Cell Wall
advertisement

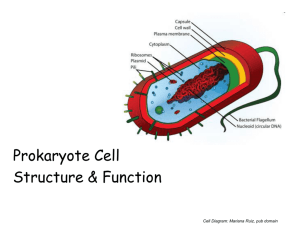
Estrutura e função da célula procariotica Cell Diagram: Mariana Ruiz, pub domain a BIOMASSA DE BACTERIAS NA TERRA É ESTIMADA A SER IGUAL QUE A DE PLANTAS. O NUMERO DE PROCARIOTES NA TERRA ESTIMADO É DE 5 × 1030, QUE REPRESENTA A METADE DA BIOMASSA GLOBAL. ^ Whitman W, Coleman D, Wiebe W (1998). "Prokaryotes: the unseen majority". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95 (12): 6578–83. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.12.6578. PMC 33863. PMID 961845 HABITAT pH ácido pH alcalino Outros habitats Arvore universal da vida derivada do sequenciamento de ssRNA. N. Pace Arvore universal da vida derivada do sequenciamento de ssRNA. N. Pace --Archaea are the least evolved type of cell (they remain closest to the common point of origin). This helps explain why contemporary Archaea are inhabitants of environments that are something like the earth 3.86 billion years ago (hot, salty, acidic, anaerobic, low in organic material, etc.) Ref. Todar microbiology. Metano e CO2= origem do efeito estufa-aquecimento da terra Size of Living Things 1 m = 100 cm = 1,000mm = 1,000,000 µm = 1,000,000,000nm 1mm = 1000 µm = 1000000nm 1 µm = 1000nm Diagrams: http://www.cellsalive.com/howbig.htm Tamanho da célula bacteriana Célula típica: diametro 1 - 2 μm (~ tamanho de mitocôndria) Megabactéria (Epulopiscium fishelsoni): 80 x 600 μm, portanto visível ao olho nú Nanobactéria Streptooccus pneumoniae Bacillus antrax=bacteria gram + E. coli E. coli durante a conjugação -E. coli - Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod prokaryote; strains undergoing conjugation, one strain has fimbriae. - E. coli can cause urinary tract infections, traveler's diarrhea and nosocomial infections. File Name:-- 71241JWA Category:-- Bacteria Type of Image:-- TEM Magnification:-- x3,645--(Based on an image size of 1 inch in the narrow dimension) Two basic types of cells _____________________ _____________________ Diagrams: Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cell, Mariana Ruiz Prokaryotes – Cell Wall Peptidoglycan is a huge polymer of interlocking chains of identical peptidoglycan monomers. Backbone of peptidoglycan molecule composed of two derivatives of glucose: N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) N-acetlymuramic acid (NAM) NAG / NAM strands are connected by interpeptide bridges. Peptidoglycan - Rigid mechanical support - Freely permeable to solutes Image: Peptindoglycan Structure: NicolasGrandjean Prokaryotes - Cell Wall: Gram-Negative & Gram-Positive Image: Prokaryotic Cell, Mariana Ruiz Gram +-, Julian Onions N-acetil glucosamina e acido muramico Chapter 4 Cell Wall • Peptido-glycan Polymer (amino acids + sugars) • Unique to bacteria • Sugars; NAG & NAM – N-acetylglucosamine – N-acetymuramic acid • D form of Amino acids used not L form – Hard to break down D form •Chapter Amino acids cross link NAG & NAM 4 Video Clip parede celular Chapter 4 Chapter 4 Cell Wall Summary • • • • • Determine shape of bacteria Strength prevents osmotic rupture 20-40% of bacteria Unique to bacteria Some antibiotics effect directly – Penicillin Chapter 4 Why are these differences in cell wall structure so important? Images: Sources unknown Prokaryotes - Glycocalyx Some bacteria have an additional layer outside of the cell wall called the glycocalyx. This additional layer can come in one of two forms: 1. Slime Layer 2. Capsule STRUCTURE OF MICOBIAL CELLS Prokaryotes - Glycocalyx Some bacteria have an additional layer outside of the cell wall called the glycocalyx. This additional layer can come in one of two forms: glycoproteins loosely associated with the cell wall. Slime layers cause bacteria to adhere to solid surfaces and help prevent the cell from drying out. Streptococcus The slime layer of Gram+ Streptococcus mutans allows it to accumulate on tooth enamel (yuck mouth and one of the causes of cavities). Other bacteria in the mouth become trapped in the slime and form a biofilm & eventually a buildup of plaque. Staphylococcus The slime layer of Gram+ Staphylococcus allows it to thrive in the salty, hypertonic environment of the skin. Glycocalyces are not specific to Gram+ or Gram- bacteria, sometimes only some members of a certain species (strains) have a glycocalyx, whereas others don’t. STRUCTURE OF MICOBIAL CELLS Prokaryotes - Glycocalyx Capsules adhere to solid surfaces and to nutrients in the environment. Adhesive power of capsules is a major factor in the initiation of some bacterial diseases. Capsule also protect bacteria from being phagocitized by cells of the hosts immune system. STRUCTURE OF PROKAROTIC CELLS Prokaryotes - Glycocalyx Bacterial Capsule and Meningococcal Infection Meningococcal infection is caused by meningococcal bacteria (Neisseria meningitidis). Causes: 1. meningococcal meningitis (infection of the meninges/spinal cord) 2. meningococcal septicaemia (blood poisoning). Of the two forms, meningococcal septicaemia is the most dangerous. Meningococcal bacteria are the most common cause of bacterial meningitis. Meningococcal bacteria grow in pairs called diplococci often surrounded by a capsule coat. Over a million of these would fit on the head of a pin. Approximately 5% of people who suffer from meningococcal meningitis will die. http://www.meningitisuk.org/about-meningitis/bacterial-meningitis.htm STRUCTURE OF PROKAROTIC CELLS Prokaryotes - Endospores Dormant, tough, non-reproductive structure produced by small number of bacteria. Primary function of endospores: _________________________ _________________________ Resistant to radiation, desiccation, lysozyme, temperature, starvation, and chemical disinfectants. A stained preparation of Bacillus subtilis showing endospores as green and the vegetative cell as red Endospores commonly found in soil and water, where they may survive for long periods of time. Image: Stain: Jerry Keplinger, James H. Quillen College of Medicine Procedure: Source link no longer works STRUCTURE OF PROKAROTIC CELLS