cell-cell interaction notes
advertisement

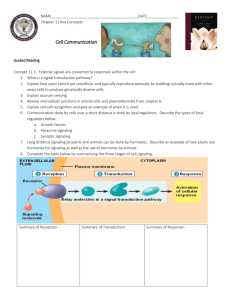
CELL -CELL INTERACTIONS CH 11 Explain why this is the result of cell to cell communication What characteristics are noted about cell communication here ? I. Evolution of Cell Communication • Bacteria communicate with each other in order to respond to environmental changes • The mechanism of cell communication is similar in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes: • o Signal molecule secreted by one cell binds to receptor on target cell • o Target cell responds • what does this tell us about the evolution of cell communication? . II. How cells communicate with each other A. Local signaling: Direct contact and cell-cell recognition B. Local signaling using local regulators: paracrine and synaptic signaling • Signal molecules only travel short distances C. Long distance signaling: endocrine signaling • Involves hormones • What characteristics are fundamentally the same in cell communication across the domains? • What allows a cell to respond to a signal? III. The transmission of a signal from one cell to another: A. The 3 stages of cell signaling: • Reception: • Transduction: • Response: Identify similarities and differences in these 2 modes of cell communication B. Reception • signal molecule binds to receptor causing it to change shape and become activated • this binding is specific 1. cell surface receptors: • hydrophilic signal molecules bind to receptors that span the cell membrane 2. If it a steroid hormone (lipid soluble): • Steroid diffuses across phospholipid bilayer, binds to its receptor in the cytoplasm, and travels to nucleus and either increases or decreases expression of certain genes http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470 /student_view0/chapter18 /animation__mechanism_ of_steroid_hormone_actio n__quiz_1_.html C. Signal Transduction :usually involves multiple steps • Identify the 3 stages of cell signaling in this diagram • What is happening during transduction? • Binding of signal activates receptor • the receptor activates another protein, which activates another, and so on, until the protein producing the response is activated • Multistep pathways can amplify a signal: A few molecules can produce a large cellular response http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter7/animations.ht ml D. Response: • Ultimately, a signal transduction pathway leads to regulation of one or more cellular activities • The response may activate transcription •The response may occur in cytoplasm