Introduction to Cell Theory
advertisement

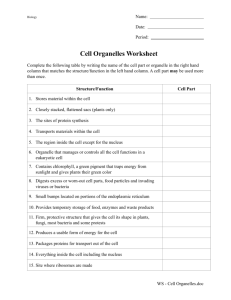
9A – New Seats! Front of room Lorena Martin Joshua Yamile Kenny Cassandra Imani Lila Joelle Erick Hajar Victor Martely Devin Naidaliz Nathy Lennin Beverly Javier Emiliano Jesse Olivia Bryan Daysia Amrita Alerte Beginning of Class: Some Reminders & Revised Class Norms In the door when the bell rings After 1 minute: In seat Notebook & HW out Write down Title and Date Work SILENTLY on the Do Now Questions/Concerns = RAISE HAND without talking! Tardy = still talking and/or not doing Do Now after 1 minute (3 Tardies = IR!) Bio 9A: Thursday, 9.23.10 Title: What are cells? Homework: None Do Now: Set up today’s notebook entry with the title and date in the proper format! Write down at least 3 observations about what you see in the picture Today’s Objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4. Identify 3 components that ALL cells have Explain why cells are important to all living things Explain where the heck cells come from Maintain a neat and organized scientific notebook Today’s Agenda: Scientific Notebook Guidelines Notes/HW Review: What are Cells? Scientific Notebook Guidelines Each entry should have… Other Guidelines: Date (outside corner, under page #) Title Do Now (clearly labeled) Notes – accurate, complete, detailed, w/ labeled diagrams! Neatness Only Bio! Never tear out a page! Use your 2-pocket folder! Key handouts stapled in! Keep it nice! You get graded on all this! Class Objectives: 1. Maintain a neat and complete scientific notebook Taking Notes in Class: Class Norms Purpose: Review and add details to the notes you took from the reading Take notes on new information Discuss and ask questions about the day’s topic Draw diagrams so you can picture what we’re learning How it works: “Cold calling” What if you don’t know? During Note-Taking, you should be: Listening and ready to answer a question Quietly writing down notes and drawing diagrams from the board UNLESS they’re a repeat of your HW Asking questions about things you don’t understand or things you want to know more about! WHAT ARE CELLS? PHA Biology 9 Moretti and Dickson What do you see? This is the first image anyone ever saw of cells! Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify 3 components that ALL cells have Explain why cells are important to All living things Explain where the heck cells come from Do Now #2: Write down ONE SIMILARITY among all of these pictures: Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify 3 components that ALL cells have Explain why cells are important to All living things Explain where the heck cells come from What makes a cell? 3 things ALL cells have: • Cell membrane (barrier) • DNA (genetic info) • Cytoplasm (fluid) Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify 3components that ALL cells have Explain why cells are important to All living things Explain where the heck cells come from Sketch both cells in your notebook. Label which is eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Cell membrane DNA Prokaryote (DNA floating in cytoplasm) Cytoplasm Eukaryote (DNA inside the nucleus) Important Ideas About Cells: (aka- the Cell Theory) 1. All living things are made of cells. • Unicellular Organisms (one-celled) • Multicellular Organisms (many cells) Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify 3 components that ALL cells have Explain why cells are important to All living things Explain where the heck cells come from Important Ideas About Cells: (aka- the Cell Theory) 2. Cells give an organism its structure and function - they control everything the organism need to do to stay alive Even the most complex organisms are made of a bunch of different types of cells working together. Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify 3 components that ALL cells have Explain why cells are important to All living things Explain where the heck cells come from Important Ideas About Cells: (aka- the Cell Theory) 3. New cells come from pre-existing cells. A prokaryotic cell splits into two identical cells by the process of binary fission. Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify 3 components that ALL cells have Explain why cells are important to All living things Explain where the heck cells come from A eukaryotic cell splits into two identical daughter cells by the process of mitosis. Bio 9A: Friday, 9.24.10 Title: Microscope Lab! Homework: ON HANDOUT Do Now: NOT in your notebook! Get a microscope lab from the kidney table Get a textbook Turn to page 1070 and label the diagram on the front of the lab Today’s Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify the parts of a compound light microscope Make a wet mount slide Use a microscope to bring a specimen into focus Today’s Agenda: Microscope Lab Parts of the Microscope Instructions on Safe Handling of the Microscope Complete the Lab Identifying the components of a Compound Microscope Class Objective: Identify the major parts of a compound microscope Eyepiece Nosepiece Objective lenses Stage clips Stage Diaphragm Light Base Arm Coarse focus Fine focus Power switch Using a Compound Microscope Microscope Tutorial Follow the instructions to complete the microscope tutorial. Do not move on to the next step until your teacher has checked your slides and has determined that you have identified the appropriate objects with your microscope. Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify the major parts of a compound microscope Prepare a wet-mount slide Use microscope adjustments to focus the microscope and bring images into view Bio 9A: Same seats as last week… Lorena Alerte Erick Amrita Devin Imani Martely Joshua Nathy Olivia Bryan Hajar Victor Kenny Javier Lennin Jesse Cassandra Lila Beverly Daysia Naidaliz Joelle Emiliano Yamile Martin Bio 9A: Monday, 9.27.10 Title: Eukaryotic Cell Parts Homework: Do Now: Complete the Cell Organelle Speed Dating Summary Get your clicker In your notebook: How would you define an organelle? Objectives for Class: 1. 2. Identify the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Explain the functions of the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Agenda HW Review with Clickers This is part of today’s HW check Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Labeling Activity Cell Organelle Speed Dating Planning HW Review w/ Clickers! What is the best definition of an organelle? A. A special type of cell B. A factory C. A “tiny organ” that does a certain job inside a cell D. An organ, such as the stomach, liver, or kidneys What is the fluid that fills a cell between the cell membrane and the nucleus? 30 A. B. C. D. 0 Chloroplast Cytoplasm Blood Syrup 25% A. 25% 25% B. C. 25% D. Which organelle is found in plant cells but NOT animal cells? 30 A. B. C. D. 0 Nucleus Mitochondria Chloroplast Cytoplasm 25% A. 25% 25% B. C. 25% D. Plant cells and animal cells are both eukaryotic because they both have 30 A. B. C. D. 0 DNA Ribosomes Mitochondria Nucleus 25% A. 25% 25% B. C. 25% D. How many miles did your biology teacher ride her bike this weekend?? 30 A. B. C. D. 0 25 miles 50 miles 95 miles 125 miles 25% A. 25% 25% B. C. 25% D. Agenda HW Review with Clickers Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Labeling Activity Cell Organelle Speed Dating Planning Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Labeling Work with a partner to label the plant and animal cell diagrams (do your best, the book diagrams and these diagrams do not match perfectly… this is a good thing!) Class Objectives: 1. 2. Identify the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Explain the functions of the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Agenda Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Labeling Activity Cell Organelle Speed Dating Planning Cell Organelle Speed Dating Planning Organelle Speed Dating Planning: Work w/ partner to research your assigned organelle Specifically, you need to know the key structures and functions of your organelle. This needs to be completed by the beginning of tomorrow’s class Class Objectives: 1. 2. Identify the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Explain the functions of the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Bio 9A: Tuesday, 9.28.10 Title: Eukaryotic Cell Organelle Speed Dating Homework: Do Now: Speed Dating Reflection and Organelle Review (worksheet) Pick up tonight’s HW and an Organelle Chart from the Kidney Table Find your organelle label at the lab benches and sit ACROSS from your organelle buddy Take out your Organelle Summary (last night’s HW) Objectives for Class: 1. 2. 