Chapter 1 PowerPoint (Filled In)
advertisement

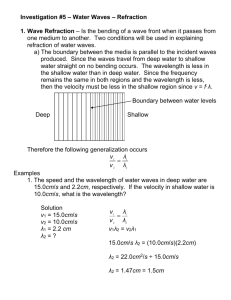
Units and Measurement Physics Mr. Austin International Space Station http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/image/0706/iss_sts117_big.jpg What is Physics? • The study of the relation between energy and matter • The study of: – Motion – Heat – Light – Energy – Much More! Math and Units • Math- the language of Physics • SI Units – International System – MKS • Meter m • Mass kg • Time s • National Bureau of Standards • Prefixes SI Unit Prefixes - Part I Name Symbol Factor tera- T 1012 giga- G 109 mega- M 106 kilo- k 103 hecto- h 102 deka- da 101 SI Unit Prefixes- Part II Name Symbol Factor deci- d 10-1 centi- c 10-2 milli- m 10-3 micro- μ 10-6 nano- n 10-9 pico- p 10-12 femto- f 10-15 SI Unit Prefixes for Length Name gigameter megameter kilometer decimeter centimeter millimeter micrometer nanometer picometer Symbol Gm Mm km dm cm mm μm nm pm 109 106 103 10-1 10-2 10-3 10-6 10-9 10-12 The Seven Base SI Units Quantity Unit Symbol Length meter m Mass kilogram kg Temperature kelvin K Time second s Amount of mole Substance Luminous Intensity candela mol Electric Current a ampere cd Derived SI Units (examples) Quantity unit Symbol Volume cubic meter m3 Density Speed kilograms per kg/m3 cubic meter meter per second m/s Newton kg m/ s2 N Energy Joule (kg m2/s2) J Pressure Pascal (kg/(ms2) Pa Scientific Notation Mx n 10 • M is the coefficient 1<M<10 • 10 is the base • n is the exponent or power of 10 Other Examples: • 5450000 = 5.45E+6 or 5.45 x 10^6 Numbers less than 1 will have a negative exponent. A millionth of a second is: 0.000001 s or 1x10-6 s or 1.0E-6 s Write in Scientific Notation • 3250 = – 3.250 x 103 • .000435 = – 4.35 x 10-4 • 425620000 = – 4.2562 x 108 Factor-Label Method of Unit Conversion • Example: Convert 5km to m: • Multiply the original measurement by a conversion factor. NEW UNIT 85km x 1,000m 1km OLD UNIT = 85,000m Factor-Label Method of Unit Conversion: Example • Example: Convert 789m to km: 789m x 1km =0.789km= 7.89x10-1km 1000m Convert 75.00 km/h to m/s 75.00 km x 1000 m x 1 h___ = 20.83m/s h 1 km 3600 s • Accuracy - a measure of how close a measurement is to the true value of the quantity being measured. Example: Accuracy • Who is more accurate when measuring a book that has a true length of 17.0cm? Susan: 17.0cm, 16.0cm, 18.0cm, 15.0cm Amy: 15.5cm, 15.0cm, 15.2cm, 15.3cm • Precision – a measure of how close a series of measurements are to one another. A measure of how exact a measurement is. Example: Precision Who is more precise when measuring the same 17.0cm book? Susan: 17.0cm, 16.0cm, 18.0cm, 15.0cm Amy: 15.5cm, 15.0cm, 15.2cm, 15.3cm Example: Evaluate whether the following are precise, accurate or both. Accurate Not Accurate Accurate Not Precise Precise Precise Solving Word Problems • Analyze – List knowns and unknowns. – Draw a diagram. – Devise a plan. – Write the math equation to be used. • Calculate – If needed, rearrange the equation to solve for the unknown. – Substitute the knowns with units in the equation and express the answer with units. • Evaluate – Is the answer reasonable? Practice! • Please complete the following problems in class. What you do not finish will be homework to be turned in tomorrow. • Pg. 24 #34, 36, 37, 41, 50, 51, 56, 67, 84, 85. • Read pages 9 and 10 and answer # 49 from pg. 25 • Short Quiz Tomorrow after HW review