AP Biology Chapter 11 Study Questions “Cell Signaling”
advertisement

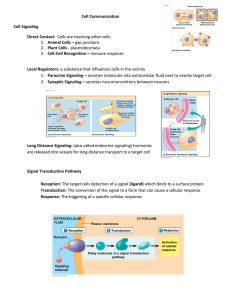
AP Biology Chapter 11 Study Questions “Cell Signaling” 1. List and briefly define the three stages of cell signaling. 2. Define local regulation and explain why hormones are not local regulators. 3. Describe how plant and animal hormones travel to target cells. 4. Describe a ligand-receptor interaction and state how such interactions initiate a signal-transduction system. 5. State where signal receptors may be located in target cells. 6. Compare and contrast G-protein linked receptors,tyrosine-kinase receptors and ligandgated ion channels. 7. Describe two advantages of using a multistep pathway in the transduction stage of cell signaling. 8. Explain how an original signal molecule can produce a cellular response when it may not even enter the target cell. 9. Distinguish between protein kinases and phosphotases. 10. Define the term second messenger. Describe their roles in signaling pathways. 11. Describe how cyclic AMP is formed and how it propogates signal information in target cells. 12. Describe how the cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ can be altered and how the increased pool of Ca2+ is involved in signal transduction. 13. Describe how signal information is transduced into cellular responses in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus. 14. Describe how signal amplification is accomplished in target cells. 15. Explain why different types of cells may respond differently to the same signal molecule. 16. Explain how scaffolding proteins help to coordinate a cell’s response to incoming signals. 17. What is apoptosis and how is this process involved in forming fingers or digits in animals species: 18. Aging is initiated at the cellular level similar to apoptotic events. Aging can be inhibited by changing the expression of genes using signaling. What are some social and ecological consequences of a society whose life expectancy increased exponentially?