3. Identify the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Explain the functions of the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Make connections between the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Agenda Cell Organelle Speed Dating Set Up Speed Dating Cell Organelle Speed Dating Organelle Speed Dating Set-Up: Pair With your organelle buddy: Your instructor will distribute slips of paper with a description of each organelle. Read each slip and pass it along until you find the one that matches your organelle! Compare this summary to the one you wrote: If the descriptions are the same… you’re all set. If the descriptions are different, use the description on the slip of paper to tell other organelles about yourself. Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Explain the functions of the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Make connections between the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Cell Organelle Speed Dating Organelle Speed Dating Rules: When you meet another organelle: Introduce yourselves and shake hands Find out each other’s jobs (2 min.) Find a connection between the two of you – how do your jobs relate? (1 min.) Record information in the Organelle Chart. People facing the board move one seat over (follow the numbers!!) HW: Speed Dating Reflection and Organelle Review worksheet Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Explain the functions of the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Make connections between the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Bio 9A: Wednesday, 9.29.10 Title: A Day in the Life of a Cell Homework: TYPED, DUE MONDAY. Silent Do Now: (in notebook, w/ title & date) Writing Assignment: Day in the Life of a Cell – see back of assignment sheet (1-2 detailed paragraphs) What comes to your mind when you think about protein? What do you think a protein is? Where do you think proteins are found? Why might proteins be important? Objectives: 1. 2. Explain 3 reasons why proteins are important for cells and living things. Explain how at least 5 organelles work together to make and use proteins in cells. Agenda: A Day in the Life of a Cell HW Collection & Do-Now Discussion Define Proteins How Cells Make & Use Proteins: Interactive Diagram/Animation Proteins – Large molecules that do many important jobs in living things, such as: Form body structures (muscle, bone, hair, eyes, nails, skin) Act as enzymes to speed up chemical reactions (like digestion) in our bodies Act as hormones that send signals through the bloodstream [And many other things we’ll learn about later!] Class Objectives: 1. Describe 3 things that proteins do for the body Agenda: A Day in the Life of a Cell Defining Proteins How Cells Make & Use Proteins: Interactive Diagram/Animation You need: • Diagram • Script/Outline • One colored pencil and your own pen/pencil Put everything else away. Proteins Proteins are large molecules that do many important jobs in living things, such as: Form body structures (muscle, bone, hair, nails, skin) Act as enzymes to speed up chemical reactions (like digestion) in our bodies Act as hormones that send signals through the bloodstream [And many other things we’ll learn about later!] (Modifies and shapes the protein) Protein being formed at Ribosome Ribosome Protein Protein could go to membrane to be released into blood stream DNA RNA RNA ATP energy (for the cell to use) (Holds genetic information) (Copies info from DNA and carries it to the Ribosome to make proteins) Cell Respiration Glucose + O2 (Modifies and shapes the protein) Protein being formed at Ribosome Protein could go to membrane to be released into blood stream DNA RNA ATP energy (for the cell to use) (Holds genetic information) (Copies info from DNA and carries it to the Ribosome to make proteins) Cell Respiration Glucose + O2 Homework Reminder Writing Assignment: A Day in the Life of a Cell 1-2 detailed paragraphs that describe: How does a cell make and use proteins? Include at least 5 different organelles in your answer, and explain how they work together to make and use proteins. Typed, due Monday. There will be other HW tomorrow night, but no other HW for the weekend. Bio 9A: Thursday, 9.30.10 Title: Eukaryotic Cell Organelle Review Homework: Cells Under the Microscope Pre-Lab (1st page of lab packet) Silent Do Now: (in notebook w/ title & date) Look at your Day in the Life of a Cell diagram from yesterday Write for at least 4 minutes about this diagram: What’s happening? Tell the story, starting in the nucleus What parts do you understand really well? What do you have questions about, or what don’t you understand? You should be writing for the whole Do Now time. Objectives for Class: 1. 