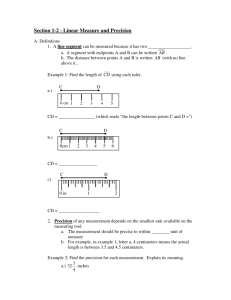
Accuracy vs Precision
advertisement

USING SCIENTIFIC MEASUREMENTS Accuracy and Precision RHS Science Department Whachathinkboutit? • Write your definition of the following terms: • Accuracy • Precision • Do they mean the same thing or is there a difference? • If there is a difference, what is the difference? (Give an example.) Accuracy vs. Precision • To most people, the words Accuracy and Precision are synonymous. • In the field of science, they have quiet distinct meanings. • Accuracy is defined as the closeness of the measurement to the correct or accepted value of the quantity measured. • Precision is defined as the closeness of a set of measurements of the same quantity to one another. Accuracy Precision Whachathinkboutit? BOTH Whachathinkboutit? NEITHER Application of Concept • Who is more accurate when measuring a book that has a true length of 17.0cm? Susan: 17.0cm, 16.0cm, 18.0cm, 15.0cm Amy: 15.5cm, 15.0cm, 15.2cm, 15.3cm Application of Concept Who is more precise when measuring the same 17.0cm book? Susan: 17.0cm, 16.0cm, 18.0cm, 15.0cm Amy: 15.5cm, 15.0cm, 15.2cm, 15.3cm Error • Due to a variety of factors (eyesight, equipment limitations, material, etc…) there is a margin of error between our experimental measurement value and the accepted value. • To calculate the error, we apply the following formula: Error = Valueexperimental - Valueaccepted Percentage Error • The amount of error is generally expressed as a percentage of the accepted value. • To calculate percent error, we apply the following formula: 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑒𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙 − 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐸𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟 = × 100 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 Practice • A student measures the mass and volume of a substance and calculates its density as 1.40 g/mL. The correct value of the density is 1.30 g/mL. What is the percentage error of the student’s measurement? • G.U.E.S.S • Given (measured = 1.40 g/mL; correct = 1.30 g/mL) • Unknown (percent error) • Equation (𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐸𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟 = 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑒𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙 −𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑒𝑑 • Substitute (𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐸𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟 = • Solve (7.7%) 1.40 𝑔/𝑚𝐿−1.30𝑔/𝑚𝐿 1.30 𝑔/𝑚𝐿 × 100 ) × 100 ) Interpreting the Results • Percent error can be positive or negative. • If it has a positive value, it means that the experimental or measured value was greater than the accepted value. • If it has a negative value, it means that the experimental or measured value was less than the accepted value.