Molecular Shapes & Metallic Bonding
advertisement

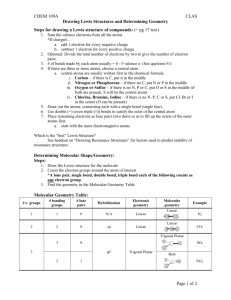
METALLIC BOND bond found in metals; holds metal atoms together very strongly Metallic Bond • Formed between atoms of metallic elements • Electron cloud around atoms • Good conductors at all states, lustrous, very high melting points • Examples; Na, Fe, Al, Au, Co Ionic Bond, A Sea of Electrons Metals Form Alloys Metals do not combine with metals. They form Alloys which is a solution of a metal in a metal. Examples are steel, brass, bronze and pewter. C. Polyatomic Ions • NH4+ 1 N × 5e- = 5e4 H × 1e- = 4e9e- 1e8e- 8e0eC. Johannesson H H N H H D. Resonance Structures • Molecules that can’t be correctly represented by a single Lewis diagram. • Actual structure is an average of all the possibilities. • Show possible structures separated by a double-headed arrow. C. Johannesson D. Resonance Structures SO3 O O S O O O S O O O S O C. Johannesson Exceptions to the Octet Rule • Molecules containing atoms of Group 3A elements, particularly boron and aluminum B Boron trifluoride : Cl Al : Cl : : : :F: : Cl : : : : : :F : : : F: 6 electrons in the valence shells of boron and aluminum Aluminum chloride Exceptions to the Octet Rule • Atoms of third-period elements have 3d orbitals and may expand their valence shells to contain more than 8 electrons – phosphorus may have up to 10 : H- O-P- O-H : Cl : : Cl : :O: : : O-H : Trimethylphosphine : Cl P : : : : CH 3 : : : : : CH 3 -P- CH 3 : Cl : Cl : Phosphorus pentachloride Phosphoric acid Exceptions to the Octet Rule – sulfur, another third-period element, forms compounds in which its valence shell contains 8, 10, or 12 electrons H-O- S-O-H : CH 3 -S-CH 3 : : : : H-S- H : : O: : : O: :O : Hydrogen sulfi de Dimethyl sulfoxide Sul furi c acid A. VSEPR Theory • Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory • Electron pairs orient themselves in order to minimize repulsive forces. C. Johannesson A. VSEPR Theory • Types of e- Pairs – Bonding pairs - form bonds – Lone pairs - nonbonding e- Lone pairs repel more strongly than bonding pairs!!! C. Johannesson A. VSEPR Theory • Lone pairs reduce the bond angle between atoms. Bond Angle C. Johannesson B. Determining Molecular Shape • Draw the Lewis Diagram. • Tally up e- pairs on central atom. – double/triple bonds = ONE pair • Shape is determined by the # of bonding pairs and lone pairs. Know the 8 common shapes & their bond angles! C. Johannesson C. Common Molecular Shapes 2 total 2 bond 0 lone BeH2 LINEAR 180° C. Johannesson C. Common Molecular Shapes 3 total 3 bond 0 lone BF3 TRIGONAL PLANAR C. Johannesson 120° C. Common Molecular Shapes 3 total 2 bond 1 lone SO2 BENT C. Johannesson <120° C. Common Molecular Shapes 4 total 4 bond 0 lone CH4 TETRAHEDRAL 109.5° C. Johannesson C. Common Molecular Shapes 4 total 3 bond 1 lone NH3 TRIGONAL PYRAMIDAL C. Johannesson 107° C. Common Molecular Shapes 4 total 2 bond 2 lone H2O BENT 104.5° C. Johannesson C. Common Molecular Shapes 5 total 5 bond 0 lone PCl5 TRIGONAL BIPYRAMIDAL 120°/90° C. Johannesson C. Common Molecular Shapes 6 total 6 bond 0 lone SF6 OCTAHEDRAL C. Johannesson 90° D. Examples • PF3 4 total 3 bond 1 lone TRIGONAL PYRAMIDAL 107° C. Johannesson D. Examples • CO2 2 total 2 bond 0 lone LINEAR 180° C. Johannesson