Cell Wall - Arrowhead High School
advertisement

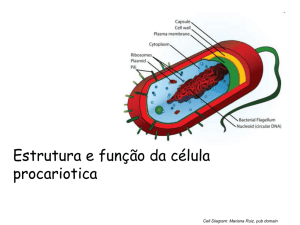
Prokaryote Cell Structure & Function Cell Diagram: Mariana Ruiz, pub domain 1 m = 100 cm = 1,000mm = 1,000,000 µm = 1,000,000,000nm 1mm = 1000 µm = 1000000nm 1 µm = 1000nm The Cellular Level of Organization Living things are constructed of cells. Living things may be unicellular or multicellular. Cell structure is diverse but all cells share common characteristics. Cells are small so they can exchange materials with their surroundings. Surface area relative to the volume decreases as size of cell increases. - limits the size of cells ___________________ states: 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in organisms. 3. All cells come only from other cells. Two basic types of cells _____________________ _____________________ Diagrams: Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cell, Mariana Ruiz Prokaryotes Binary Fission Tell me about Prokaryotes… Diagrams: Prokaryotic Mariana Ruiz Binary Fission, JW Schmidt Prokaryotes ______________ Also known as proto-plasm. Gel-like matrix of water, enzymes, nutrients, wastes, and gases and contains cell structures. Location of growth, metabolism, and replication. Prokaryotes _______________ Found within cytoplasm or attached to plasma membrane. What are they made of? What do they do? Composed of a small (30S) subunit and a large (50S) subunit. Cell may contain thousands of ribosomes. Eukaryotic Cells _________________ Cellular "scaffolding" or "skeleton" within the cytoplasm. Major advance in prokaryotic cell biology in the last decade has been discovery of the prokaryotic cytoskeleton. Previously thought to be a feature only of eukaryotic cells. Diagrams/Photos: Fluorescent Cell: NIH, Pub Domain Prokaryotes - Plasma Membrane Separates the cell from its environment. Phospholipid molecules oriented so that hydrophilic (__________) heads directed outward and hydrophobic (__________) tails directed inward. Proteins embedded in two layers of lipids (lipid bilayer). ___________________ to allow substances to pass into and out of the cell. Diagrams: Prokaryotic Cell, Mariana Ruiz Membrane: NIST Prokaryotes – Plasma Membrane as a Barrier Primary function of plasma membrane → regulate movement of molecules entering or leaving cell. Movement of molecules across plasma membrane requires energy. Prokaryotes – Cell Wall Peptidoglycan is a huge polymer of interlocking chains of identical peptidoglycan monomers. Peptidoglycan - Rigid mechanical support - Freely permeable to solutes Image: Peptindoglycan Structure: NicolasGrandjean Prokaryotes - Cell Wall From the peptidoglycan inwards all bacteria are very similar. Going further out, the bacterial world divides into two major classes (plus a couple of odd types). These are: Gram-positive Gram-negative Images: PHIL Public Health Image Library Prokaryotes - Cell Wall: Gram-Negative & Gram-Positive Image: Prokaryotic Cell, Mariana Ruiz Gram +-, Julian Onions Why are these differences in cell wall structure so important? Images: Sources unknown Prokaryotes - Glycocalyx Some bacteria have an additional layer outside of the cell wall called the glycocalyx. This additional layer can come in one of two forms: 1. Slime Layer 2. Capsule STRUCTURE OF MICOBIAL CELLS Prokaryotes - Glycocalyx Some bacteria have an additional layer outside of the cell wall called the glycocalyx. This additional layer can come in one of two forms: 1. ______________________ glycoproteins loosely associated with the cell wall. Slime layers cause bacteria to adhere to solid surfaces and help prevent the cell from drying out. Streptococcus The slime layer of Gram+ Streptococcus mutans allows it to accumulate on tooth enamel (yuck mouth and one of the causes of cavities). Other bacteria in the mouth become trapped in the slime and form a biofilm & eventually a buildup of plaque. Staphylococcus The slime layer of Gram+ Staphylococcus allows it to thrive in the salty, hypertonic environment of the skin. Glycocalyces are not specific to Gram+ or Gram- bacteria, sometimes only some members of a certain species (strains) have a glycocalyx, whereas others don’t. STRUCTURE OF MICOBIAL CELLS Prokaryotes - Glycocalyx 2. ___________________ polysaccharides firmly attached to the cell wall. Capsules adhere to solid surfaces and to nutrients in the environment. Adhesive power of capsules is a major factor in the initiation of some bacterial diseases. Capsule also protect bacteria from being phagocitized by cells of the hosts immune system. STRUCTURE OF PROKAROTIC CELLS Prokaryotes - Glycocalyx Bacterial Capsule and Meningococcal Infection Meningococcal infection is caused by meningococcal bacteria (Neisseria meningitidis). Causes: 1. meningococcal meningitis (infection of the meninges/spinal cord) 2. meningococcal septicaemia (blood poisoning). Of the two forms, meningococcal septicaemia is the most dangerous. Meningococcal bacteria are the most common cause of bacterial meningitis. Meningococcal bacteria grow in pairs called diplococci often surrounded by a capsule coat. Over a million of these would fit on the head of a pin. Approximately 5% of people who suffer from meningococcal meningitis will die. http://www.meningitisuk.org/about-meningitis/bacterial-meningitis.htm STRUCTURE OF PROKAROTIC CELLS