Linear Measure & Precision Geometry Worksheet
advertisement

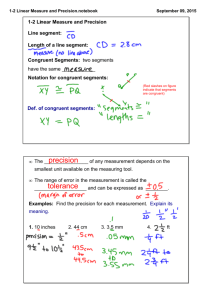
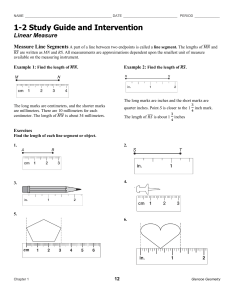
Section 1-2 - Linear Measure and Precision A. Definitions 1. A line segment can be measured because it has two ___________________. a. A segment with endpoints A and B can be written AB . b. The distance between points A and B is written AB (with no line above it.. Example 1: Find the length of CD using each ruler. a.) C D 0 cm 1 2 3 4 5 CD = ________________ (which reads “the length between points C and D =”) C D b.) 0cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 CD = _________________ c) C 0 in D 1 2 CD = __________________ 2. Precision of any measurement depends on the smallest unit available on the measuring tool. a. The measurement should be precise to within ________ unit of measure b. For example, in example 1, letter a, 4 centimeters means the actual length is between 3.5 and 4.5 centimeters. Example 2: Find the precision for each measurement. Explain its meaning. 3 a.) 32 inches 4 b.) 15 millimeters Example 3: Find the measurements. L a.) Find LM N 2.5 cm M 4 cm LM = ____________ b.) Find XZ X 4 5 8 Y 2 1 2 Z XZ = ____________ c.) Find x and ST if T is Between S and U, ST = 7x , SU = 45, and TU = 5 x − 3 . U 5x − 3 T 7x S x = ________ ST = ________ 3. If two segments are the same length they are said to be congruent segments. a.) This is represented on a drawing by an equal number of slashes on the congruent segments. HW Geom 1-2 p. 17-19 12-15, 16-32 even, 34-39, 56-65