2 functions of the Respiratory System
advertisement

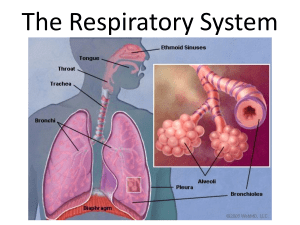
2 functions of the Respiratory System 1. Moves oxygen from the outside environment into the body. 2. Removes carbon dioxide and water from the body (aka waste). Human Lungs NOT Hollow Balloons but, A Spongy Organ The respiratory system includes: nasal passages pharynx larynx trachea bronchi and bronchioles alveoli The Path of Air 1. Air first enters the Nose or Mouth – Air is moistened and heated before going into the trachea. Cilia and mucus, in the nose, trap dirt from the air. Cilia – cells with hair like extensions. Mucus – sticky material, keeps nose from drying out. Traps dust particles. Cilia push the mucus to the back of your throat and you swallow it!! **On average, you swallow a pint of mucus per day (milk carton in cafeteria) The Path of Air cont. 2. Air moves to the Pharynx – (the throat) 3. Into the Larynx (voice box) Epiglottis - flap of tissue that covers the opening of the larynx when you are eating. Also protects from sinus drainage. If food goes down the larynx you ________. The Path of Air cont. 4. Air moves into the trachea (aka the windpipe) a 4 inch long tube that moves air into your lungs. The walls of the trachea have rings of cartilage to protect it and prevent it from collapsing. The trachea splits into 2 bronchi. The Path of Air (Cont.) 5. Bronchi (tubes) – You have 2 bronchi. One leads into your right lung and one into your left lung. Each bronchus (singular) leads air into the lungs and divides into smaller and smaller tubes, called bronchioles. **Think of how a tree trunk divides into smaller and smaller branches. 6. The last stop for air is in the Alveoli – grape-like structures at the end of the bronchioles. Capillaries, very tiny blood vessels, surround each alveoli cluster so the blood can pick up large amounts of oxygen. Breathing vs. Respiration Breathing – Movement of air in and out of the lungs. Respiration – The release of energy that takes place inside of cells. Oxygen and sugar are used by the cell to generate energy for your body to use, for growth and function. Diaphragm – a large dome-shaped MUSCLE, just under the lungs, that moves to inflate the lungs with air. This is the muscle that contracts and relaxes to fill the lungs with air! The brainstem controls this muscle. The left lung is a little smaller than the right lung because it shares space in the left side of the chest with the heart.