Explain_Keys_to_the_Kingdom / Microsoft
advertisement

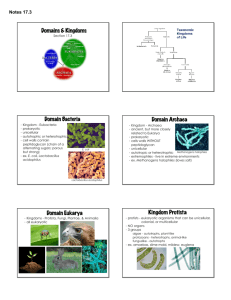
Keys to the Kingdom Classification The arrangement of things into orderly groups based on similarities. Taxonomy The science of identifying, classifying, and naming living things. Founded by Carolus Linnaeus Carolus Linnaeus He founded taxonomy and created the seven-level system of classification that we still use today. Scientists later added “Domain” to the classification system. 8 Levels of Classification Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species Dear King Phillip Came Over For Good Soup Example: Dog Eukarya Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Canidae Canis familiaris Domain The broadest (most general) level of classification for living things 3 Domains – Eukarya, Bacteria, and Archaea We belong in Domain Eukarya. Kingdom The 2nd most general category of the eight levels of classification There are 6 kingdoms that we know of today: Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Archaebacteria, and Eubacteria Species The most specific level of classification for living things Organisms all have a scientific name that is the Genus and species together. Human= Homo sapiens Dog= Canis familiaris Cat= Felis domesticus Domain: Archaea Kingdom: Archaebacteria Have existed for at least 3 billion years All are very small single-celled organisms Are prokaryotic Some are autotrophic and some are heterotrophic Reproduce asexually Only live in extreme environments – Dead Sea, hot springs, swamps, etc. Archaebacteria Examples: methanogens, halophiles, thermophiles Domain: Bacteria Kingdom:Eubacteria All are single-celled organisms Prokaryotic Some are autotrophic and some are heterotrophic Come in many shapes and sizes Reproduce asexually Prokaryotes that may be found in the human body; most common type of bacteria found everywhere Eubacteria Examples: E. coli; Staphylococcus aureus Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Protista Appeared about 2 billion years ago Most are single-celled organisms or simple multicellular organisms Eukaryotic Some are autotrophic and others are heterotrophic Most reproduce asexually Environment: freshwater pond Protista Examples: all eukaryotes that are not plants, animals, or fungi such as: Paramecium, slime molds, Euglena, giant kelp Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Plantae Use the sun’s energy to make sugar (food) through photosynthesis Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Asexual and sexual Environment: all over the world; in water and on land Plantae Examples: ferns, giant sequoia trees, grass, moss, conifers Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Fungi Break down material outside their body and then absorb (soak up) the nutrients Most are multicellular Eukaryotic Heterotrophic Some are asexual and others are sexual Environment: dark, moist forest floor Fungi Examples: molds, mushrooms, mildew, lichens, yeast Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia Has a nervous system that helps them sense and react to their surroundings Multicellular Eukaryotic Heterotrophic Sexual Animalia Examples: fish, dog, human, squid, snail, beetle