • Psychology is the systematic study of people’s thoughts, feelings and behaviour • There are several fields of psychological study including: – Cognitive Psychology studies how people perceive & deal with their environment & how they learn, remember & forget – Behavioural Psychology studies how to predict and control human behaviour Sociology • Sociology is the scientific study of the development, structure & functioning of human society • Sociology studies how groups of people who share common characteristics function Critics of Social Science ‘The only possible conclusion the social sciences can draw is: some do, some don’t’ Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) • Their primary problem is that many of the social sciences are deemed “soft sciences” since they do not always rely on strict scientific methodology or rigorous, repeated data. Example • Think back to a time when a friend with a problem came to you for advice, and then later on, another friend came to with you the same problem. Did you give the same advice? Well, maybe so, maybe not…it probably depended on the friend right? Response • Most social scientists would argue that humans (and their problems) are too complex to boil down to a single, simple solution, and so variation is necessary. • Moreover, many of the social sciences do employ quantitative and qualitative research and data collection strategies, as well as an adoption of the scientific method. Other Criticisms… • Another criticism is that the social sciences are more heavily influenced by of-themoment political agendas and societal pressures and influences. However... • Social science attempts to understand ourselves. As with any theory, sometimes there is success, oftentimes there is not, and occasionally the search yields unconsidered questions. Discussion... 1) What area of the Social Sciences (Anthropology, Psychology, and Sociology) do you know the most about and which do you know the least about? Discussion… 2) Briefly share what you know. Is Ernest Rutherford correct in his criticism of the social sciences? Why / Why not? Discussion… 3) What are the top 3 social science based questions you would want answers to? Unit 1 Vocabulary List • • • • • • Social Sciences Statistics Anthropology Psychology Sociology Culture