2. Explain how the organelles in a cell work together to make and use proteins. Identify the functions of the major organelles HW Multiple Choice Question #2: Why do some cells have more mitochondria than other cells? A. The cells use more energy B. The cells store more nutrients C. The cells degrade more proteins D. The cells divide more frequently 100% 0% A. 0% B. C. 0% D. Agenda Organelle Review Session (with Clickers) Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Review Defining Proteins Organelle Review with Clickers Follow along with the chart on the review sheet For each question, choose the organelle that best matches the function Record the correct answer in your chart – this will be a great study guide! Makes proteins by following instructions from DNA. 1. 2. 3. 4. Nucleus Ribosome Mitochondria Vacuole 92% 4% 1 4% 2 3 0% 4 Uses sunlight energy to make sugar (photosynthesis) 1. 2. 3. 4. Mitochondria Cytoplasm Chloroplast Cell wall 88% 8% 1 4% 2 0% 3 4 Contains DNA, which controls cell activities and reproduction. 1. 2. 3. 4. Ribosome Cell membrane Golgi apparatus Nucleus 88% 4% 1 8% 0% 2 3 4 Digests food and cell wastes. 1. 2. 3. 4. Ribosome Lysosome Chromosome Endoplasmic reticulum 96% 0% 1 0% 2 3 4% 4 Breaks down food to release energy that the cell can use (cell respiration) 1. 2. 3. 4. Mitochondria Cytoplasm Chloroplast Cell wall 76% 8% 1 2 12% 4% 3 4 Stores water and nutrients for the cell. It is especially large in plant cells. 1. 2. 3. 4. Nucleus Ribosome Mitochondria Vacuole 96% 0% 1 0% 2 4% 3 4 Modifies and transports proteins, and assembles lipids into membranes. 1. 2. 3. 4. Nucleus Ribosome Endoplasmic reticulum Lysosome 96% 0% 1 4% 2 0% 3 4 Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for storage or to be shipped out of the cell. 1. 2. 3. 4. Cell membrane Golgi apparatus Endoplasmic reticulum Chloroplast 84% 8% 1 4% 2 3 4% 4 A barrier around all cells that controls what enters and leaves the cell. 1. 2. 3. 4. Cell membrane Cell wall DNA Nucleus 96% 4% 1 2 0% 3 0% 4 Supports the inside of the cell and gives it shape. Helps with cell and organelle movement. 1. 2. 3. 4. Nucleus Cytoskeleton Cell wall Endoplasmic reticulum 88% 12% 0% 1 0% 2 3 4 A sturdy structure outside the cell membrane that provides protection and support. 1. 2. 3. 4. Nucleus Cytoskeleton Cell wall Endoplasmic reticulum 96% 4% 1 0% 2 0% 3 4 The entire part of the cell between the nucleus and the cell membrane. Filled with water, nutrients, and organelles. 1. 2. 3. 4. Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cell wall Cytoplasm 92% 4% 1 4% 2 0% 3 4 Agenda Eukaryotic Cell Organelles’ Structure & Function Wrap-up Session (with Clickers) Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Review Defining Proteins Take out your Eukaryotic Cell Diagrams, please… Plant Cell Diagram: Lysosome Golgi Apparatus Nucleus Ribosome Chloroplast E.R. (rough) E.R. (smooth) Cell Wall Vacuole Mitochondrion Cell Cytoplasm Membrane Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Explain the functions of the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Make connections between the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Animal Cell Diagram Cytoskeleton Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Ribosome Mitochondrion Golgi Apparatus Nucleus Mitochondrion E.R. Lysosome Ribosomes Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Explain the functions of the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Make connections between the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell Bio 9A: Friday, 10/1/10 Title: Cells Under the Microscope Lab Homework: Due Monday: Detailed paragraph (must be typed) on a Day in the Life of a Cell Silent Do Now: (in notebook w/ title and date) Describe how the organelles in a cell work together to make and use. Include at least 5 different organelles in your essay. Describe one safety rule that you think is important for this lab. Why do you think this is important? If you have time, describe and explain the importance of other lab safety rules. You should be writing for the entire Do Now time. Objectives for Class: 1. 