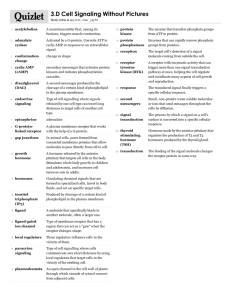
CELL SIGNALLING HW AP BIOLOGY DR WEINER Multiple Choice
advertisement

CELL SIGNALLING HW AP BIOLOGY DR WEINER Multiple Choice (7 pt) 1. Receptor protein activation occurs when a. ADP is phosphorylated to ATP b. ATP is converted to cAMP c. There is a conformational change in the rector protein d. The receptor protein binds to a second messenger 2. A consequence of a signaling cascade is that it a. Supplies energy to the cell b. Accelerates mRNA activity c. Is less susceptible to the impact of mutations d. Amplifies the signaling response 3. Which of the following is a likely explanation of why natural selection favored the evolution of signals for sexual reproduction? a. Even in the simplest organisms, sexual reproduction requires several coordinated responses by cells b. Multicellular eukaryotes required signals that were responded to by multiple organ systems. c. Cells of several different mating types needed to sort themselves to allow for self recognition d. Rooted plants required chemical diffusible signals that could travel throughout the organism 4. When a neuron responds to a particular neurotransmitter by opening gated ion channels, the neurotransmitter is serving which part of the signaling athwy? a. A receptor b. A relay molecule c. A signal molecule d. A transducer 5. Because most receptors are membrane bound proteins, which of the following is usually true? a. They lead to changes in intracellular ion concentrations b. They open and close in response to protein signals c. They are only attached to one membrane surface, either interior or exterior d. They change their conformation after binding with signal molecules 6. Since steroid hormone receptors are located intracellularly, which of the following is true? a. The steroid/receptor complex can cross the nuclear membrane b. The unbound steroid receptors are quickly recycled by lysosomes c. The concentration of steroid receptors must be relatively high in most cells d. The receptor molecules are free to move in and out of most organelles 7. Paracrine signaling a. involves secreting cells acting on nearby target cells by discharging a local regulator into the extracellular fluid. b. requires nerve cells to release a neurotransmitter into the synapse. c. has been found in plants but not animals. d. involves mating factors attaching to target cells and causing production of new paracrine cells. 8. From the perspective of the cell receiving the message, the three stages of cell signaling are a. the paracrine, local, and synaptic stages. b. signal reception, signal transduction, and cellular response. c. signal reception, nucleus disintegration, and new cell generation. d. signal reception, cellular response, and cell division. 9. 9. The process of transduction usually begins a. when the chemical signal is released from the alpha cell. b. when the signal molecule changes the receptor protein in some way. c. after the target cell divides. d. when the hormone is released from the gland into the blood. 10. Synaptic signaling between adjacent neurons is like hormone signaling in which of the following ways? a. It sends its signal molecules through the blood. b. It sends its signal molecules quite a distance. c. It requires calcium ions. d. It requires binding of a signaling molecule to a receptor. 11. At puberty, an adolescent female body changes in both structure and function of several organ systems, primarily under the influence of changing concentrations of estrogens and other steroid hormones. How can one hormone, such as estrogen, mediate so many effects? a. Estrogen is produced in very large concentration and therefore diffuses widely b. Estrogen has specific receptors in different cell types, but each cell responds in the same way c. Estrogen is kept away from the surface of any cells not able to bind it at its surface d. Estrogen binds to specific receptors inside many kinds of cells, each of which has a different response Short answer (25 pts) 1. The following diagrams represent the actions of the 4 major kinds of signaling pathways. Ligand gated ion channel G protein Tyrosine kinase Intracellular a. For EACH describe how the receptor protein is activated and the signal transduction pathway b. Although there are differences among the mechanisms of receptor protein actions, two aspects of their activity are the same. In a few sentences describe the two aspects of their mechanisms that are the same