Forces Unit Plan
advertisement

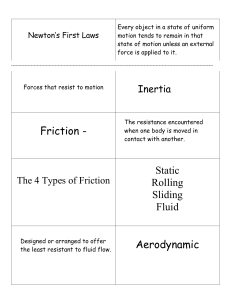
Forces Teacher: Colquitt Course: College Preparatory Physics SP1. Students will analyze the relationships between force, mass, gravity, and the motion of objects. Understandings: SP1d. Measure and calculate the magnitude of frictional forces and Newton’s three Laws of motion. SP1e. Measure and calculate the magnitude of gravitational forces. Essential Questions: a) b) c) To measure and calculate the magnitude of frictional forces. To measure and calculate the magnitude of Newton’s three Laws of Motion. To measure and calculate the magnitude of gravitational forces. SP1h. Determine the conditions required to maintain a body in a state of static equilibrium. Students will Know… a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) l) m) n) o) p) q) r) s) t) u) v) w) x) y) z) aa) bb) cc) dd) ee) ff) gg) hh) ii) Newton’s 1st Law Newton’s 2nd Law Newton’s 3rd Law Vectors Concurrent Forces Resultant Force Equilibrium Equilibrant Force Composition of forces Resolution of forces Vector Addition Inertia Force A = 0 m/s2 F = 0 N Matter Mass Weight Acceleration Gravity Velocity Friction Kinetic friction Static friction Vector component Vector Resultant Newton Fnet = MA Constant Velocity Inverse Relationship Direct Relationship Terminal Velocity Fwt = mg Law of Inertia Law of Acceleration Law of Action – Reaction Students will be Able to … a) Determine the force that produces equilibrium when three forces act on an object b) Analyze the motion of an object on an inclined plane with and without friction c) Describe how fore affects the motion of an object d) Interpret and construct free-body diagrams e) Explain the relationship between the motion of an object and the net external force acting on the object f) Determine the net external force on an object g) Calculate the force required to bring an object into equilibrium h) Describe an object’s acceleration in terms of its mass and the net force acting on it i) Predict the direction and magnitude of the acceleration caused by a known net force j) Identify action-reaction pairs k) Explain the difference between mass and weight l) Find the direction and magnitude of normal forces m) Describe air resistance as a form of friction n) Use coefficients of friction to calculate friction force. Measure and calculate force, mass, and acceleration from F = ma, Newton’s 2nd Law equation. o) Understand and apply the concepts of Newton’s 1st, 2nd, and 3rd law. p) Algebraically calculate the resultant component from two perpendicular vector component q) Algebraically calculate the resultant component from non-perpendicular vector components r) Calculate the Force of weight of an object s) Add and subtract vector components t) Comprehend the concept of Terminal velocity Assessments: a) Class work practice problems b) Homework practice problems c) Laboratory Activities d) Quizzes e) Multiple choice and Short Answer Test Unit Launch 1) Demonstration: Examples of Pushing and Pulling on objects Lesson Plans