2. 3. Follow proper lab safety rules and procedures. Identify the visible organelles in a Eukaryotic Cell Use microscope adjustments to focus the microscope and bring images into view Agenda Review Safety Rules Cells Under the Microscope Lab Lab Safety Rules DO’s Use water droppers and iodine to make a proper wet-mount slide Look at cheek cells and Elodea plant cells under the microscope Be patient – seeing this stuff can be difficult! Look carefully and persevere. Use forceps and scissors to manipulate specimens on the slides Work quietly and productively w/ your assigned partner Clean up by rinsing slides as the sink by your lab table Put Elodea leaves in the trash when cleaning up Put notebooks away, put bags under your chairs. Take only the lab packet and a pen/pencil back to your lab station. DON’Ts Don’t squirt water or iodine anywhere other than on the slide Don’t put anything else on microscope slides (pen ink has ruined some slides!) Don’t stick/cut anything else with forceps or scissors Don’t move to other tables or talk across the room Don’t move across the room to clean up or get materials. If you need something, raise your hand! Don’t rinse leaves down the drain! Take anything other than the lab packet and a pen/pencil to your lab table. Cells Under the Microscope Lab Listen silently to your teacher’s instructions (remember: time wasted is time you don’t get to work on the lab) Send one person to get materials Follow each step of the lab (read it out loud) Record results on results page Class Objectives: 1. 2. 3. Identify the visible organelles in a Eukaryotic Cell Prepare a wet-mount slide Use microscope adjustments to focus the microscope and bring images into view Front of Room Nathy Emiliano Joelle Jesse Beverly Lennin Kenny Martely Devin Martin Daysia Olivia Hajar Amrita Javier Cassandra Joshua Lila Alerte Victor Lorena Erick Naidaliz Bryan Yamile Imani Homework Reminder Writing Assignment: A Day in the Life of a Cell 1-2 detailed paragraphs that describe: How does a cell make and use proteins? Include at least 5 different organelles in your answer, and explain how they work together to make and use proteins. Typed, due Monday. Bio 9A: Monday, 10.4.10 Title: Cells - Review and Wrap-Up Homework: Study for Tomorrow’s Quiz! See assignment sheet for details. Silent Do Now: (in notebook w/ title & date) Reflect on Friday’s lab and the cells you saw under the microscope: How were the cells similar to what you expected to see? How were the cells different from what you expected to see? What was the coolest part of the lab? What was the most frustrating part of the lab? At this point, how good are you at making slides and finding/focusing on specimens under the microscope? Explain! If you weren’t here, write about what you hoped/expected to see, and what you did instead. Continue to write about the lab for the entire Do Now time. Objectives: 1. Review the major structures and functions of a eukaryotic cell in order to be prepared for tomorrow’s quiz Agenda Video: Inside a Eukaryotic Cell… Eukaryotic Cell Wrap-up and Review VIDEO: INSIDE A EUKARYOTIC CELL Agenda Video: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles working together Eukaryotic Cell Wrap-up and Review Review: Organelle Functions Function Makes proteins by following instructions from DNA. Uses sunlight energy to make sugar (photosynthesis) Contains DNA, which controls cell activities and reproduction. Digests food and cell wastes. Breaks down food to release energy that the cell can use (cell respiration) Stores water and nutrients for the cell. It is especially large in plant cells. Modifies and transports proteins, and assembles lipids into membranes. Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for storage or to be shipped out of the cell. A barrier around all cells that controls what enters and leaves the cell. Helps to support the cell and give it shape, and helps with moving organelles or moving the whole cell. A sturdy structure outside the cell membrane that provides protection and support. Found in plant but not animal cells. The entire part of the cell between the nucleus and the cell membrane. Filled with water, nutrients, and organelles. Cell Structure/Organelle RIBOSOME CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS LYSOSOME MITOCHONDRIA VACUOLE E.R. GOLGI CELL MEMBRANE CYTOSKELETON CELL WALL CYTOPLASM