Sociology Unit 1
advertisement

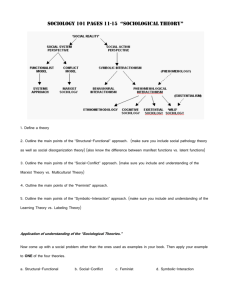
Sociology Unit 1 Sociological Perspective Vocabulary Sociology • Definition: – Social science that studies human society and social behavior. Social Interaction • Definition: – How people relate to one another and influence each other’s behavior. Society • Definition: – A group of mutually interdependent people who have organized in such a way as to share a common culture and have a feeling of unity. Sociological Perspective • Definition: – A viewing of the behavior of groups in systematic ways. Social Sciences • Definition: – Related disciplines that study various aspects of human social behavior. Class Conflict • Definition: – Conflict between entire classes over the distribution of a society’s wealth and power. Auguste Comte • Definition: – Considered the father of sociology. He proposed using the scientific method to study society. Herbert Spencer • Definition: – Used Darwin’s theory of evolution to describe the nature of society. He believed the best aspects of society, and the fittest societies, would survive over time (“survival of the fittest”). Karl Marx • Definition: – German sociologist who believed that the structure of society is influenced by how its economy is organized. He felt that conflict is the primary cause of social change. Emile Durkheim • Definition: • French sociologist interested in the functions of different elements of society in maintaining social order Max Weber • Definition – German sociologist interested in groups within society and the effect of society on the individual. positivism • Definition: – Used by Auguste Comte, it is the idea of applying the scientific method to the social world. Structural-functional approach • Definition: – A framework for building theory that sees society as a complex system whose parts work together to promote solidarity and stability. Social-conflict approach • Definition: – A framework for building theory that sees society as an arena of inequality that generates conflict and change. Symbolic-interaction approach • Definition: – A framework for building theory that sees society as the product of the everyday interactions of individuals Gender-conflict approach • Definition: – A point of view that focuses on inequality and conflict between men and women Race-conflict approach • Definition: – A point of view that focuses on inequality and conflict between people of different racial and ethnic categories.